Peng Song
Multi-modal Speech Emotion Recognition via Feature Distribution Adaptation Network
Nov 02, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel deep inductive transfer learning framework, named feature distribution adaptation network, to tackle the challenging multi-modal speech emotion recognition problem. Our method aims to use deep transfer learning strategies to align visual and audio feature distributions to obtain consistent representation of emotion, thereby improving the performance of speech emotion recognition. In our model, the pre-trained ResNet-34 is utilized for feature extraction for facial expression images and acoustic Mel spectrograms, respectively. Then, the cross-attention mechanism is introduced to model the intrinsic similarity relationships of multi-modal features. Finally, the multi-modal feature distribution adaptation is performed efficiently with feed-forward network, which is extended using the local maximum mean discrepancy loss. Experiments are carried out on two benchmark datasets, and the results demonstrate that our model can achieve excellent performance compared with existing ones.
Feature distribution Adaptation Network for Speech Emotion Recognition
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel deep inductive transfer learning framework, named feature distribution adaptation network, to tackle the challenging multi-modal speech emotion recognition problem. Our method aims to use deep transfer learning strategies to align visual and audio feature distributions to obtain consistent representation of emotion, thereby improving the performance of speech emotion recognition. In our model, the pre-trained ResNet-34 is utilized for feature extraction for facial expression images and acoustic Mel spectrograms, respectively. Then, the cross-attention mechanism is introduced to model the intrinsic similarity relationships of multi-modal features. Finally, the multi-modal feature distribution adaptation is performed efficiently with feed-forward network, which is extended using the local maximum mean discrepancy loss. Experiments are carried out on two benchmark datasets, and the results demonstrate that our model can achieve excellent performance compared with existing ones.Our code is available at https://github.com/shaokai1209/FDAN.
An Advert Creation System for 3D Product Placements
Jun 26, 2020
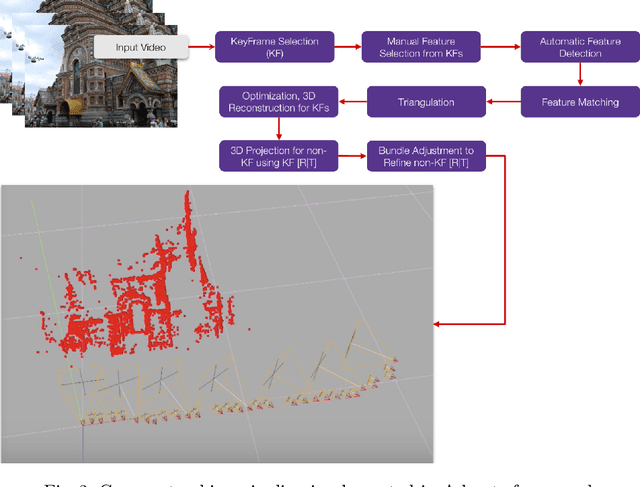

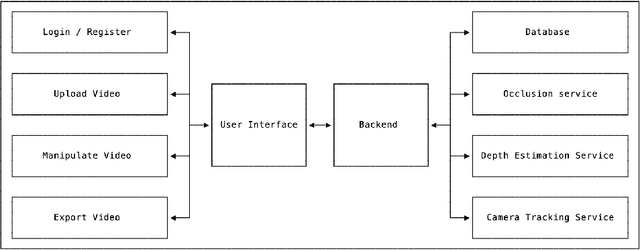
Abstract:Over the past decade, the evolution of video-sharing platforms has attracted a significant amount of investments on contextual advertising. The common contextual advertising platforms utilize the information provided by users to integrate 2D visual ads into videos. The existing platforms face many technical challenges such as ad integration with respect to occluding objects and 3D ad placement. This paper presents a Video Advertisement Placement & Integration (Adverts) framework, which is capable of perceiving the 3D geometry of the scene and camera motion to blend 3D virtual objects in videos and create the illusion of reality. The proposed framework contains several modules such as monocular depth estimation, object segmentation, background-foreground separation, alpha matting and camera tracking. Our experiments conducted using Adverts framework indicates the significant potential of this system in contextual ad integration, and pushing the limits of advertising industry using mixed reality technologies.
Machine Learning Guided Discovery of Gigantic Magnetocaloric Effect in HoB$_{2}$ Near Hydrogen Liquefaction Temperature
May 12, 2020

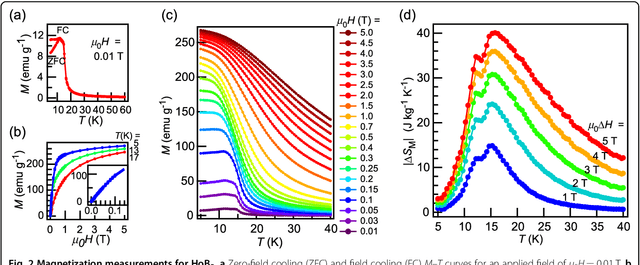
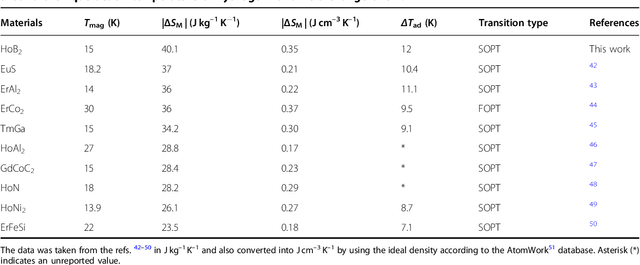
Abstract:Magnetic refrigeration exploits the magnetocaloric effect which is the entropy change upon application and removal of magnetic fields in materials, providing an alternate path for refrigeration other than the conventional gas cycles. While intensive research has uncovered a vast number of magnetic materials which exhibits large magnetocaloric effect, these properties for a large number of compounds still remain unknown. To explore new functional materials in this unknown space, machine learning is used as a guide for selecting materials which could exhibit large magnetocaloric effect. By this approach, HoB$_{2}$ is singled out, synthesized and its magnetocaloric properties are evaluated, leading to the experimental discovery of gigantic magnetic entropy change 40.1 J kg$^{-1}$ K$^{-1}$ (0.35 J cm$^{-3}$ K$^{-1}$) for a field change of 5 T in the vicinity of a ferromagnetic second-order phase transition with a Curie temperature of 15 K. This is the highest value reported so far, to our knowledge, near the hydrogen liquefaction temperature thus it is a highly suitable material for hydrogen liquefaction and low temperature magnetic cooling applications.
* 12 pages including 3 figures and 1 table + 11 pages of supplementary information. Published version available at: https://rdcu.be/b36ep
Decision Propagation Networks for Image Classification
Nov 27, 2019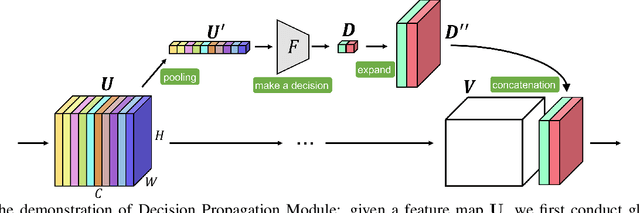
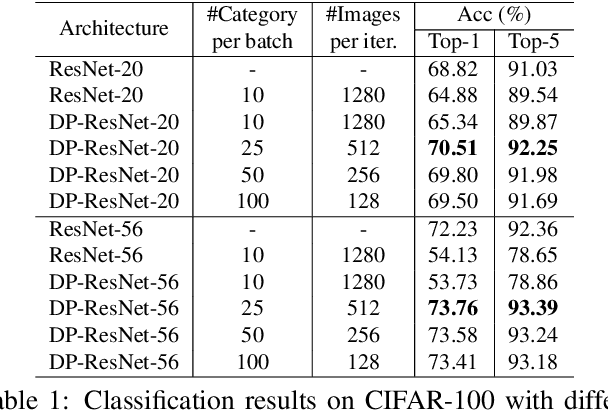
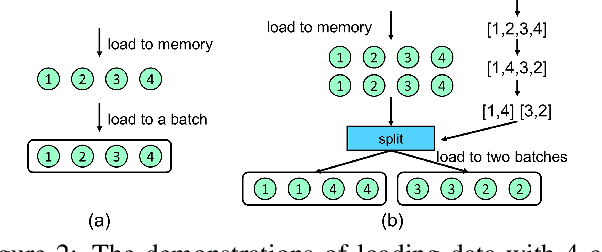
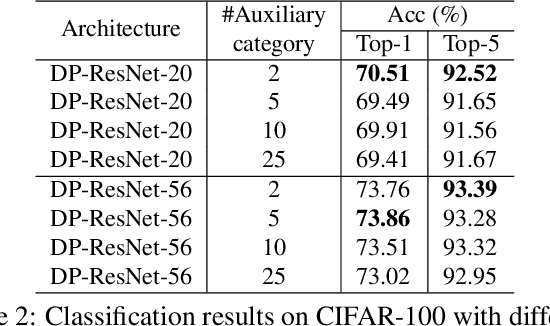
Abstract:High-level (e.g., semantic) features encoded in the latter layers of convolutional neural networks are extensively exploited for image classification, leaving low-level (e.g., color) features in the early layers underexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel Decision Propagation Module (DPM) to make an intermediate decision that could act as category-coherent guidance extracted from early layers, and then propagate it to the latter layers. Therefore, by stacking a collection of DPMs into a classification network, the generated Decision Propagation Network is explicitly formulated as to progressively encode more discriminative features guided by the decision, and then refine the decision based on the new generated features layer by layer. Comprehensive results on four publicly available datasets validate DPM could bring significant improvements for existing classification networks with minimal additional computational cost and is superior to the state-of-the-art methods.
Signature of Geometric Centroids for 3D Local Shape Description and Partial Shape Matching
Dec 26, 2016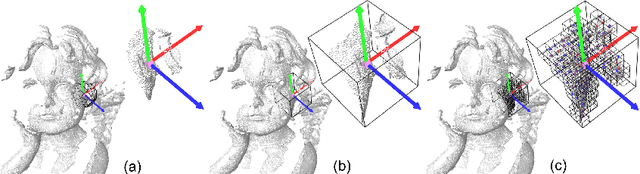
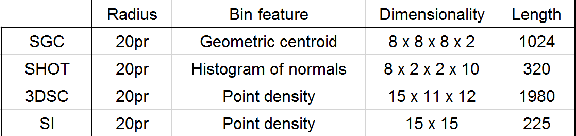
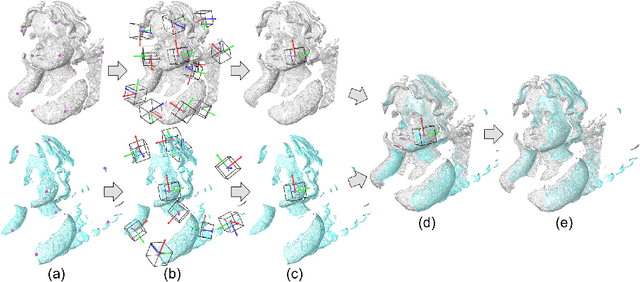
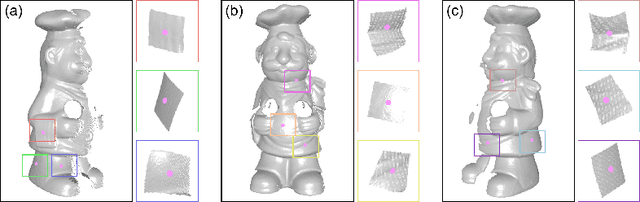
Abstract:Depth scans acquired from different views may contain nuisances such as noise, occlusion, and varying point density. We propose a novel Signature of Geometric Centroids descriptor, supporting direct shape matching on the scans, without requiring any preprocessing such as scan denoising or converting into a mesh. First, we construct the descriptor by voxelizing the local shape within a uniquely defined local reference frame and concatenating geometric centroid and point density features extracted from each voxel. Second, we compare two descriptors by employing only corresponding voxels that are both non-empty, thus supporting matching incomplete local shape such as those close to scan boundary. Third, we propose a descriptor saliency measure and compute it from a descriptor-graph to improve shape matching performance. We demonstrate the descriptor's robustness and effectiveness for shape matching by comparing it with three state-of-the-art descriptors, and applying it to object/scene reconstruction and 3D object recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge