Patrick Thoral
Yet Another ICU Benchmark: A Flexible Multi-Center Framework for Clinical ML
Jun 08, 2023Abstract:Medical applications of machine learning (ML) have experienced a surge in popularity in recent years. The intensive care unit (ICU) is a natural habitat for ML given the abundance of available data from electronic health records. Models have been proposed to address numerous ICU prediction tasks like the early detection of complications. While authors frequently report state-of-the-art performance, it is challenging to verify claims of superiority. Datasets and code are not always published, and cohort definitions, preprocessing pipelines, and training setups are difficult to reproduce. This work introduces Yet Another ICU Benchmark (YAIB), a modular framework that allows researchers to define reproducible and comparable clinical ML experiments; we offer an end-to-end solution from cohort definition to model evaluation. The framework natively supports most open-access ICU datasets (MIMIC III/IV, eICU, HiRID, AUMCdb) and is easily adaptable to future ICU datasets. Combined with a transparent preprocessing pipeline and extensible training code for multiple ML and deep learning models, YAIB enables unified model development. Our benchmark comes with five predefined established prediction tasks (mortality, acute kidney injury, sepsis, kidney function, and length of stay) developed in collaboration with clinicians. Adding further tasks is straightforward by design. Using YAIB, we demonstrate that the choice of dataset, cohort definition, and preprocessing have a major impact on the prediction performance - often more so than model class - indicating an urgent need for YAIB as a holistic benchmarking tool. We provide our work to the clinical ML community to accelerate method development and enable real-world clinical implementations. Software Repository: https://github.com/rvandewater/YAIB.
Out-of-Distribution Detection for Medical Applications: Guidelines for Practical Evaluation
Sep 30, 2021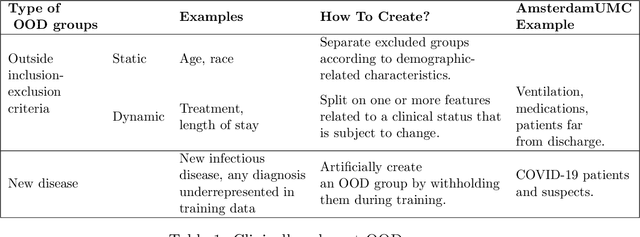
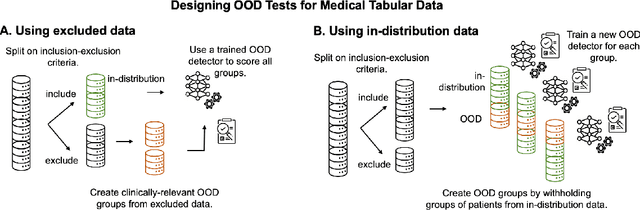
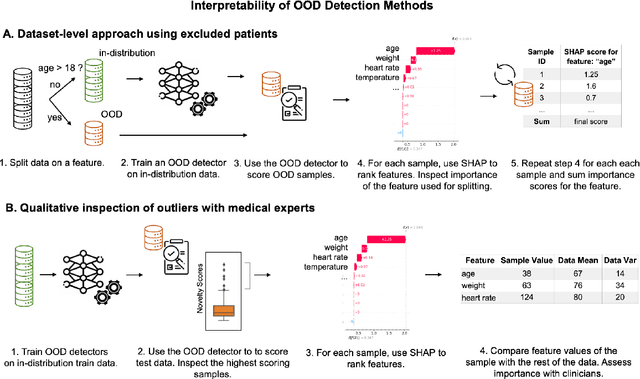
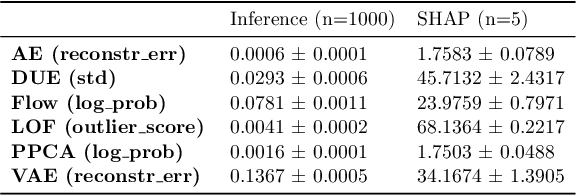
Abstract:Detection of Out-of-Distribution (OOD) samples in real time is a crucial safety check for deployment of machine learning models in the medical field. Despite a growing number of uncertainty quantification techniques, there is a lack of evaluation guidelines on how to select OOD detection methods in practice. This gap impedes implementation of OOD detection methods for real-world applications. Here, we propose a series of practical considerations and tests to choose the best OOD detector for a specific medical dataset. These guidelines are illustrated on a real-life use case of Electronic Health Records (EHR). Our results can serve as a guide for implementation of OOD detection methods in clinical practice, mitigating risks associated with the use of machine learning models in healthcare.
Hide-and-Seek Privacy Challenge
Jul 24, 2020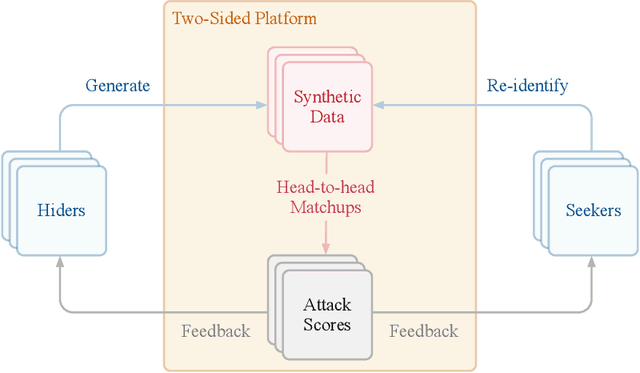
Abstract:The clinical time-series setting poses a unique combination of challenges to data modeling and sharing. Due to the high dimensionality of clinical time series, adequate de-identification to preserve privacy while retaining data utility is difficult to achieve using common de-identification techniques. An innovative approach to this problem is synthetic data generation. From a technical perspective, a good generative model for time-series data should preserve temporal dynamics, in the sense that new sequences respect the original relationships between high-dimensional variables across time. From the privacy perspective, the model should prevent patient re-identification by limiting vulnerability to membership inference attacks. The NeurIPS 2020 Hide-and-Seek Privacy Challenge is a novel two-tracked competition to simultaneously accelerate progress in tackling both problems. In our head-to-head format, participants in the synthetic data generation track (i.e. "hiders") and the patient re-identification track (i.e. "seekers") are directly pitted against each other by way of a new, high-quality intensive care time-series dataset: the AmsterdamUMCdb dataset. Ultimately, we seek to advance generative techniques for dense and high-dimensional temporal data streams that are (1) clinically meaningful in terms of fidelity and predictivity, as well as (2) capable of minimizing membership privacy risks in terms of the concrete notion of patient re-identification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge