Mihaela van der Schaar
No More, No Less: Least-Privilege Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Least privilege is a core security principle: grant each request only the minimum access needed to achieve its goal. Deployed language models almost never follow it, instead being exposed through a single API endpoint that serves all users and requests. This gap exists not because least privilege would be unhelpful; deployments would benefit greatly from reducing unnecessary capability exposure. The real obstacle is definitional and mechanistic: what does "access" mean inside a language model, and how can we enforce it without retraining or deploying multiple models? We take inspiration from least privilege in computer systems and define a class of models called least-privilege language models, where privilege is reachable internal computation during the forward pass. In this view, lowering privilege literally shrinks the model's accessible function class, as opposed to denying access via learned policies. We formalize deployment-time control as a monitor-allocator-enforcer stack, separating (i) request-time signals, (ii) a decision rule that allocates privilege, and (iii) an inference-time mechanism that selects privilege. We then propose Nested Least-Privilege Networks, a shape-preserving, rank-indexed intervention that provides a smooth, reversible control knob. We show that this knob yields policy-usable privilege-utility frontiers and enables selective suppression of targeted capabilities with limited collateral degradation across various policies. Most importantly, we argue for a new deployment paradigm that challenges the premise that language models can only be controlled at the output level.
AgentScore: Autoformulation of Deployable Clinical Scoring Systems
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Modern clinical practice relies on evidence-based guidelines implemented as compact scoring systems composed of a small number of interpretable decision rules. While machine-learning models achieve strong performance, many fail to translate into routine clinical use due to misalignment with workflow constraints such as memorability, auditability, and bedside execution. We argue that this gap arises not from insufficient predictive power, but from optimizing over model classes that are incompatible with guideline deployment. Deployable guidelines often take the form of unit-weighted clinical checklists, formed by thresholding the sum of binary rules, but learning such scores requires searching an exponentially large discrete space of possible rule sets. We introduce AgentScore, which performs semantically guided optimization in this space by using LLMs to propose candidate rules and a deterministic, data-grounded verification-and-selection loop to enforce statistical validity and deployability constraints. Across eight clinical prediction tasks, AgentScore outperforms existing score-generation methods and achieves AUC comparable to more flexible interpretable models despite operating under stronger structural constraints. On two additional externally validated tasks, AgentScore achieves higher discrimination than established guideline-based scores.
Knowledge-Informed Kernel State Reconstruction for Interpretable Dynamical System Discovery
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Recovering governing equations from data is central to scientific discovery, yet existing methods often break down under noisy, partial observations, or rely on black-box latent dynamics that obscure mechanism. We introduce MAAT (Model Aware Approximation of Trajectories), a framework for symbolic discovery built on knowledge-informed Kernel State Reconstruction. MAAT formulates state reconstruction in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space and directly incorporates structural and semantic priors such as non-negativity, conservation laws, and domain-specific observation models into the reconstruction objective, while accommodating heterogeneous sampling and measurement granularity. This yields smooth, physically consistent state estimates with analytic time derivatives, providing a principled interface between fragmented sensor data and symbolic regression. Across twelve diverse scientific benchmarks and multiple noise regimes, MAAT substantially reduces state-estimation MSE for trajectories and derivatives used by downstream symbolic regression relative to strong baselines.
Nonparametric LLM Evaluation from Preference Data
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Evaluating the performance of large language models (LLMs) from human preference data is crucial for obtaining LLM leaderboards. However, many existing approaches either rely on restrictive parametric assumptions or lack valid uncertainty quantification when flexible machine learning methods are used. In this paper, we propose a nonparametric statistical framework, DMLEval, for comparing and ranking LLMs from preference data using debiased machine learning (DML). For this, we introduce generalized average ranking scores (GARS), which generalize commonly used ranking models, including the Bradley-Terry model or PageRank/ Rank centrality, with complex human responses such as ties. DMLEval comes with the following advantages: (i) It produces statistically efficient estimates of GARS ranking scores. (ii) It naturally allows the incorporation of black-box machine learning methods for estimation. (iii) It can be combined with pre-trained LLM evaluators (e.g., using LLM-as-a-judge). (iv) It suggests optimal policies for collecting preference data under budget constraints. We demonstrate these advantages both theoretically and empirically using both synthetic and real-world preference datasets. In summary, our framework provides practitioners with powerful, state-of-the-art methods for comparing or ranking LLMs.
GameTalk: Training LLMs for Strategic Conversation
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Strategic decision-making in multi-agent settings is a key challenge for large language models (LLMs), particularly when coordination and negotiation must unfold over extended conversations. While recent work has explored the use of LLMs in isolated decision tasks, little attention has been given to optimizing long-term objectives through dialogue. We introduce \textbf{GameTalk}, a framework for training LLMs to make strategic decisions via multi-turn interactions. Unlike prior work that focuses on single-turn objectives or static action prediction, we train LLMs to optimize a global objective across full conversations. We achieve this by adapting fine-tuning methods like GRPO, DPO, and STaR to incorporate reward signals that depend on the entire interaction. We evaluate this approach on a suite of increasingly complex games, designed to stress different aspects of reasoning, coordination, and opponent modeling. Our results show that GameTalk significantly outperforms untrained models, especially under reward shaping, with DPO consistently yielding the strongest gains. These findings position conversational fine-tuning as a promising path for LLMs to reason, negotiate, and act in interactive environments.
The Reasoning-Creativity Trade-off: Toward Creativity-Driven Problem Solving
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:State-of-the-art large language model (LLM) pipelines rely on bootstrapped reasoning loops: sampling diverse chains of thought and reinforcing the highest-scoring ones, mainly optimizing correctness. We analyze how this design choice is sensitive to the collapse of the model's distribution over reasoning paths, slashing semantic entropy and undermining creative problem-solving. To analyze this failure, we introduce Distributional Creative Reasoning (DCR), a unified variational objective that casts training as gradient flow through probability measures on solution traces. STaR, GRPO, and DPO, as well as entropy bonuses, and other methods, all constitute special cases of the same loss. The framework delivers three core results: (i) the diversity decay theorem, describing how correctness-based objectives lead to distinct modes of diversity decay for STaR, GRPO, and DPO; (ii) designs that ensure convergence to a stable and diverse policy, effectively preventing collapse; and (iii) simple, actionable recipes to achieve this in practice. DCR thus offers the first principled recipe for LLMs that remain both correct and creative.
Visualizing token importance for black-box language models
Dec 12, 2025



Abstract:We consider the problem of auditing black-box large language models (LLMs) to ensure they behave reliably when deployed in production settings, particularly in high-stakes domains such as legal, medical, and regulatory compliance. Existing approaches for LLM auditing often focus on isolated aspects of model behavior, such as detecting specific biases or evaluating fairness. We are interested in a more general question -- can we understand how the outputs of black-box LLMs depend on each input token? There is a critical need to have such tools in real-world applications that rely on inaccessible API endpoints to language models. However, this is a highly non-trivial problem, as LLMs are stochastic functions (i.e. two outputs will be different by chance), while computing prompt-level gradients to approximate input sensitivity is infeasible. To address this, we propose Distribution-Based Sensitivity Analysis (DBSA), a lightweight model-agnostic procedure to evaluate the sensitivity of the output of a language model for each input token, without making any distributional assumptions about the LLM. DBSA is developed as a practical tool for practitioners, enabling quick, plug-and-play visual exploration of LLMs reliance on specific input tokens. Through illustrative examples, we demonstrate how DBSA can enable users to inspect LLM inputs and find sensitivities that may be overlooked by existing LLM interpretability methods.
Timely Clinical Diagnosis through Active Test Selection
Oct 21, 2025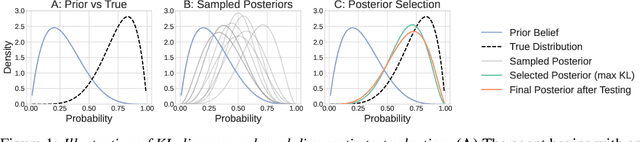



Abstract:There is growing interest in using machine learning (ML) to support clinical diag- nosis, but most approaches rely on static, fully observed datasets and fail to reflect the sequential, resource-aware reasoning clinicians use in practice. Diagnosis remains complex and error prone, especially in high-pressure or resource-limited settings, underscoring the need for frameworks that help clinicians make timely and cost-effective decisions. We propose ACTMED (Adaptive Clinical Test selection via Model-based Experimental Design), a diagnostic framework that integrates Bayesian Experimental Design (BED) with large language models (LLMs) to better emulate real-world diagnostic reasoning. At each step, ACTMED selects the test expected to yield the greatest reduction in diagnostic uncertainty for a given patient. LLMs act as flexible simulators, generating plausible patient state distributions and supporting belief updates without requiring structured, task-specific training data. Clinicians can remain in the loop; reviewing test suggestions, interpreting intermediate outputs, and applying clinical judgment throughout. We evaluate ACTMED on real-world datasets and show it can optimize test selection to improve diagnostic accuracy, interpretability, and resource use. This represents a step to- ward transparent, adaptive, and clinician-aligned diagnostic systems that generalize across settings with reduced reliance on domain-specific data.
Learning a Dense Reasoning Reward Model from Expert Demonstration via Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:We reframe and operationalise adversarial inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) to large language model reasoning, learning a dense, token-level reward model for process supervision directly from expert demonstrations rather than imitating style via supervised fine-tuning. The learned reasoning reward serves two complementary roles: (i) it provides step-level feedback to optimise a reasoning policy during training; and (ii) it functions at inference as a critic to rerank sampled traces under fixed compute budgets. We demonstrate that our approach prioritises correctness over surface form, yielding scores that correlate with eventual answer validity and enabling interpretable localisation of errors within a trace. Empirically, on GSM8K with Llama3 and Qwen2.5 backbones, we demonstrate: (i) dense reasoning rewards can be used as a learning signal to elicit reasoning, and (ii) predictive performance is improved from reward-guided reranking (notably for Llama-based policies). By unifying training signals, inference-time selection, and token-level diagnostics into a single reasoning reward, this work suggests reusable process-level rewards with broad potential to enhance multi-step reasoning in language models.
Inverse Reinforcement Learning Meets Large Language Model Post-Training: Basics, Advances, and Opportunities
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:In the era of Large Language Models (LLMs), alignment has emerged as a fundamental yet challenging problem in the pursuit of more reliable, controllable, and capable machine intelligence. The recent success of reasoning models and conversational AI systems has underscored the critical role of reinforcement learning (RL) in enhancing these systems, driving increased research interest at the intersection of RL and LLM alignment. This paper provides a comprehensive review of recent advances in LLM alignment through the lens of inverse reinforcement learning (IRL), emphasizing the distinctions between RL techniques employed in LLM alignment and those in conventional RL tasks. In particular, we highlight the necessity of constructing neural reward models from human data and discuss the formal and practical implications of this paradigm shift. We begin by introducing fundamental concepts in RL to provide a foundation for readers unfamiliar with the field. We then examine recent advances in this research agenda, discussing key challenges and opportunities in conducting IRL for LLM alignment. Beyond methodological considerations, we explore practical aspects, including datasets, benchmarks, evaluation metrics, infrastructure, and computationally efficient training and inference techniques. Finally, we draw insights from the literature on sparse-reward RL to identify open questions and potential research directions. By synthesizing findings from diverse studies, we aim to provide a structured and critical overview of the field, highlight unresolved challenges, and outline promising future directions for improving LLM alignment through RL and IRL techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge