Patrick Liu
The Spatial Blindspot of Vision-Language Models
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have advanced rapidly, but their ability to capture spatial relationships remains a blindspot. Current VLMs are typically built with contrastive language-image pretraining (CLIP) style image encoders. The training recipe often flattens images into 1D patch sequences, discarding the 2D structure necessary for spatial reasoning. We argue that this lack of spatial awareness is a missing dimension in VLM design and a bottleneck for applications requiring spatial grounding, such as robotics and embodied AI. To address this, we investigate (i) image encoders trained with alternative objectives and (ii) 2D positional encodings. Our experiments show that these architectural choices can lead to improved spatial reasoning on several benchmarks.
DiffusionSat: A Generative Foundation Model for Satellite Imagery
Dec 06, 2023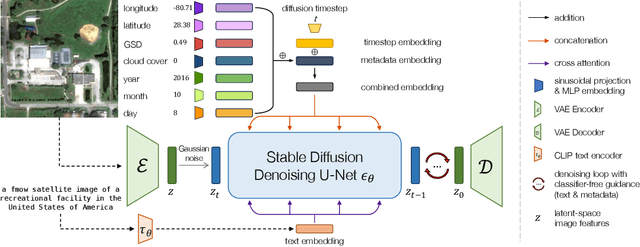
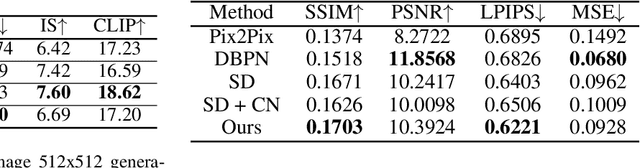
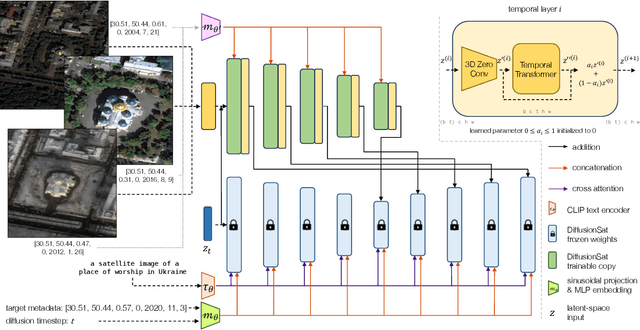

Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved state-of-the-art results on many modalities including images, speech, and video. However, existing models are not tailored to support remote sensing data, which is widely used in important applications including environmental monitoring and crop-yield prediction. Satellite images are significantly different from natural images -- they can be multi-spectral, irregularly sampled across time -- and existing diffusion models trained on images from the Web do not support them. Furthermore, remote sensing data is inherently spatio-temporal, requiring conditional generation tasks not supported by traditional methods based on captions or images. In this paper, we present DiffusionSat, to date the largest generative foundation model trained on a collection of publicly available large, high-resolution remote sensing datasets. As text-based captions are sparsely available for satellite images, we incorporate the associated metadata such as geolocation as conditioning information. Our method produces realistic samples and can be used to solve multiple generative tasks including temporal generation, superresolution given multi-spectral inputs and in-painting. Our method outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods for satellite image generation and is the first large-scale $\textit{generative}$ foundation model for satellite imagery.
Enhancing Self-Consistency and Performance of Pre-Trained Language Models through Natural Language Inference
Nov 21, 2022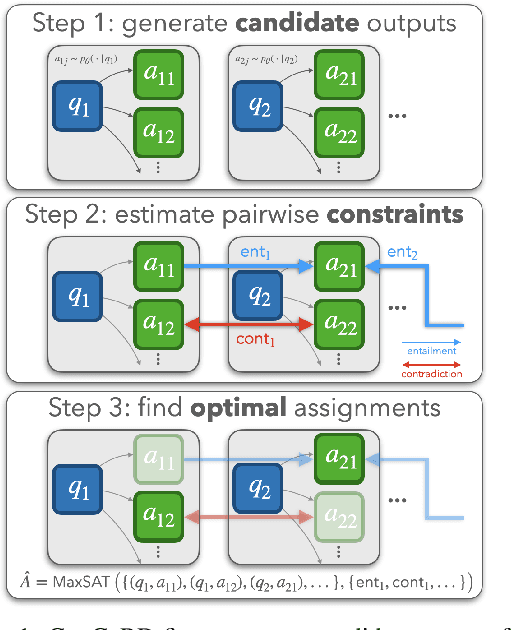
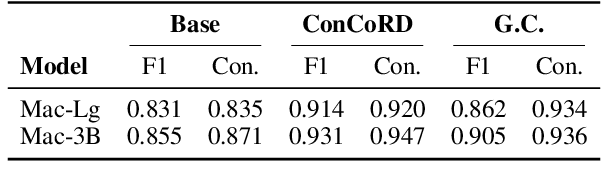
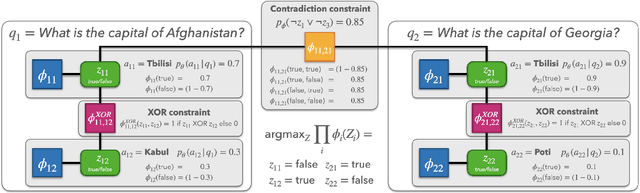
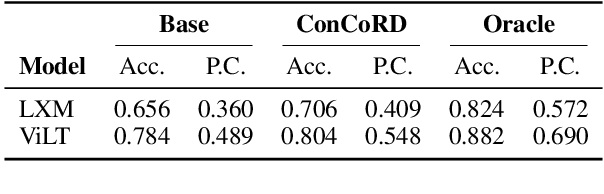
Abstract:While large pre-trained language models are powerful, their predictions often lack logical consistency across test inputs. For example, a state-of-the-art Macaw question-answering (QA) model answers 'Yes' to 'Is a sparrow a bird?' and 'Does a bird have feet?' but answers 'No' to 'Does a sparrow have feet?'. To address this failure mode, we propose a framework, Consistency Correction through Relation Detection, or ConCoRD, for boosting the consistency and accuracy of pre-trained NLP models using pre-trained natural language inference (NLI) models without fine-tuning or re-training. Given a batch of test inputs, ConCoRD samples several candidate outputs for each input and instantiates a factor graph that accounts for both the model's belief about the likelihood of each answer choice in isolation and the NLI model's beliefs about pair-wise answer choice compatibility. We show that a weighted MaxSAT solver can efficiently compute high-quality answer choices under this factor graph, improving over the raw model's predictions. Our experiments demonstrate that ConCoRD consistently boosts accuracy and consistency of off-the-shelf closed-book QA and VQA models using off-the-shelf NLI models, notably increasing accuracy of LXMERT on ConVQA by 5% absolute. See https://ericmitchell.ai/emnlp-2022-concord/ for code and data.
SatMAE: Pre-training Transformers for Temporal and Multi-Spectral Satellite Imagery
Jul 17, 2022
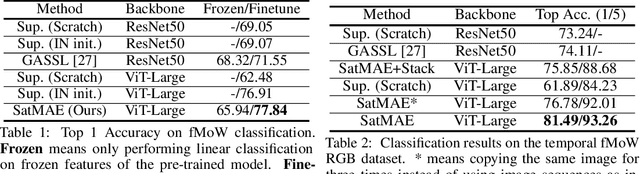
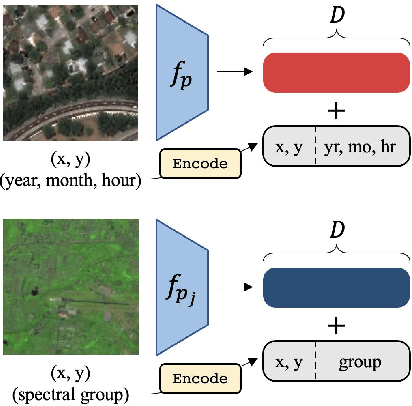
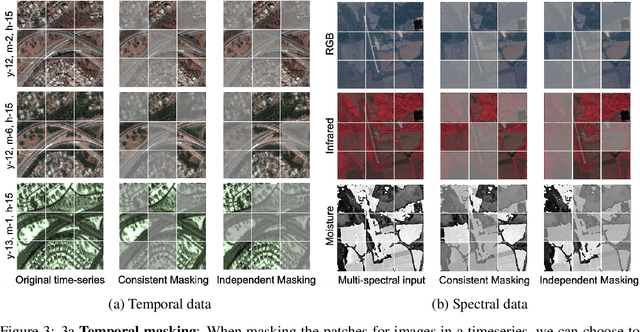
Abstract:Unsupervised pre-training methods for large vision models have shown to enhance performance on downstream supervised tasks. Developing similar techniques for satellite imagery presents significant opportunities as unlabelled data is plentiful and the inherent temporal and multi-spectral structure provides avenues to further improve existing pre-training strategies. In this paper, we present SatMAE, a pre-training framework for temporal or multi-spectral satellite imagery based on Masked Autoencoder (MAE). To leverage temporal information, we include a temporal embedding along with independently masking image patches across time. In addition, we demonstrate that encoding multi-spectral data as groups of bands with distinct spectral positional encodings is beneficial. Our approach yields strong improvements over previous state-of-the-art techniques, both in terms of supervised learning performance on benchmark datasets (up to $\uparrow$ 7\%), and transfer learning performance on downstream remote sensing tasks, including land cover classification (up to $\uparrow$ 14\%) and semantic segmentation.
SustainBench: Benchmarks for Monitoring the Sustainable Development Goals with Machine Learning
Nov 08, 2021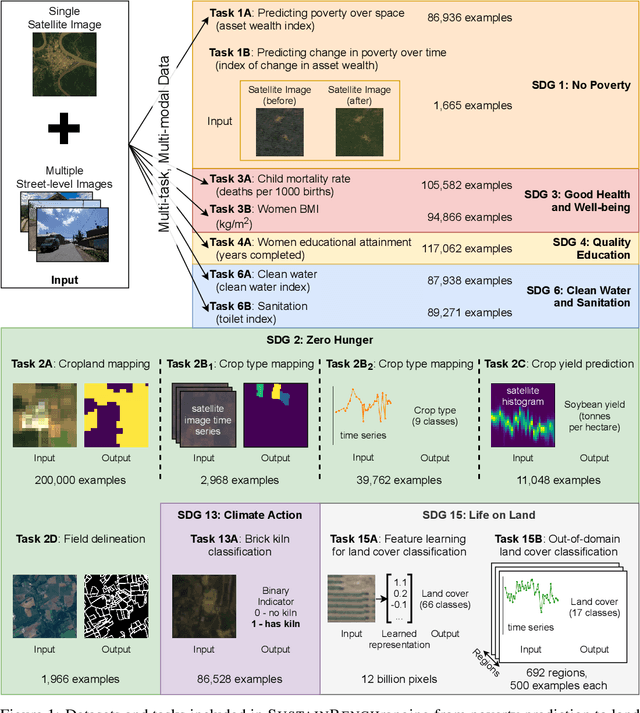
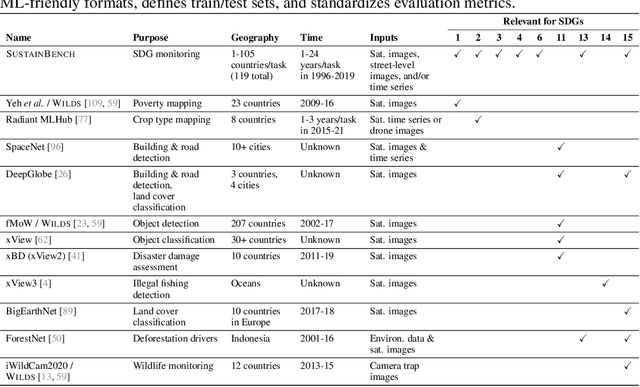
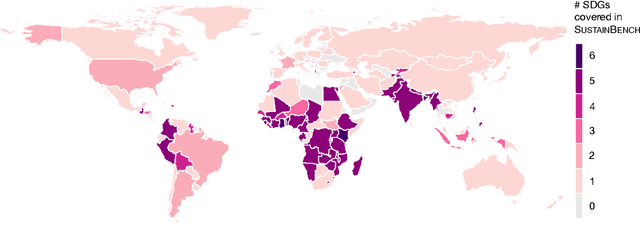
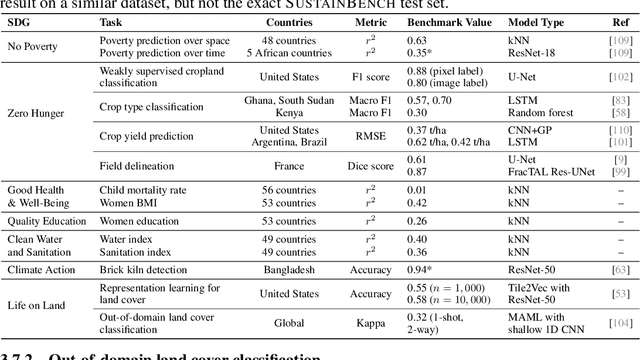
Abstract:Progress toward the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) has been hindered by a lack of data on key environmental and socioeconomic indicators, which historically have come from ground surveys with sparse temporal and spatial coverage. Recent advances in machine learning have made it possible to utilize abundant, frequently-updated, and globally available data, such as from satellites or social media, to provide insights into progress toward SDGs. Despite promising early results, approaches to using such data for SDG measurement thus far have largely evaluated on different datasets or used inconsistent evaluation metrics, making it hard to understand whether performance is improving and where additional research would be most fruitful. Furthermore, processing satellite and ground survey data requires domain knowledge that many in the machine learning community lack. In this paper, we introduce SustainBench, a collection of 15 benchmark tasks across 7 SDGs, including tasks related to economic development, agriculture, health, education, water and sanitation, climate action, and life on land. Datasets for 11 of the 15 tasks are released publicly for the first time. Our goals for SustainBench are to (1) lower the barriers to entry for the machine learning community to contribute to measuring and achieving the SDGs; (2) provide standard benchmarks for evaluating machine learning models on tasks across a variety of SDGs; and (3) encourage the development of novel machine learning methods where improved model performance facilitates progress towards the SDGs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge