Omkar Patil
PokeNet: Learning Kinematic Models of Articulated Objects from Human Observations
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Articulation modeling enables robots to learn joint parameters of articulated objects for effective manipulation which can then be used downstream for skill learning or planning. Existing approaches often rely on prior knowledge about the objects, such as the number or type of joints. Some of these approaches also fail to recover occluded joints that are only revealed during interaction. Others require large numbers of multi-view images for every object, which is impractical in real-world settings. Furthermore, prior works neglect the order of manipulations, which is essential for many multi-DoF objects where one joint must be operated before another, such as a dishwasher. We introduce PokeNet, an end-to-end framework that estimates articulation models from a single human demonstration without prior object knowledge. Given a sequence of point cloud observations of a human manipulating an unknown object, PokeNet predicts joint parameters, infers manipulation order, and tracks joint states over time. PokeNet outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, improving joint axis and state estimation accuracy by an average of over 27% across diverse objects, including novel and unseen categories. We demonstrate these gains in both simulation and real-world environments.
Learning Sequential Kinematic Models from Demonstrations for Multi-Jointed Articulated Objects
May 09, 2025Abstract:As robots become more generalized and deployed in diverse environments, they must interact with complex objects, many with multiple independent joints or degrees of freedom (DoF) requiring precise control. A common strategy is object modeling, where compact state-space models are learned from real-world observations and paired with classical planning. However, existing methods often rely on prior knowledge or focus on single-DoF objects, limiting their applicability. They also fail to handle occluded joints and ignore the manipulation sequences needed to access them. We address this by learning object models from human demonstrations. We introduce Object Kinematic Sequence Machines (OKSMs), a novel representation capturing both kinematic constraints and manipulation order for multi-DoF objects. To estimate these models from point cloud data, we present Pokenet, a deep neural network trained on human demonstrations. We validate our approach on 8,000 simulated and 1,600 real-world annotated samples. Pokenet improves joint axis and state estimation by over 20 percent on real-world data compared to prior methods. Finally, we demonstrate OKSMs on a Sawyer robot using inverse kinematics-based planning to manipulate multi-DoF objects.
Composing Diffusion Policies for Few-shot Learning of Movement Trajectories
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Humans can perform various combinations of physical skills without having to relearn skills from scratch every single time. For example, we can swing a bat when walking without having to re-learn such a policy from scratch by composing the individual skills of walking and bat swinging. Enabling robots to combine or compose skills is essential so they can learn novel skills and tasks faster with fewer real world samples. To this end, we propose a novel compositional approach called DSE- Diffusion Score Equilibrium that enables few-shot learning for novel skills by utilizing a combination of base policy priors. Our method is based on probabilistically composing diffusion policies to better model the few-shot demonstration data-distribution than any individual policy. Our goal here is to learn robot motions few-shot and not necessarily goal oriented trajectories. Unfortunately we lack a general purpose metric to evaluate the error between a skill or motion and the provided demonstrations. Hence, we propose a probabilistic measure - Maximum Mean Discrepancy on the Forward Kinematics Kernel (MMD-FK), that is task and action space agnostic. By using our few-shot learning approach DSE, we show that we are able to achieve a reduction of over 30% in MMD-FK across skills and number of demonstrations. Moreover, we show the utility of our approach through real world experiments by teaching novel trajectories to a robot in 5 demonstrations.
Document Automation Architectures: Updated Survey in Light of Large Language Models
Aug 18, 2023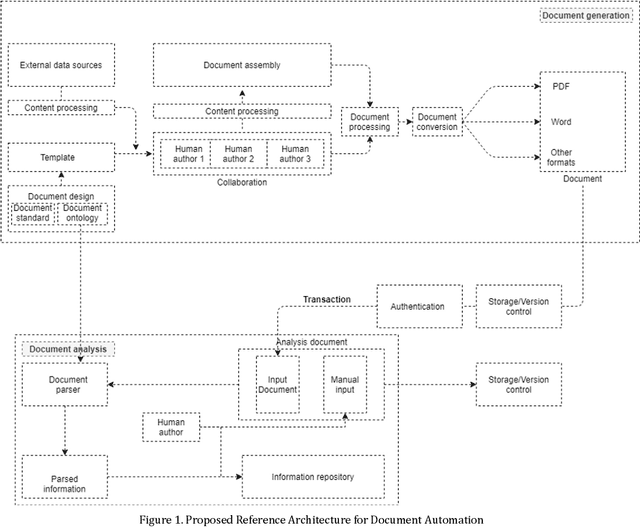
Abstract:This paper surveys the current state of the art in document automation (DA). The objective of DA is to reduce the manual effort during the generation of documents by automatically creating and integrating input from different sources and assembling documents conforming to defined templates. There have been reviews of commercial solutions of DA, particularly in the legal domain, but to date there has been no comprehensive review of the academic research on DA architectures and technologies. The current survey of DA reviews the academic literature and provides a clearer definition and characterization of DA and its features, identifies state-of-the-art DA architectures and technologies in academic research, and provides ideas that can lead to new research opportunities within the DA field in light of recent advances in generative AI and large language models.
Athena 2.0: Discourse and User Modeling in Open Domain Dialogue
Aug 03, 2023



Abstract:Conversational agents are consistently growing in popularity and many people interact with them every day. While many conversational agents act as personal assistants, they can have many different goals. Some are task-oriented, such as providing customer support for a bank or making a reservation. Others are designed to be empathetic and to form emotional connections with the user. The Alexa Prize Challenge aims to create a socialbot, which allows the user to engage in coherent conversations, on a range of popular topics that will interest the user. Here we describe Athena 2.0, UCSC's conversational agent for Amazon's Socialbot Grand Challenge 4. Athena 2.0 utilizes a novel knowledge-grounded discourse model that tracks the entity links that Athena introduces into the dialogue, and uses them to constrain named-entity recognition and linking, and coreference resolution. Athena 2.0 also relies on a user model to personalize topic selection and other aspects of the conversation to individual users.
Understanding Metrics for Paraphrasing
May 26, 2022



Abstract:Paraphrase generation is a difficult problem. This is not only because of the limitations in text generation capabilities but also due that to the lack of a proper definition of what qualifies as a paraphrase and corresponding metrics to measure how good it is. Metrics for evaluation of paraphrasing quality is an on going research problem. Most of the existing metrics in use having been borrowed from other tasks do not capture the complete essence of a good paraphrase, and often fail at borderline-cases. In this work, we propose a novel metric $ROUGE_P$ to measure the quality of paraphrases along the dimensions of adequacy, novelty and fluency. We also provide empirical evidence to show that the current natural language generation metrics are insufficient to measure these desired properties of a good paraphrase. We look at paraphrase model fine-tuning and generation from the lens of metrics to gain a deeper understanding of what it takes to generate and evaluate a good paraphrase.
Athena 2.0: Contextualized Dialogue Management for an Alexa Prize SocialBot
Nov 03, 2021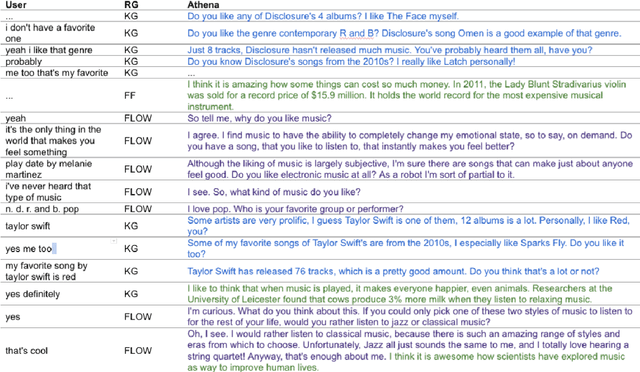

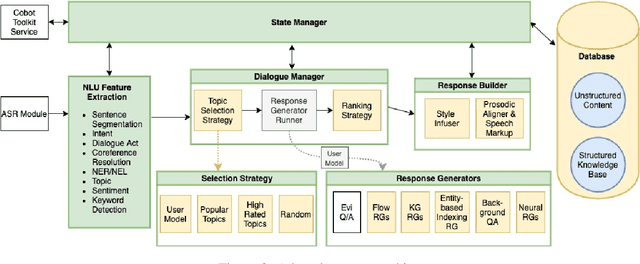
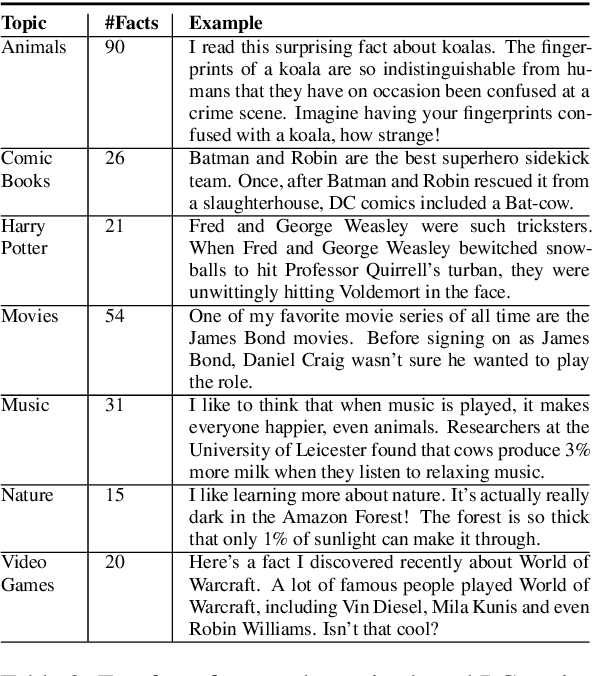
Abstract:Athena 2.0 is an Alexa Prize SocialBot that has been a finalist in the last two Alexa Prize Grand Challenges. One reason for Athena's success is its novel dialogue management strategy, which allows it to dynamically construct dialogues and responses from component modules, leading to novel conversations with every interaction. Here we describe Athena's system design and performance in the Alexa Prize during the 20/21 competition. A live demo of Athena as well as video recordings will provoke discussion on the state of the art in conversational AI.
Document Automation Architectures and Technologies: A Survey
Sep 23, 2021



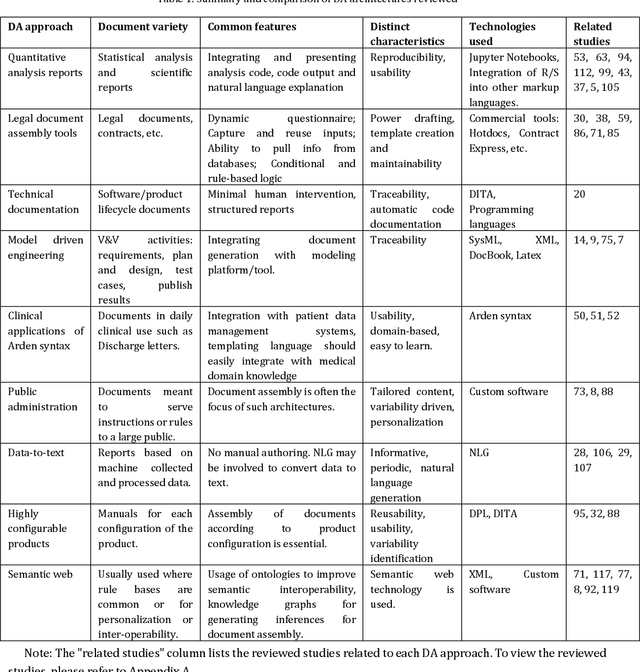
Abstract:This paper surveys the current state of the art in document automation (DA). The objective of DA is to reduce the manual effort during the generation of documents by automatically integrating input from different sources and assembling documents conforming to defined templates. There have been reviews of commercial solutions of DA, particularly in the legal domain, but to date there has been no comprehensive review of the academic research on DA architectures and technologies. The current survey of DA reviews the academic literature and provides a clearer definition and characterization of DA and its features, identifies state-of-the-art DA architectures and technologies in academic research, and provides ideas that can lead to new research opportunities within the DA field in light of recent advances in artificial intelligence and deep neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge