Rishi Rajasekaran
ATLAS: Actor-Critic Task-Completion with Look-ahead Action Simulation
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:We observe that current state-of-the-art web-agents are unable to effectively adapt to new environments without neural network fine-tuning, without which they produce inefficient execution plans due to a lack of awareness of the structure and dynamics of the new environment. To address this limitation, we introduce ATLAS (Actor-Critic Task-completion with Look-ahead Action Simulation), a memory-augmented agent that is able to make plans grounded in a model of the environment by simulating the consequences of those actions in cognitive space. Our agent starts by building a "cognitive map" by performing a lightweight curiosity driven exploration of the environment. The planner proposes candidate actions; the simulator predicts their consequences in cognitive space; a critic analyzes the options to select the best roll-out and update the original plan; and a browser executor performs the chosen action. On the WebArena-Lite Benchmark, we achieve a 63% success rate compared to 53.9% success rate for the previously published state-of-the-art. Unlike previous systems, our modular architecture requires no website-specific LLM fine-tuning. Ablations show sizable drops without the world-model, hierarchical planner, and look-ahead-based replanner confirming their complementary roles within the design of our system
Athena 2.0: Discourse and User Modeling in Open Domain Dialogue
Aug 03, 2023



Abstract:Conversational agents are consistently growing in popularity and many people interact with them every day. While many conversational agents act as personal assistants, they can have many different goals. Some are task-oriented, such as providing customer support for a bank or making a reservation. Others are designed to be empathetic and to form emotional connections with the user. The Alexa Prize Challenge aims to create a socialbot, which allows the user to engage in coherent conversations, on a range of popular topics that will interest the user. Here we describe Athena 2.0, UCSC's conversational agent for Amazon's Socialbot Grand Challenge 4. Athena 2.0 utilizes a novel knowledge-grounded discourse model that tracks the entity links that Athena introduces into the dialogue, and uses them to constrain named-entity recognition and linking, and coreference resolution. Athena 2.0 also relies on a user model to personalize topic selection and other aspects of the conversation to individual users.
A Transformer-based Response Evaluator for Open-Domain Spoken Conversation
Feb 09, 2023
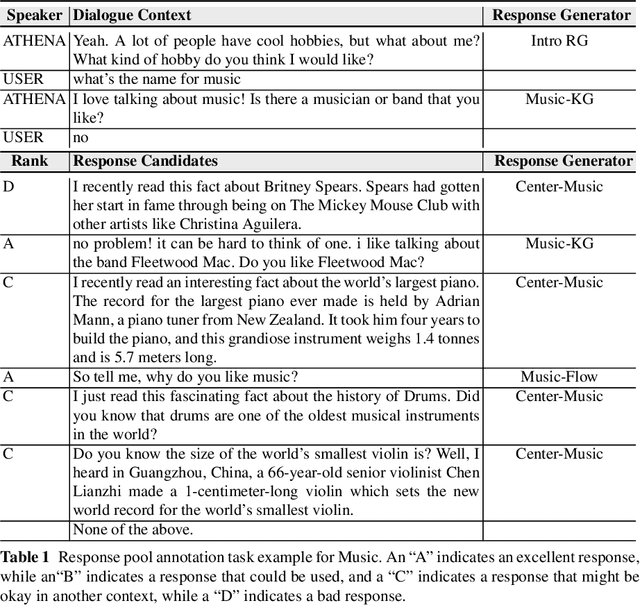

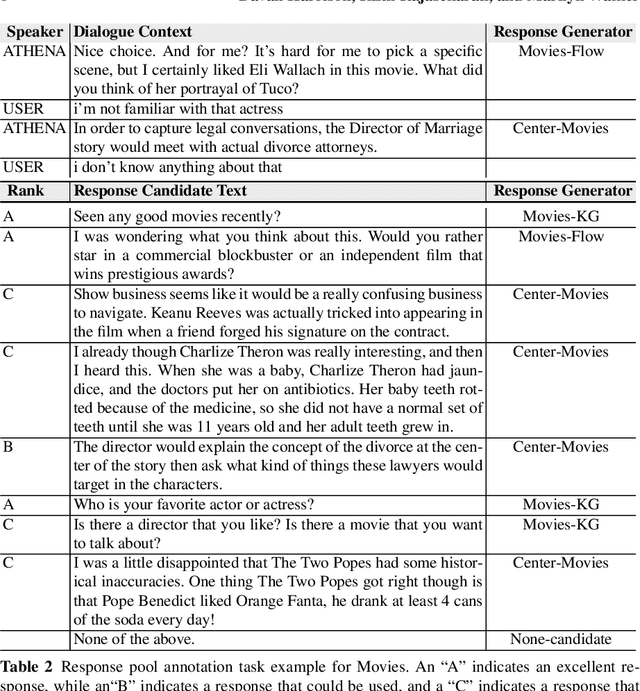
Abstract:Many open-domain dialogue systems rely on multiple response generators, any of which can contribute a response to the dialogue in a particular context. Thus the ability to compare potential responses and then select the best plays an important role in ensuring a dialogue system is coherent and engaging. Dialogue coherence goes beyond simply remaining on topic -- some trivia may be on topic and engaging when mentioned out of the blue, but may not be coherent and grounded in the context of the conversation. We carry out experiments on response selection in the Athena system, an Alexa Prize SocialBot that has dedicated content and multiple topic-specific response generators for a large number of topics. First, we collect a corpus of Athena conversations with live human traffic, where potential responses from all enabled response generators are logged and subsequently annotated for response quality. We compare several off-the-shelf response ranking methods for open-domain dialogue to Athena-Heuristic, a heuristic response ranker that was field-tested in Athena during the third Alexa Prize competition. We also compare these to a transformer-based response ranker we call Athena-RR, that we train on our Athena conversations. Athena-RR uses both the conversational context and the dialogue state to rank the potential responses. We find that Athena-RR with a Recall@1 of 70.79\% outperforms Athena-Heuristic and all of the off-the-shelf rankers by a large margin. We then conduct a live A/B study comparing Athena-Heuristic to Athena-RR in a 6,358 conversations with Alexa users. We show that Athena-RR leads to significantly longer conversations that receive significantly higher user ratings than the heuristic rule-based ranker.
Athena 2.0: Contextualized Dialogue Management for an Alexa Prize SocialBot
Nov 03, 2021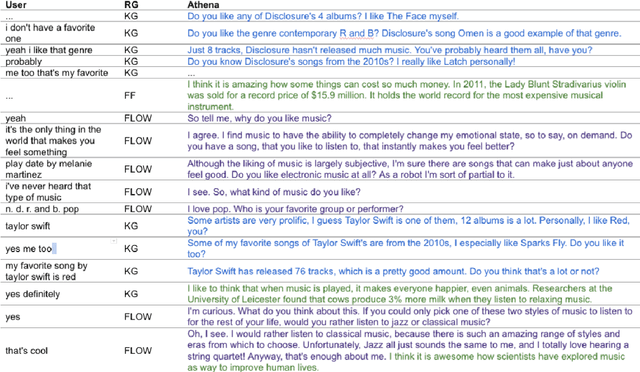

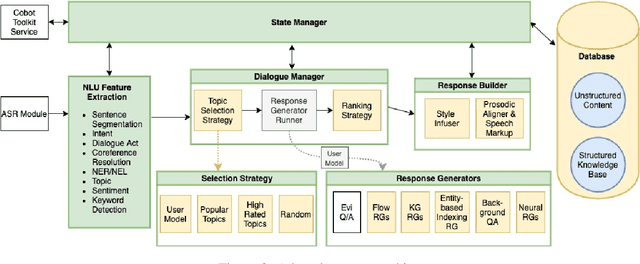
Abstract:Athena 2.0 is an Alexa Prize SocialBot that has been a finalist in the last two Alexa Prize Grand Challenges. One reason for Athena's success is its novel dialogue management strategy, which allows it to dynamically construct dialogues and responses from component modules, leading to novel conversations with every interaction. Here we describe Athena's system design and performance in the Alexa Prize during the 20/21 competition. A live demo of Athena as well as video recordings will provoke discussion on the state of the art in conversational AI.
Athena: Constructing Dialogues Dynamically with Discourse Constraints
Nov 21, 2020
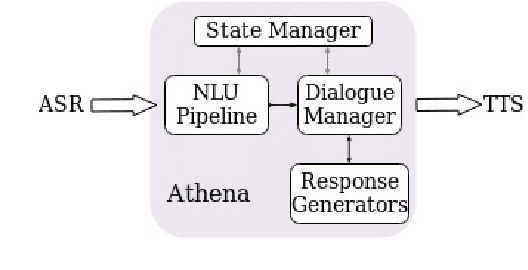
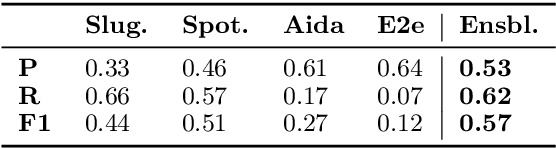
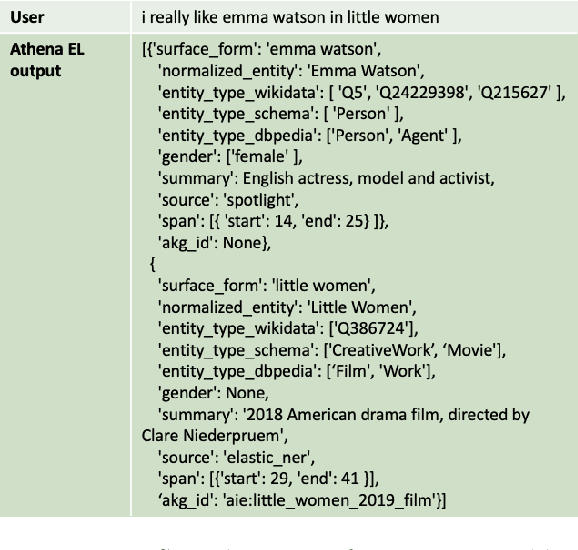
Abstract:This report describes Athena, a dialogue system for spoken conversation on popular topics and current events. We develop a flexible topic-agnostic approach to dialogue management that dynamically configures dialogue based on general principles of entity and topic coherence. Athena's dialogue manager uses a contract-based method where discourse constraints are dispatched to clusters of response generators. This allows Athena to procure responses from dynamic sources, such as knowledge graph traversals and feature-based on-the-fly response retrieval methods. After describing the dialogue system architecture, we perform an analysis of conversations that Athena participated in during the 2019 Alexa Prize Competition. We conclude with a report on several user studies we carried out to better understand how individual user characteristics affect system ratings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge