Brian Schwarzmann
Athena: Constructing Dialogues Dynamically with Discourse Constraints
Nov 21, 2020
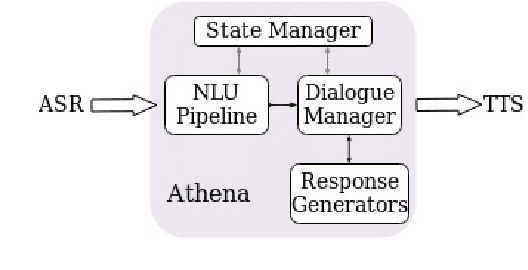
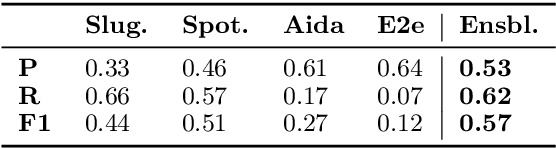
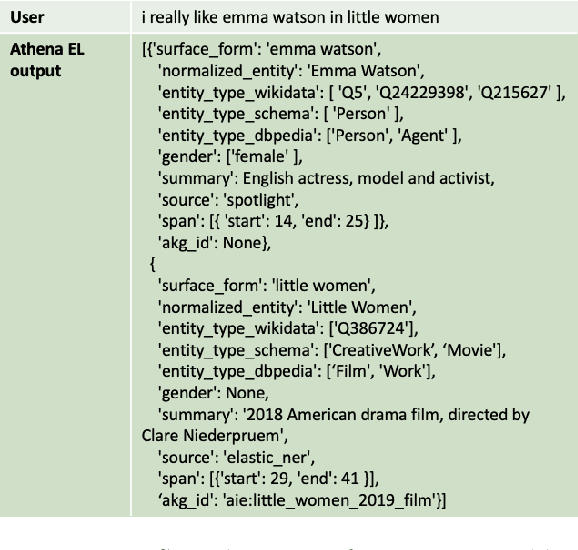
Abstract:This report describes Athena, a dialogue system for spoken conversation on popular topics and current events. We develop a flexible topic-agnostic approach to dialogue management that dynamically configures dialogue based on general principles of entity and topic coherence. Athena's dialogue manager uses a contract-based method where discourse constraints are dispatched to clusters of response generators. This allows Athena to procure responses from dynamic sources, such as knowledge graph traversals and feature-based on-the-fly response retrieval methods. After describing the dialogue system architecture, we perform an analysis of conversations that Athena participated in during the 2019 Alexa Prize Competition. We conclude with a report on several user studies we carried out to better understand how individual user characteristics affect system ratings.
Entertaining and Opinionated but Too Controlling: A Large-Scale User Study of an Open Domain Alexa Prize System
Aug 13, 2019

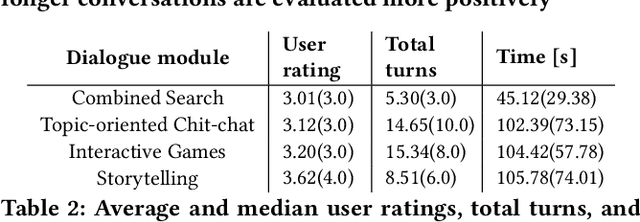
Abstract:Conversational systems typically focus on functional tasks such as scheduling appointments or creating todo lists. Instead we design and evaluate SlugBot (SB), one of 8 semifinalists in the 2018 AlexaPrize, whose goal is to support casual open-domain social inter-action. This novel application requires both broad topic coverage and engaging interactive skills. We developed a new technical approach to meet this demanding situation by crowd-sourcing novel content and introducing playful conversational strategies based on storytelling and games. We collected over 10,000 conversations during August 2018 as part of the Alexa Prize competition. We also conducted an in-lab follow-up qualitative evaluation. Over-all users found SB moderately engaging; conversations averaged 3.6 minutes and involved 26 user turns. However, users reacted very differently to different conversation subtypes. Storytelling and games were evaluated positively; these were seen as entertaining with predictable interactive structure. They also led users to impute personality and intelligence to SB. In contrast, search and general Chit-Chat induced coverage problems; here users found it hard to infer what topics SB could understand, with these conversations seen as being too system-driven. Theoretical and design implications suggest a move away from conversational systems that simply provide factual information. Future systems should be designed to have their own opinions with personal stories to share, and SB provides an example of how we might achieve this.
SlugBot: Developing a Computational Model andFramework of a Novel Dialogue Genre
Jul 22, 2019
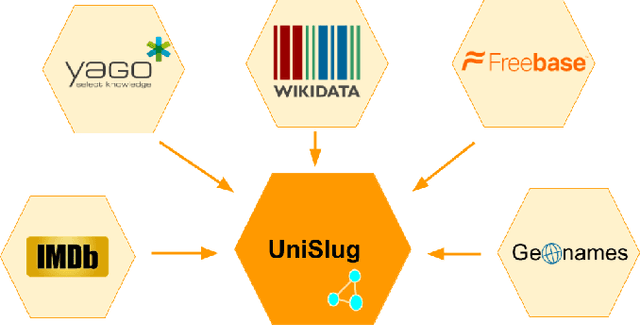
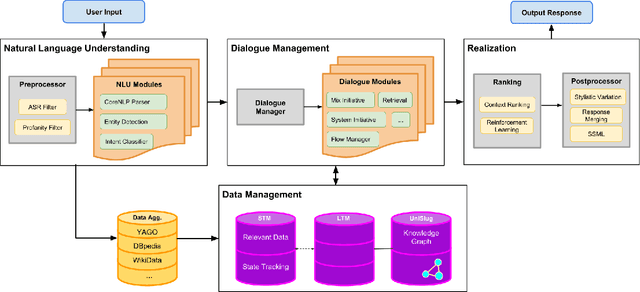

Abstract:One of the most interesting aspects of the Amazon Alexa Prize competition is that the framing of the competition requires the development of new computational models of dialogue and its structure. Traditional computational models of dialogue are of two types: (1) task-oriented dialogue, supported by AI planning models,or simplified planning models consisting of frames with slots to be filled; or (2)search-oriented dialogue where every user turn is treated as a search query that may elaborate and extend current search results. Alexa Prize dialogue systems such as SlugBot must support conversational capabilities that go beyond what these traditional models can do. Moreover, while traditional dialogue systems rely on theoretical computational models, there are no existing computational theories that circumscribe the expected system and user behaviors in the intended conversational genre of the Alexa Prize Bots. This paper describes how UCSC's SlugBot team has combined the development of a novel computational theoretical model, Discourse Relation Dialogue Model, with its implementation in a modular system in order to test and refine it. We highlight how our novel dialogue model has led us to create a novel ontological resource, UniSlug, and how the structure of UniSlug determine show we curate and structure content so that our dialogue manager implements and tests our novel computational dialogue model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge