Niels van Berkel
Chaplains' Reflections on the Design and Usage of AI for Conversational Care
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Despite growing recognition that responsible AI requires domain knowledge, current work on conversational AI primarily draws on clinical expertise that prioritises diagnosis and intervention. However, much of everyday emotional support needs occur in non-clinical contexts, and therefore requires different conversational approaches. We examine how chaplains, who guide individuals through personal crises, grief, and reflection, perceive and engage with conversational AI. We recruited eighteen chaplains to build AI chatbots. While some chaplains viewed chatbots with cautious optimism, the majority expressed limitations of chatbots' ability to support everyday well-being. Our analysis reveals how chaplains perceive their pastoral care duties and areas where AI chatbots fall short, along the themes of Listening, Connecting, Carrying, and Wanting. These themes resonate with the idea of attunement, recently highlighted as a relational lens for understanding the delicate experiences care technologies provide. This perspective informs chatbot design aimed at supporting well-being in non-clinical contexts.
Polite But Boring? Trade-offs Between Engagement and Psychological Reactance to Chatbot Feedback Styles
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:As conversational agents become increasingly common in behaviour change interventions, understanding optimal feedback delivery mechanisms becomes increasingly important. However, choosing a style that both lessens psychological reactance (perceived threats to freedom) while simultaneously eliciting feelings of surprise and engagement represents a complex design problem. We explored how three different feedback styles: 'Direct', 'Politeness', and 'Verbal Leakage' (slips or disfluencies to reveal a desired behaviour) affect user perceptions and behavioural intentions. Matching expectations from literature, the 'Direct' chatbot led to lower behavioural intentions and higher reactance, while the 'Politeness' chatbot evoked higher behavioural intentions and lower reactance. However, 'Politeness' was also seen as unsurprising and unengaging by participants. In contrast, 'Verbal Leakage' evoked reactance, yet also elicited higher feelings of surprise, engagement, and humour. These findings highlight that effective feedback requires navigating trade-offs between user reactance and engagement, with novel approaches such as 'Verbal Leakage' offering promising alternative design opportunities.
The Impact of a Chatbot's Ephemerality-Framing on Self-Disclosure Perceptions
May 26, 2025Abstract:Self-disclosure, the sharing of one's thoughts and feelings, is affected by the perceived relationship between individuals. While chatbots are increasingly used for self-disclosure, the impact of a chatbot's framing on users' self-disclosure remains under-explored. We investigated how a chatbot's description of its relationship with users, particularly in terms of ephemerality, affects self-disclosure. Specifically, we compared a Familiar chatbot, presenting itself as a companion remembering past interactions, with a Stranger chatbot, presenting itself as a new, unacquainted entity in each conversation. In a mixed factorial design, participants engaged with either the Familiar or Stranger chatbot in two sessions across two days, with one conversation focusing on Emotional- and another Factual-disclosure. When Emotional-disclosure was sought in the first chatting session, Stranger-condition participants felt more comfortable self-disclosing. However, when Factual-disclosure was sought first, these differences were replaced by more enjoyment among Familiar-condition participants. Qualitative findings showed Stranger afforded anonymity and reduced judgement, whereas Familiar sometimes felt intrusive unless rapport was built via low-risk Factual-disclosure.
From Voice to Value: Leveraging AI to Enhance Spoken Online Reviews on the Go
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Online reviews help people make better decisions. Review platforms usually depend on typed input, where leaving a good review requires significant effort because users must carefully organize and articulate their thoughts. This may discourage users from leaving comprehensive and high-quality reviews, especially when they are on the go. To address this challenge, we developed Vocalizer, a mobile application that enables users to provide reviews through voice input, with enhancements from a large language model (LLM). In a longitudinal study, we analysed user interactions with the app, focusing on AI-driven features that help refine and improve reviews. Our findings show that users frequently utilized the AI agent to add more detailed information to their reviews. We also show how interactive AI features can improve users self-efficacy and willingness to share reviews online. Finally, we discuss the opportunities and challenges of integrating AI assistance into review-writing systems.
FairComp: Workshop on Fairness and Robustness in Machine Learning for Ubiquitous Computing
Sep 22, 2023Abstract:How can we ensure that Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp) research outcomes are both ethical and fair? While fairness in machine learning (ML) has gained traction in recent years, fairness in UbiComp remains unexplored. This workshop aims to discuss fairness in UbiComp research and its social, technical, and legal implications. From a social perspective, we will examine the relationship between fairness and UbiComp research and identify pathways to ensure that ubiquitous technologies do not cause harm or infringe on individual rights. From a technical perspective, we will initiate a discussion on data practices to develop bias mitigation approaches tailored to UbiComp research. From a legal perspective, we will examine how new policies shape our community's work and future research. We aim to foster a vibrant community centered around the topic of responsible UbiComp, while also charting a clear path for future research endeavours in this field.
DDoD: Dual Denial of Decision Attacks on Human-AI Teams
Dec 07, 2022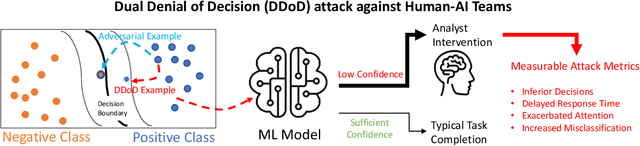
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems have been increasingly used to make decision-making processes faster, more accurate, and more efficient. However, such systems are also at constant risk of being attacked. While the majority of attacks targeting AI-based applications aim to manipulate classifiers or training data and alter the output of an AI model, recently proposed Sponge Attacks against AI models aim to impede the classifier's execution by consuming substantial resources. In this work, we propose \textit{Dual Denial of Decision (DDoD) attacks against collaborative Human-AI teams}. We discuss how such attacks aim to deplete \textit{both computational and human} resources, and significantly impair decision-making capabilities. We describe DDoD on human and computational resources and present potential risk scenarios in a series of exemplary domains.
Quantifying Synthesis and Fusion and their Impact on Machine Translation
May 06, 2022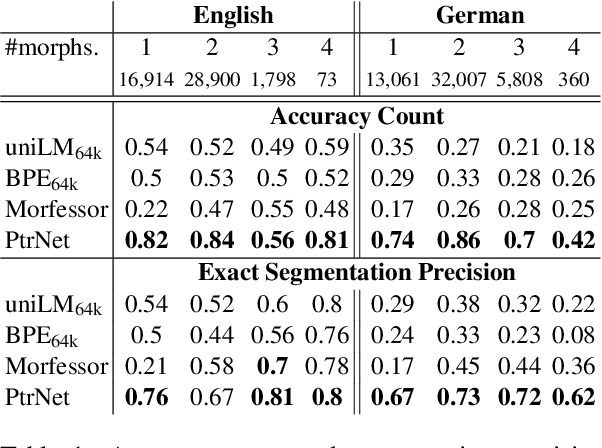
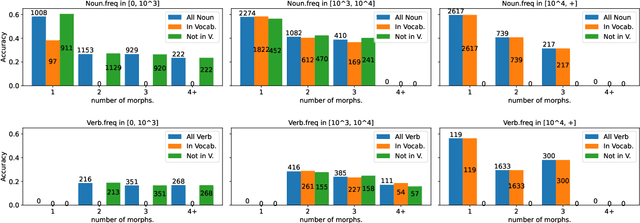
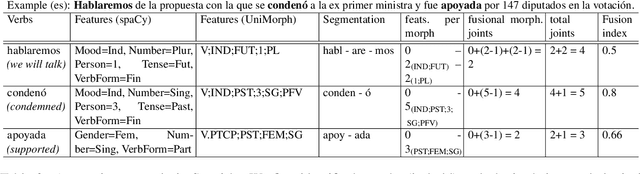
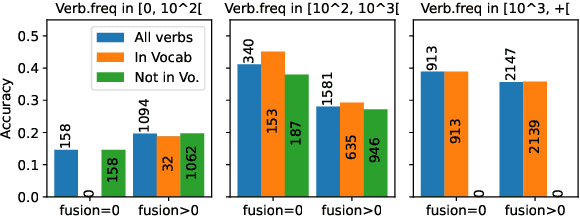
Abstract:Theoretical work in morphological typology offers the possibility of measuring morphological diversity on a continuous scale. However, literature in Natural Language Processing (NLP) typically labels a whole language with a strict type of morphology, e.g. fusional or agglutinative. In this work, we propose to reduce the rigidity of such claims, by quantifying morphological typology at the word and segment level. We consider Payne (2017)'s approach to classify morphology using two indices: synthesis (e.g. analytic to polysynthetic) and fusion (agglutinative to fusional). For computing synthesis, we test unsupervised and supervised morphological segmentation methods for English, German and Turkish, whereas for fusion, we propose a semi-automatic method using Spanish as a case study. Then, we analyse the relationship between machine translation quality and the degree of synthesis and fusion at word (nouns and verbs for English-Turkish, and verbs in English-Spanish) and segment level (previous language pairs plus English-German in both directions). We complement the word-level analysis with human evaluation, and overall, we observe a consistent impact of both indexes on machine translation quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge