Nasrin Mostafazadeh
Kenneth
GLUCOSE: GeneraLized and COntextualized Story Explanations
Sep 16, 2020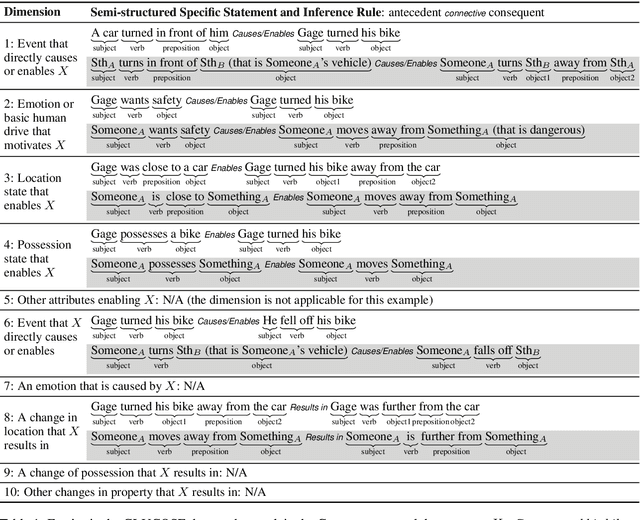
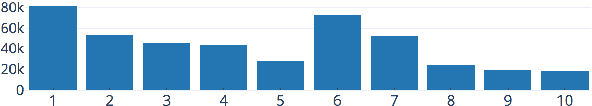

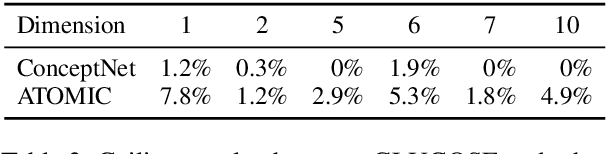
Abstract:When humans read or listen, they make implicit commonsense inferences that frame their understanding of what happened and why. As a step toward AI systems that can build similar mental models, we introduce GLUCOSE, a large-scale dataset of implicit commonsense causal knowledge, encoded as causal mini-theories about the world, each grounded in a narrative context. To construct GLUCOSE, we drew on cognitive psychology to identify ten dimensions of causal explanation, focusing on events, states, motivations, and emotions. Each GLUCOSE entry includes a story-specific causal statement paired with an inference rule generalized from the statement. This paper details two concrete contributions: First, we present our platform for effectively crowdsourcing GLUCOSE data at scale, which uses semi-structured templates to elicit causal explanations. Using this platform, we collected 440K specific statements and general rules that capture implicit commonsense knowledge about everyday situations. Second, we show that existing knowledge resources and pretrained language models do not include or readily predict GLUCOSE's rich inferential content. However, when state-of-the-art neural models are trained on this knowledge, they can start to make commonsense inferences on unseen stories that match humans' mental models.
Image-Grounded Conversations: Multimodal Context for Natural Question and Response Generation
Apr 20, 2017


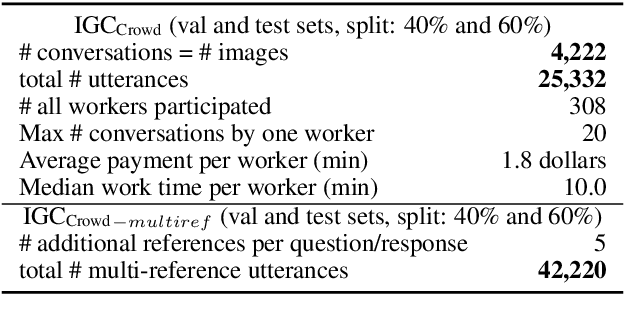
Abstract:The popularity of image sharing on social media and the engagement it creates between users reflects the important role that visual context plays in everyday conversations. We present a novel task, Image-Grounded Conversations (IGC), in which natural-sounding conversations are generated about a shared image. To benchmark progress, we introduce a new multiple-reference dataset of crowd-sourced, event-centric conversations on images. IGC falls on the continuum between chit-chat and goal-directed conversation models, where visual grounding constrains the topic of conversation to event-driven utterances. Experiments with models trained on social media data show that the combination of visual and textual context enhances the quality of generated conversational turns. In human evaluation, the gap between human performance and that of both neural and retrieval architectures suggests that multi-modal IGC presents an interesting challenge for dialogue research.
Generating Natural Questions About an Image
Jun 09, 2016
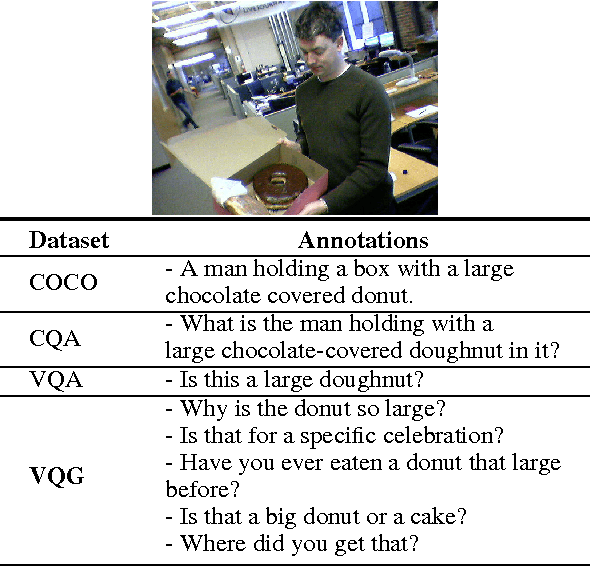


Abstract:There has been an explosion of work in the vision & language community during the past few years from image captioning to video transcription, and answering questions about images. These tasks have focused on literal descriptions of the image. To move beyond the literal, we choose to explore how questions about an image are often directed at commonsense inference and the abstract events evoked by objects in the image. In this paper, we introduce the novel task of Visual Question Generation (VQG), where the system is tasked with asking a natural and engaging question when shown an image. We provide three datasets which cover a variety of images from object-centric to event-centric, with considerably more abstract training data than provided to state-of-the-art captioning systems thus far. We train and test several generative and retrieval models to tackle the task of VQG. Evaluation results show that while such models ask reasonable questions for a variety of images, there is still a wide gap with human performance which motivates further work on connecting images with commonsense knowledge and pragmatics. Our proposed task offers a new challenge to the community which we hope furthers interest in exploring deeper connections between vision & language.
Visual Storytelling
Apr 13, 2016

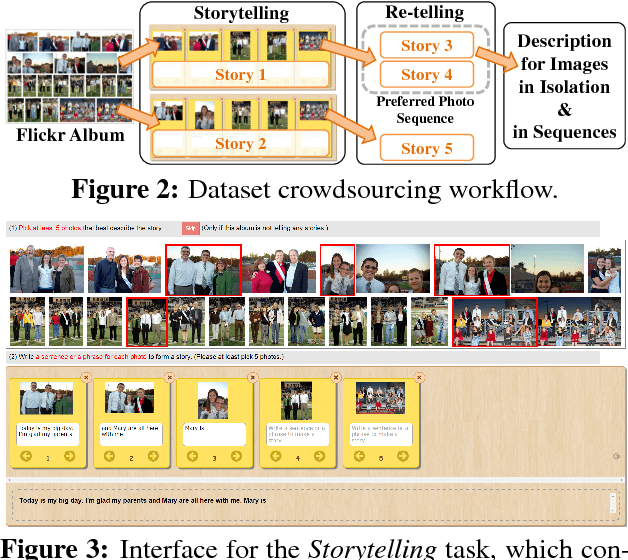
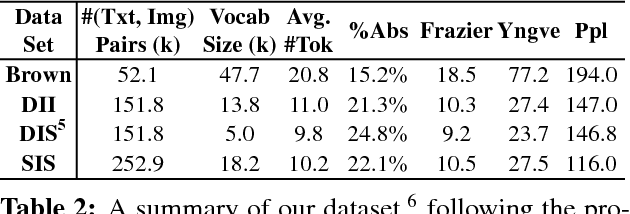
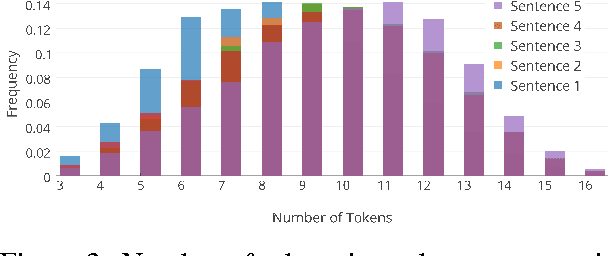
Abstract:We introduce the first dataset for sequential vision-to-language, and explore how this data may be used for the task of visual storytelling. The first release of this dataset, SIND v.1, includes 81,743 unique photos in 20,211 sequences, aligned to both descriptive (caption) and story language. We establish several strong baselines for the storytelling task, and motivate an automatic metric to benchmark progress. Modelling concrete description as well as figurative and social language, as provided in this dataset and the storytelling task, has the potential to move artificial intelligence from basic understandings of typical visual scenes towards more and more human-like understanding of grounded event structure and subjective expression.
A Corpus and Evaluation Framework for Deeper Understanding of Commonsense Stories
Apr 06, 2016

Abstract:Representation and learning of commonsense knowledge is one of the foundational problems in the quest to enable deep language understanding. This issue is particularly challenging for understanding casual and correlational relationships between events. While this topic has received a lot of interest in the NLP community, research has been hindered by the lack of a proper evaluation framework. This paper attempts to address this problem with a new framework for evaluating story understanding and script learning: the 'Story Cloze Test'. This test requires a system to choose the correct ending to a four-sentence story. We created a new corpus of ~50k five-sentence commonsense stories, ROCStories, to enable this evaluation. This corpus is unique in two ways: (1) it captures a rich set of causal and temporal commonsense relations between daily events, and (2) it is a high quality collection of everyday life stories that can also be used for story generation. Experimental evaluation shows that a host of baselines and state-of-the-art models based on shallow language understanding struggle to achieve a high score on the Story Cloze Test. We discuss these implications for script and story learning, and offer suggestions for deeper language understanding.
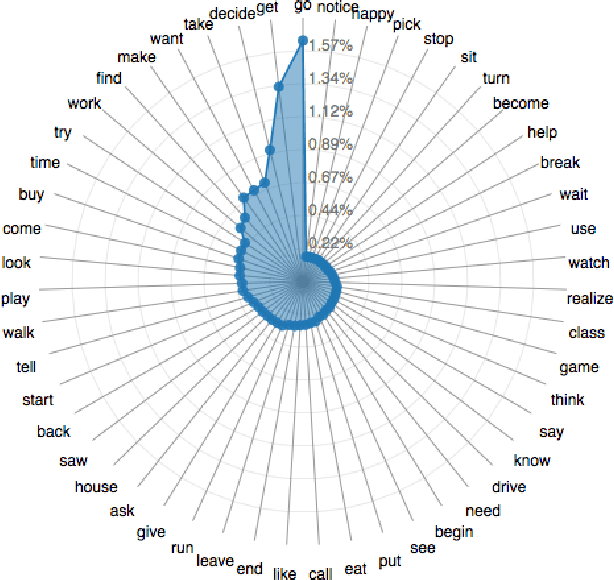
A Survey of Current Datasets for Vision and Language Research
Aug 19, 2015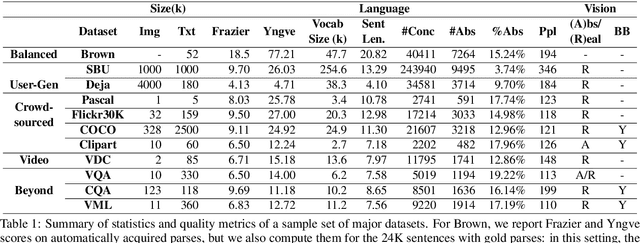
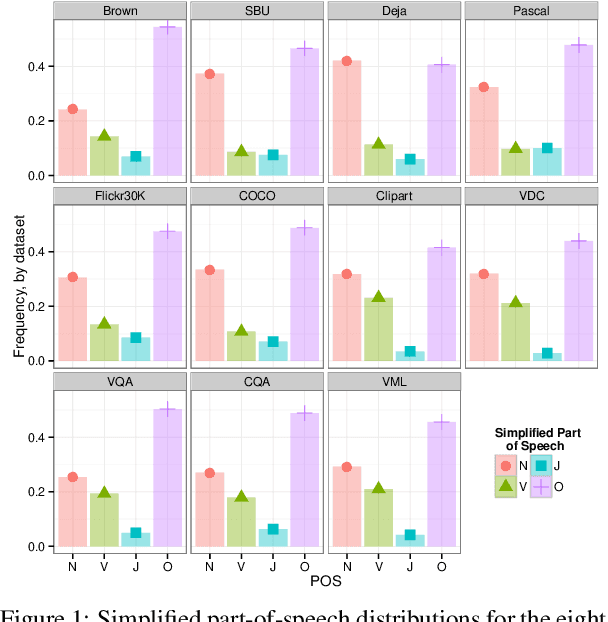
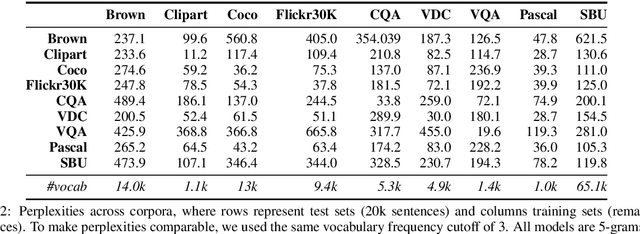
Abstract:Integrating vision and language has long been a dream in work on artificial intelligence (AI). In the past two years, we have witnessed an explosion of work that brings together vision and language from images to videos and beyond. The available corpora have played a crucial role in advancing this area of research. In this paper, we propose a set of quality metrics for evaluating and analyzing the vision & language datasets and categorize them accordingly. Our analyses show that the most recent datasets have been using more complex language and more abstract concepts, however, there are different strengths and weaknesses in each.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge