Nan Wei
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Water Preservation in Soan River Basin using Deep Learning Techniques
Jun 26, 2019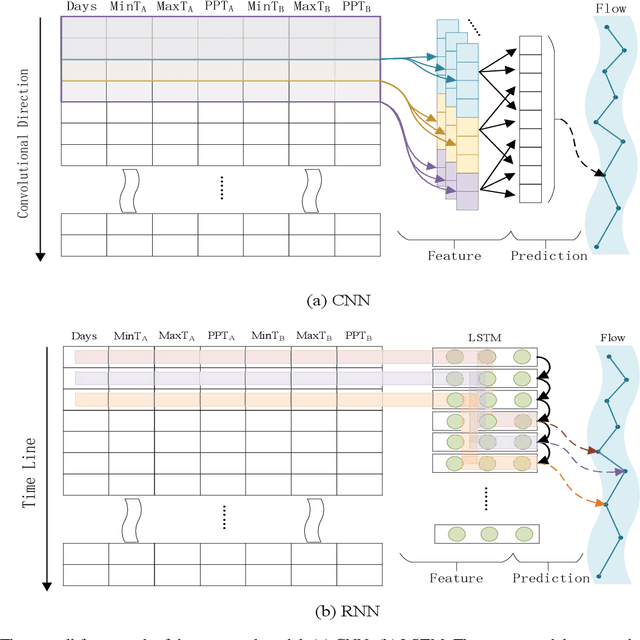
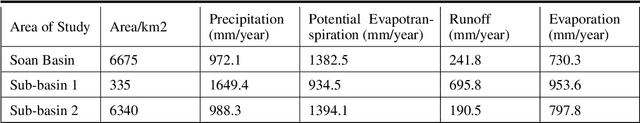
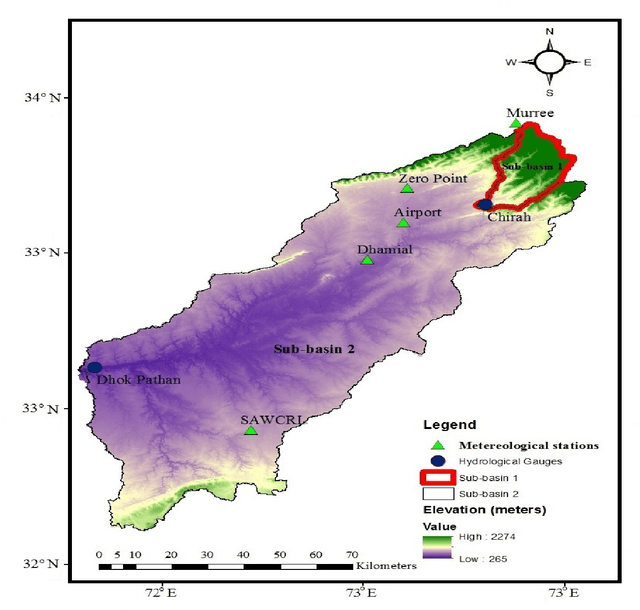
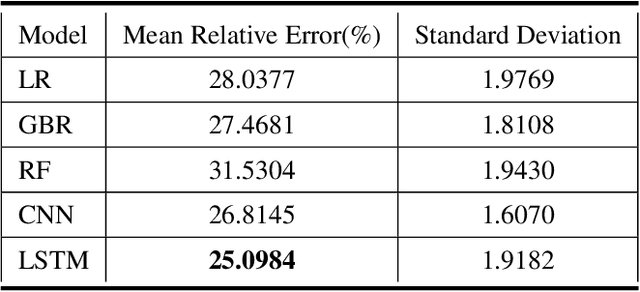
Abstract:Water supplies are crucial for the development of living beings. However, change in the hydrological process i.e. climate and land usage are the key issues. Sustaining water level and accurate estimating for dynamic conditions is a critical job for hydrologists, but predicting hydrological extremes is an open issue. In this paper, we proposed two deep learning techniques and three machine learning algorithms to predict stream flow, given the present climate conditions. The results showed that the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) or Long Short-term Memory (LSTM), an artificial neural network based method, outperform other conventional and machine-learning algorithms for predicting stream flow. Furthermore, we analyzed that stream flow is directly affected by precipitation, land usage, and temperature. These indexes are critical, which can be used by hydrologists to identify the potential for stream flow. We make the dataset publicly available (https://github.com/sadaqat007/Dataset) so that others should be able to replicate and build upon the results published.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge