Sadaqat ur Rehman
An Experimental Analysis of Attack Classification Using Machine Learning in IoT Networks
Jan 10, 2021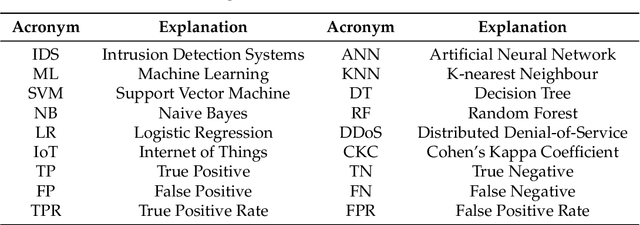

Abstract:In recent years, there has been a massive increase in the amount of Internet of Things (IoT) devices as well as the data generated by such devices. The participating devices in IoT networks can be problematic due to their resource-constrained nature, and integrating security on these devices is often overlooked. This has resulted in attackers having an increased incentive to target IoT devices. As the number of attacks possible on a network increases, it becomes more difficult for traditional intrusion detection systems (IDS) to cope with these attacks efficiently. In this paper, we highlight several machine learning (ML) methods such as k-nearest neighbour (KNN), support vector machine (SVM), decision tree (DT), naive Bayes (NB), random forest (RF), artificial neural network (ANN), and logistic regression (LR) that can be used in IDS. In this work, ML algorithms are compared for both binary and multi-class classification on Bot-IoT dataset. Based on several parameters such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and log loss, we experimentally compared the aforementioned ML algorithms. In the case of HTTP distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack, the accuracy of RF is 99%. Furthermore, other simulation results-based precision, recall, F1 score, and log loss metric reveal that RF outperforms on all types of attacks in binary classification. However, in multi-class classification, KNN outperforms other ML algorithms with an accuracy of 99%, which is 4% higher than RF.
Deep Learning Techniques for Future Intelligent Cross-Media Retrieval
Jul 21, 2020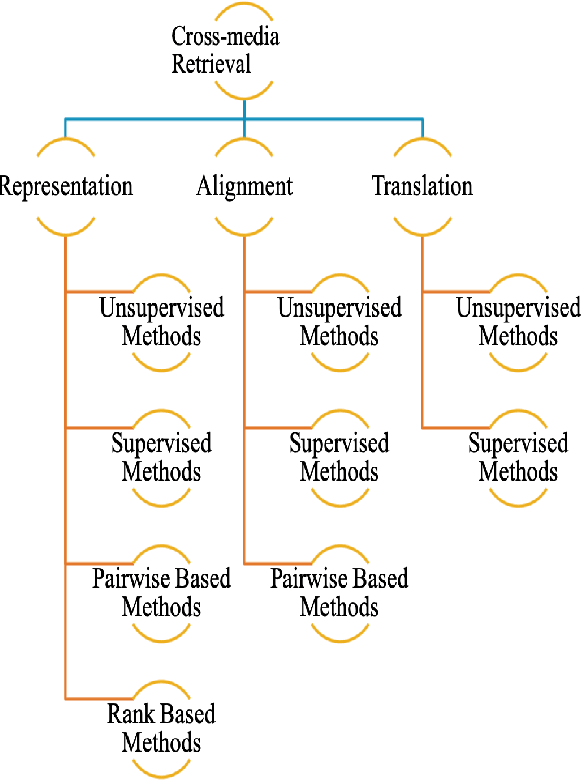



Abstract:With the advancement in technology and the expansion of broadcasting, cross-media retrieval has gained much attention. It plays a significant role in big data applications and consists in searching and finding data from different types of media. In this paper, we provide a novel taxonomy according to the challenges faced by multi-modal deep learning approaches in solving cross-media retrieval, namely: representation, alignment, and translation. These challenges are evaluated on deep learning (DL) based methods, which are categorized into four main groups: 1) unsupervised methods, 2) supervised methods, 3) pairwise based methods, and 4) rank based methods. Then, we present some well-known cross-media datasets used for retrieval, considering the importance of these datasets in the context in of deep learning based cross-media retrieval approaches. Moreover, we also present an extensive review of the state-of-the-art problems and its corresponding solutions for encouraging deep learning in cross-media retrieval. The fundamental objective of this work is to exploit Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) for bridging the "media gap", and provide researchers and developers with a better understanding of the underlying problems and the potential solutions of deep learning assisted cross-media retrieval. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive survey to address cross-media retrieval under deep learning methods.
Water Preservation in Soan River Basin using Deep Learning Techniques
Jun 26, 2019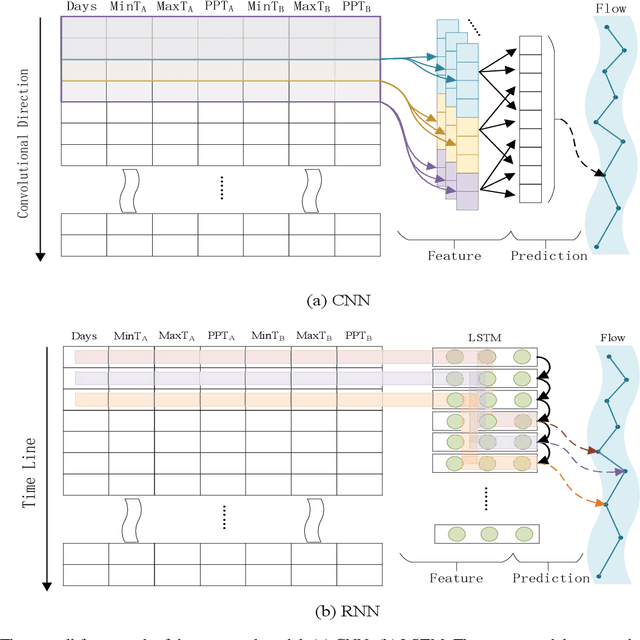
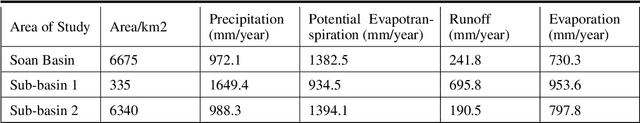
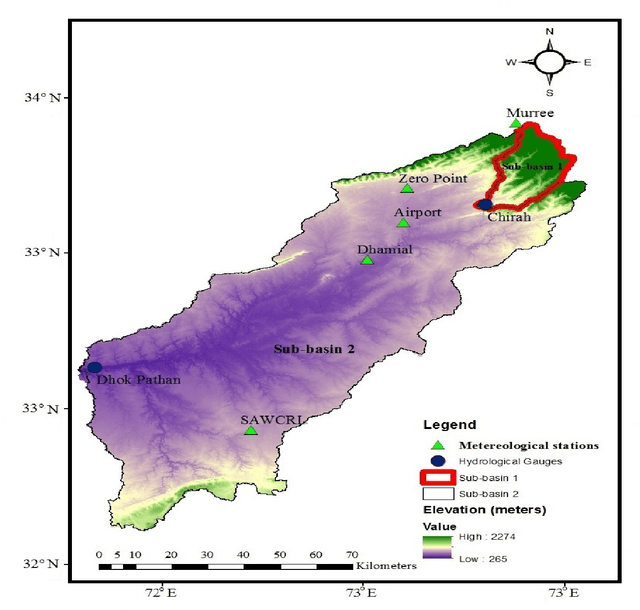
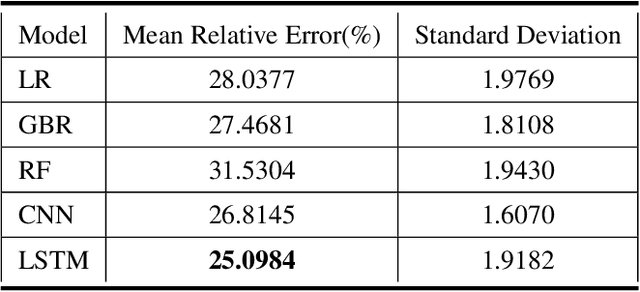
Abstract:Water supplies are crucial for the development of living beings. However, change in the hydrological process i.e. climate and land usage are the key issues. Sustaining water level and accurate estimating for dynamic conditions is a critical job for hydrologists, but predicting hydrological extremes is an open issue. In this paper, we proposed two deep learning techniques and three machine learning algorithms to predict stream flow, given the present climate conditions. The results showed that the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) or Long Short-term Memory (LSTM), an artificial neural network based method, outperform other conventional and machine-learning algorithms for predicting stream flow. Furthermore, we analyzed that stream flow is directly affected by precipitation, land usage, and temperature. These indexes are critical, which can be used by hydrologists to identify the potential for stream flow. We make the dataset publicly available (https://github.com/sadaqat007/Dataset) so that others should be able to replicate and build upon the results published.
Image Captioning with Object Detection and Localization
Jun 08, 2017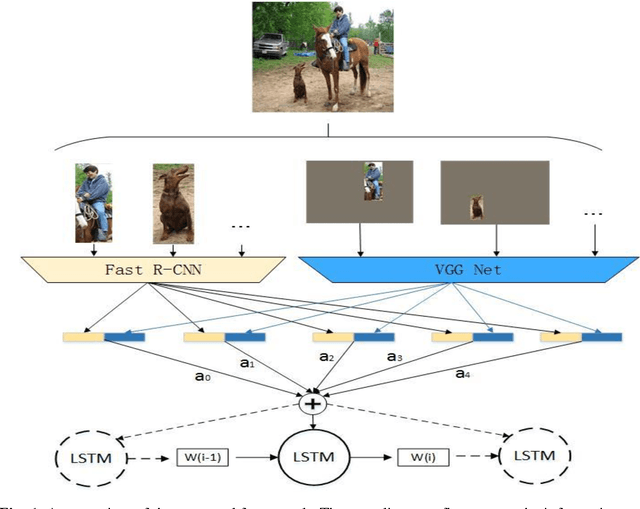
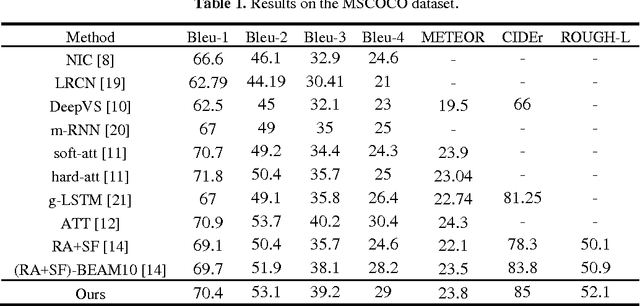
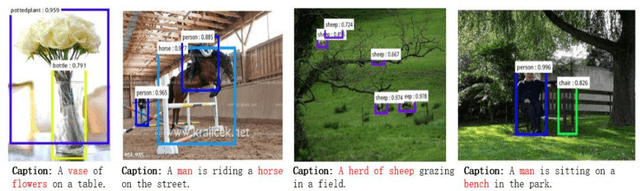

Abstract:Automatically generating a natural language description of an image is a task close to the heart of image understanding. In this paper, we present a multi-model neural network method closely related to the human visual system that automatically learns to describe the content of images. Our model consists of two sub-models: an object detection and localization model, which extract the information of objects and their spatial relationship in images respectively; Besides, a deep recurrent neural network (RNN) based on long short-term memory (LSTM) units with attention mechanism for sentences generation. Each word of the description will be automatically aligned to different objects of the input image when it is generated. This is similar to the attention mechanism of the human visual system. Experimental results on the COCO dataset showcase the merit of the proposed method, which outperforms previous benchmark models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge