Nadun Ranawaka Arachchige
Joint Model-based Model-free Diffusion for Planning with Constraints
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Model-free diffusion planners have shown great promise for robot motion planning, but practical robotic systems often require combining them with model-based optimization modules to enforce constraints, such as safety. Naively integrating these modules presents compatibility challenges when diffusion's multi-modal outputs behave adversarially to optimization-based modules. To address this, we introduce Joint Model-based Model-free Diffusion (JM2D), a novel generative modeling framework. JM2D formulates module integration as a joint sampling problem to maximize compatibility via an interaction potential, without additional training. Using importance sampling, JM2D guides modules outputs based only on evaluations of the interaction potential, thus handling non-differentiable objectives commonly arising from non-convex optimization modules. We evaluate JM2D via application to aligning diffusion planners with safety modules on offline RL and robot manipulation. JM2D significantly improves task performance compared to conventional safety filters without sacrificing safety. Further, we show that conditional generation is a special case of JM2D and elucidate key design choices by comparing with SOTA gradient-based and projection-based diffusion planners. More details at: https://jm2d-corl25.github.io/.
What Matters in Learning from Large-Scale Datasets for Robot Manipulation
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning from large multi-task demonstration datasets has emerged as a promising path for building generally-capable robots. As a result, 1000s of hours have been spent on building such large-scale datasets around the globe. Despite the continuous growth of such efforts, we still lack a systematic understanding of what data should be collected to improve the utility of a robotics dataset and facilitate downstream policy learning. In this work, we conduct a large-scale dataset composition study to answer this question. We develop a data generation framework to procedurally emulate common sources of diversity in existing datasets (such as sensor placements and object types and arrangements), and use it to generate large-scale robot datasets with controlled compositions, enabling a suite of dataset composition studies that would be prohibitively expensive in the real world. We focus on two practical settings: (1) what types of diversity should be emphasized when future researchers collect large-scale datasets for robotics, and (2) how should current practitioners retrieve relevant demonstrations from existing datasets to maximize downstream policy performance on tasks of interest. Our study yields several critical insights -- for example, we find that camera poses and spatial arrangements are crucial dimensions for both diversity in collection and alignment in retrieval. In real-world robot learning settings, we find that not only do our insights from simulation carry over, but our retrieval strategies on existing datasets such as DROID allow us to consistently outperform existing training strategies by up to 70%. More results at https://robo-mimiclabs.github.io/
SAIL: Faster-than-Demonstration Execution of Imitation Learning Policies
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Offline Imitation Learning (IL) methods such as Behavior Cloning are effective at acquiring complex robotic manipulation skills. However, existing IL-trained policies are confined to executing the task at the same speed as shown in demonstration data. This limits the task throughput of a robotic system, a critical requirement for applications such as industrial automation. In this paper, we introduce and formalize the novel problem of enabling faster-than-demonstration execution of visuomotor policies and identify fundamental challenges in robot dynamics and state-action distribution shifts. We instantiate the key insights as SAIL (Speed Adaptation for Imitation Learning), a full-stack system integrating four tightly-connected components: (1) a consistency-preserving action inference algorithm for smooth motion at high speed, (2) high-fidelity tracking of controller-invariant motion targets, (3) adaptive speed modulation that dynamically adjusts execution speed based on motion complexity, and (4) action scheduling to handle real-world system latencies. Experiments on 12 tasks across simulation and two real, distinct robot platforms show that SAIL achieves up to a 4x speedup over demonstration speed in simulation and up to 3.2x speedup in the real world. Additional detail is available at https://nadunranawaka1.github.io/sail-policy
RAIL: Reachability-Aided Imitation Learning for Safe Policy Execution
Sep 28, 2024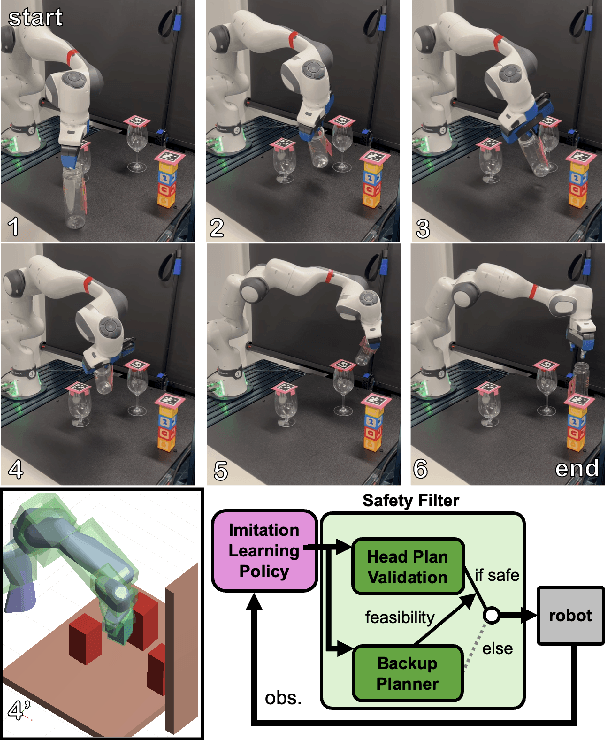
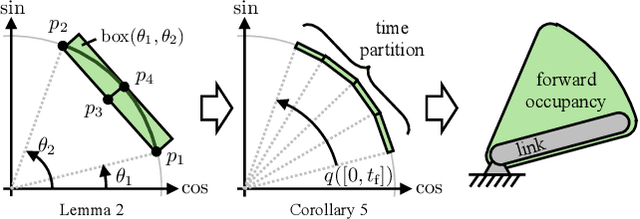

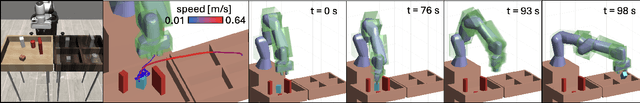
Abstract:Imitation learning (IL) has shown great success in learning complex robot manipulation tasks. However, there remains a need for practical safety methods to justify widespread deployment. In particular, it is important to certify that a system obeys hard constraints on unsafe behavior in settings when it is unacceptable to design a tradeoff between performance and safety via tuning the policy (i.e. soft constraints). This leads to the question, how does enforcing hard constraints impact the performance (meaning safely completing tasks) of an IL policy? To answer this question, this paper builds a reachability-based safety filter to enforce hard constraints on IL, which we call Reachability-Aided Imitation Learning (RAIL). Through evaluations with state-of-the-art IL policies in mobile robots and manipulation tasks, we make two key findings. First, the highest-performing policies are sometimes only so because they frequently violate constraints, and significantly lose performance under hard constraints. Second, surprisingly, hard constraints on the lower-performing policies can occasionally increase their ability to perform tasks safely. Finally, hardware evaluation confirms the method can operate in real time.
The Utility of Explainable AI in Ad Hoc Human-Machine Teaming
Sep 08, 2022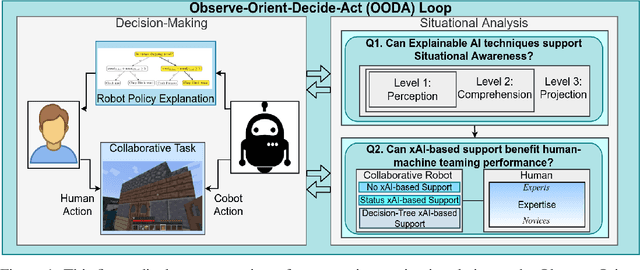
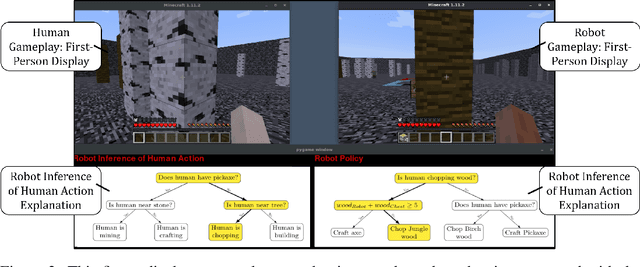
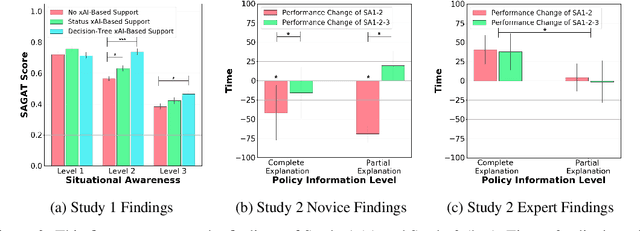
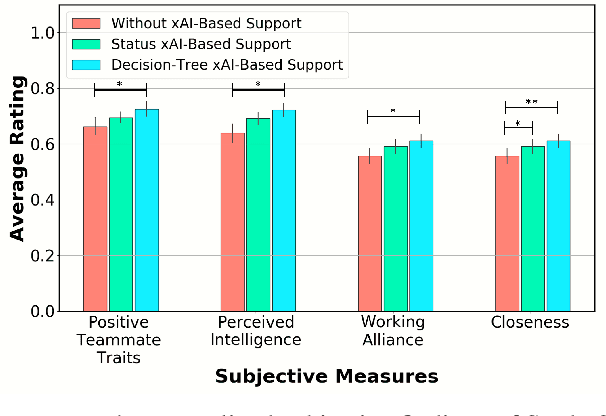
Abstract:Recent advances in machine learning have led to growing interest in Explainable AI (xAI) to enable humans to gain insight into the decision-making of machine learning models. Despite this recent interest, the utility of xAI techniques has not yet been characterized in human-machine teaming. Importantly, xAI offers the promise of enhancing team situational awareness (SA) and shared mental model development, which are the key characteristics of effective human-machine teams. Rapidly developing such mental models is especially critical in ad hoc human-machine teaming, where agents do not have a priori knowledge of others' decision-making strategies. In this paper, we present two novel human-subject experiments quantifying the benefits of deploying xAI techniques within a human-machine teaming scenario. First, we show that xAI techniques can support SA ($p<0.05)$. Second, we examine how different SA levels induced via a collaborative AI policy abstraction affect ad hoc human-machine teaming performance. Importantly, we find that the benefits of xAI are not universal, as there is a strong dependence on the composition of the human-machine team. Novices benefit from xAI providing increased SA ($p<0.05$) but are susceptible to cognitive overhead ($p<0.05$). On the other hand, expert performance degrades with the addition of xAI-based support ($p<0.05$), indicating that the cost of paying attention to the xAI outweighs the benefits obtained from being provided additional information to enhance SA. Our results demonstrate that researchers must deliberately design and deploy the right xAI techniques in the right scenario by carefully considering human-machine team composition and how the xAI method augments SA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge