Mohammed Atiquzzaman
Joint UAV-UGV Positioning and Trajectory Planning via Meta A3C for Reliable Emergency Communications
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Joint deployment of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) has been shown to be an effective method to establish communications in areas affected by disasters. However, ensuring good Quality of Services (QoS) while using as few UAVs as possible also requires optimal positioning and trajectory planning for UAVs and UGVs. This paper proposes a joint UAV-UGV-based positioning and trajectory planning framework for UAVs and UGVs deployment that guarantees optimal QoS for ground users. To model the UGVs' mobility, we introduce a road graph, which directs their movement along valid road segments and adheres to the road network constraints. To solve the sum rate optimization problem, we reformulate the problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) and propose a novel asynchronous Advantage Actor Critic (A3C) incorporated with meta-learning for rapid adaptation to new environments and dynamic conditions. Numerical results demonstrate that our proposed Meta-A3C approach outperforms A3C and DDPG, delivering 13.1\% higher throughput and 49\% faster execution while meeting the QoS requirements.
A Trustworthy Multi-LLM Network: Challenges,Solutions, and A Use Case
May 06, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate strong potential across a variety of tasks in communications and networking due to their advanced reasoning capabilities. However, because different LLMs have different model structures and are trained using distinct corpora and methods, they may offer varying optimization strategies for the same network issues. Moreover, the limitations of an individual LLM's training data, aggravated by the potential maliciousness of its hosting device, can result in responses with low confidence or even bias. To address these challenges, we propose a blockchain-enabled collaborative framework that connects multiple LLMs into a Trustworthy Multi-LLM Network (MultiLLMN). This architecture enables the cooperative evaluation and selection of the most reliable and high-quality responses to complex network optimization problems. Specifically, we begin by reviewing related work and highlighting the limitations of existing LLMs in collaboration and trust, emphasizing the need for trustworthiness in LLM-based systems. We then introduce the workflow and design of the proposed Trustworthy MultiLLMN framework. Given the severity of False Base Station (FBS) attacks in B5G and 6G communication systems and the difficulty of addressing such threats through traditional modeling techniques, we present FBS defense as a case study to empirically validate the effectiveness of our approach. Finally, we outline promising future research directions in this emerging area.
A Survey on Congestion Control and Scheduling for Multipath TCP: Machine Learning vs Classical Approaches
Sep 17, 2023Abstract:Multipath TCP (MPTCP) has been widely used as an efficient way for communication in many applications. Data centers, smartphones, and network operators use MPTCP to balance the traffic in a network efficiently. MPTCP is an extension of TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), which provides multiple paths, leading to higher throughput and low latency. Although MPTCP has shown better performance than TCP in many applications, it has its own challenges. The network can become congested due to heavy traffic in the multiple paths (subflows) if the subflow rates are not determined correctly. Moreover, communication latency can occur if the packets are not scheduled correctly between the subflows. This paper reviews techniques to solve the above-mentioned problems based on two main approaches; non data-driven (classical) and data-driven (Machine Learning) approaches. This paper compares these two approaches and highlights their strengths and weaknesses with a view to motivating future researchers in this exciting area of machine learning for communications. This paper also provides details on the simulation of MPTCP and its implementations in real environments.
Smart Policy Control for Securing Federated Learning Management System
May 18, 2023



Abstract:The widespread adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in smart cities, intelligent healthcare systems, and various real-world applications have resulted in the generation of vast amounts of data, often analyzed using different Machine Learning (ML) models. Federated learning (FL) has been acknowledged as a privacy-preserving machine learning technology, where multiple parties cooperatively train ML models without exchanging raw data. However, the current FL architecture does not allow for an audit of the training process due to the various data-protection policies implemented by each FL participant. Furthermore, there is no global model verifiability available in the current architecture. This paper proposes a smart contract-based policy control for securing the Federated Learning (FL) management system. First, we develop and deploy a smart contract-based local training policy control on the FL participants' side. This policy control is used to verify the training process, ensuring that the evaluation process follows the same rules for all FL participants. We then enforce a smart contract-based aggregation policy to manage the global model aggregation process. Upon completion, the aggregated model and policy are stored on blockchain-based storage. Subsequently, we distribute the aggregated global model and the smart contract to all FL participants. Our proposed method uses smart policy control to manage access and verify the integrity of machine learning models. We conducted multiple experiments with various machine learning architectures and datasets to evaluate our proposed framework, such as MNIST and CIFAR-10.
Privacy-Preserving Ensemble Infused Enhanced Deep Neural Network Framework for Edge Cloud Convergence
May 16, 2023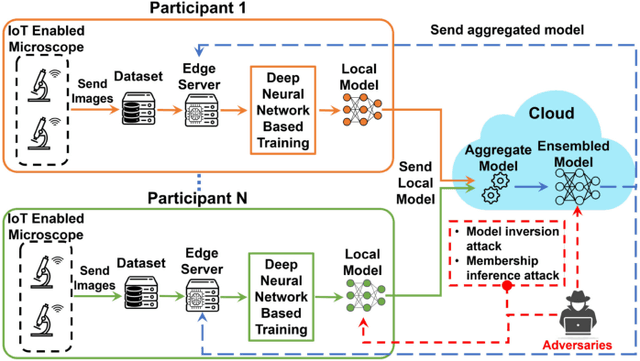
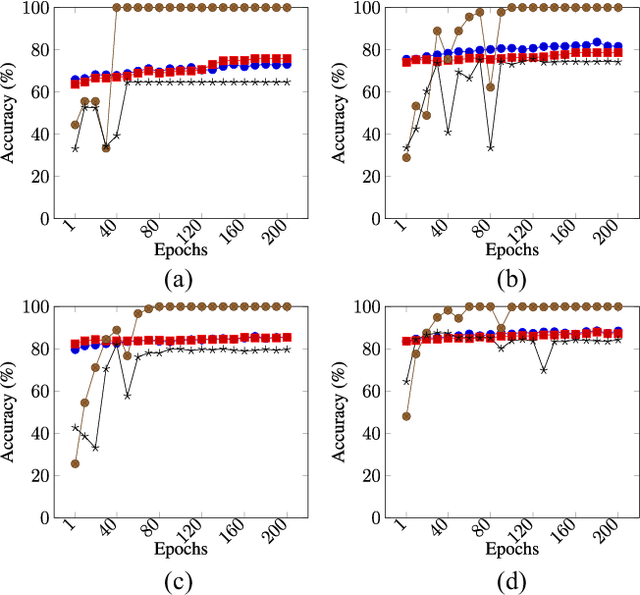
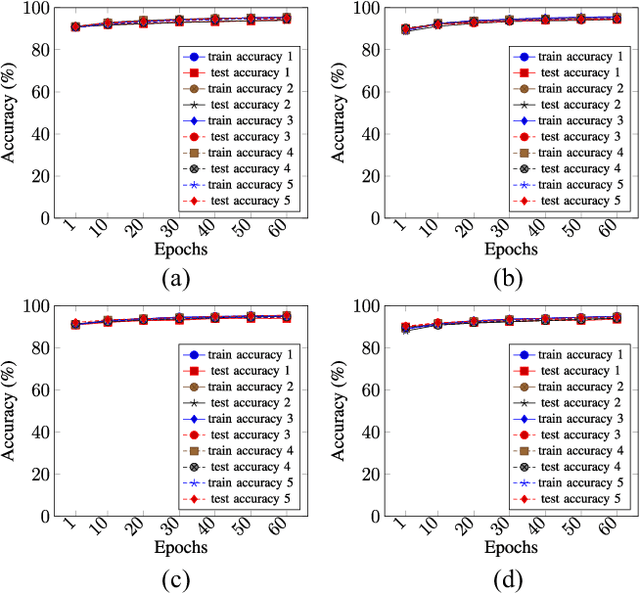
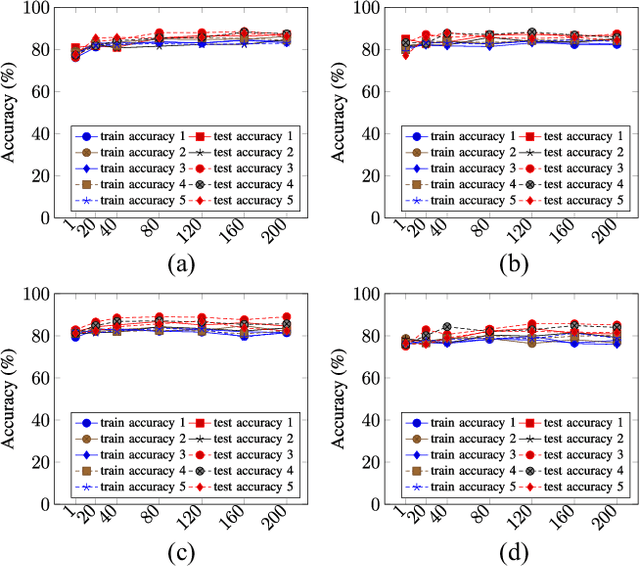
Abstract:We propose a privacy-preserving ensemble infused enhanced Deep Neural Network (DNN) based learning framework in this paper for Internet-of-Things (IoT), edge, and cloud convergence in the context of healthcare. In the convergence, edge server is used for both storing IoT produced bioimage and hosting DNN algorithm for local model training. The cloud is used for ensembling local models. The DNN-based training process of a model with a local dataset suffers from low accuracy, which can be improved by the aforementioned convergence and Ensemble Learning. The ensemble learning allows multiple participants to outsource their local model for producing a generalized final model with high accuracy. Nevertheless, Ensemble Learning elevates the risk of leaking sensitive private data from the final model. The proposed framework presents a Differential Privacy-based privacy-preserving DNN with Transfer Learning for a local model generation to ensure minimal loss and higher efficiency at edge server. We conduct several experiments to evaluate the performance of our proposed framework.
Trustworthy Privacy-preserving Hierarchical Ensemble and Federated Learning in Healthcare 4.0 with Blockchain
May 16, 2023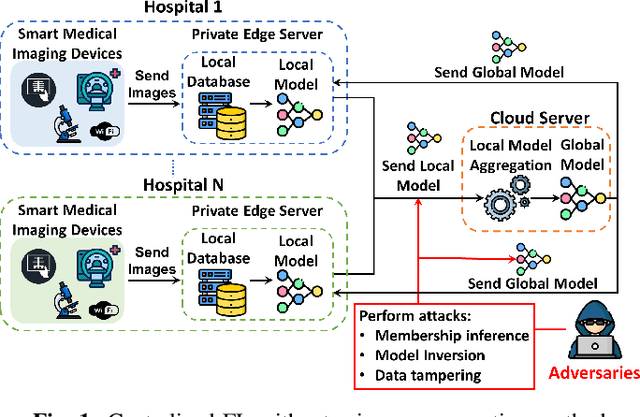
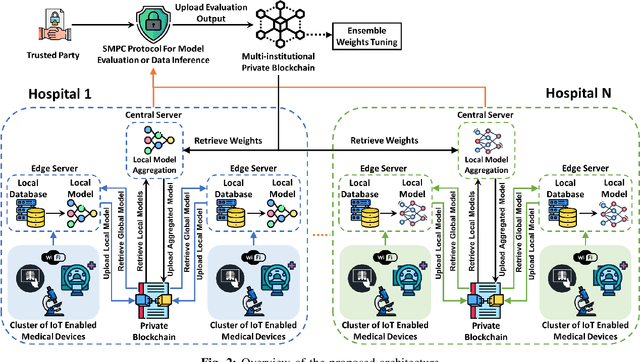
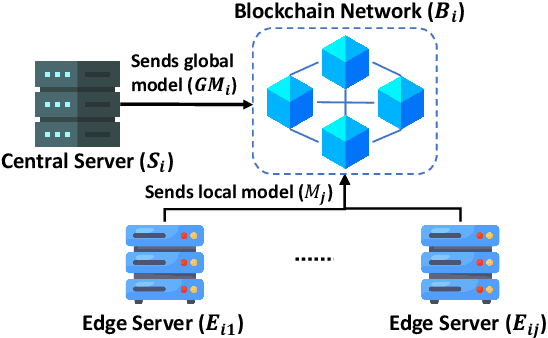
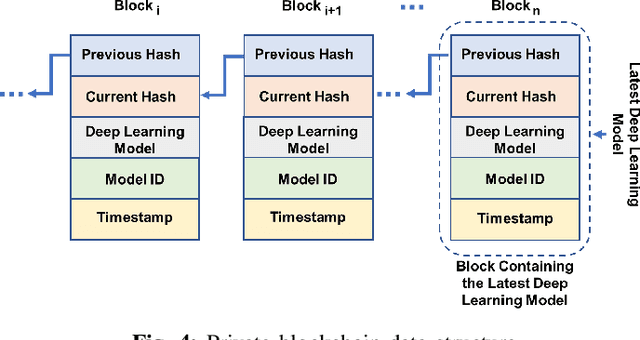
Abstract:The advancement of Internet and Communication Technologies (ICTs) has led to the era of Industry 4.0. This shift is followed by healthcare industries creating the term Healthcare 4.0. In Healthcare 4.0, the use of IoT-enabled medical imaging devices for early disease detection has enabled medical practitioners to increase healthcare institutions' quality of service. However, Healthcare 4.0 is still lagging in Artificial Intelligence and big data compared to other Industry 4.0 due to data privacy concerns. In addition, institutions' diverse storage and computing capabilities restrict institutions from incorporating the same training model structure. This paper presents a secure multi-party computation-based ensemble federated learning with blockchain that enables heterogeneous models to collaboratively learn from healthcare institutions' data without violating users' privacy. Blockchain properties also allow the party to enjoy data integrity without trust in a centralized server while also providing each healthcare institution with auditability and version control capability.
Blockchain-based Federated Learning with Secure Aggregation in Trusted Execution Environment for Internet-of-Things
Apr 25, 2023



Abstract:This paper proposes a blockchain-based Federated Learning (FL) framework with Intel Software Guard Extension (SGX)-based Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) to securely aggregate local models in Industrial Internet-of-Things (IIoTs). In FL, local models can be tampered with by attackers. Hence, a global model generated from the tampered local models can be erroneous. Therefore, the proposed framework leverages a blockchain network for secure model aggregation. Each blockchain node hosts an SGX-enabled processor that securely performs the FL-based aggregation tasks to generate a global model. Blockchain nodes can verify the authenticity of the aggregated model, run a blockchain consensus mechanism to ensure the integrity of the model, and add it to the distributed ledger for tamper-proof storage. Each cluster can obtain the aggregated model from the blockchain and verify its integrity before using it. We conducted several experiments with different CNN models and datasets to evaluate the performance of the proposed framework.
How Can Optical Communications Shape the Future of Deep Space Communications? A Survey
Dec 07, 2022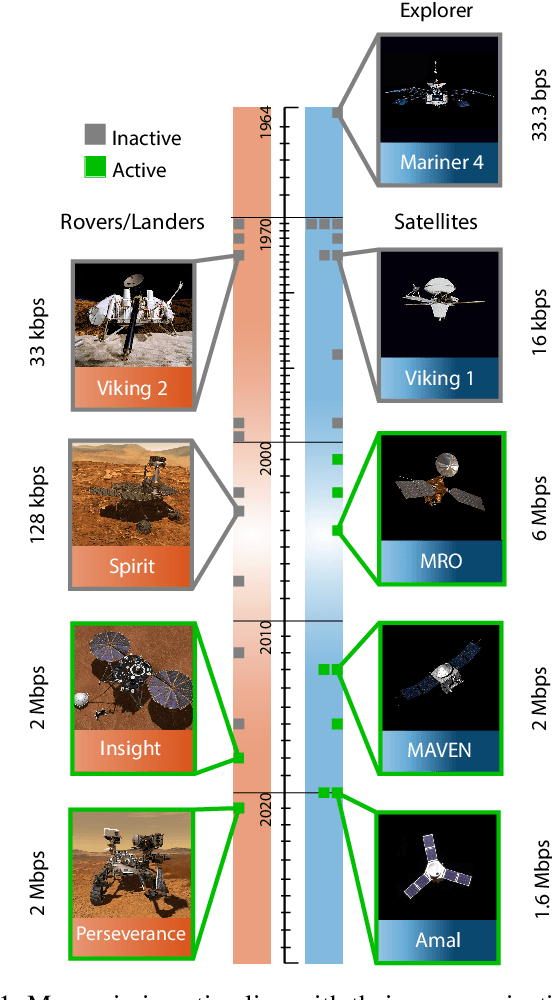
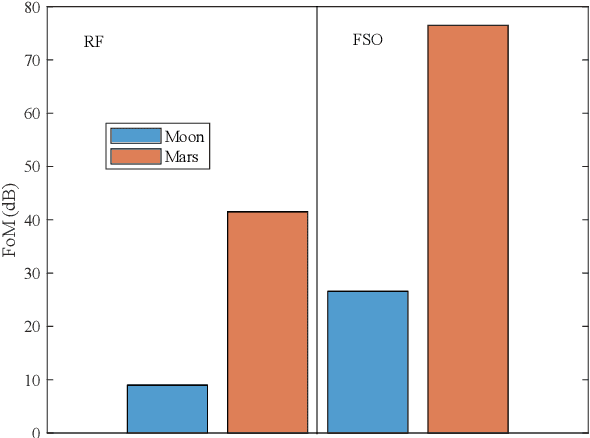
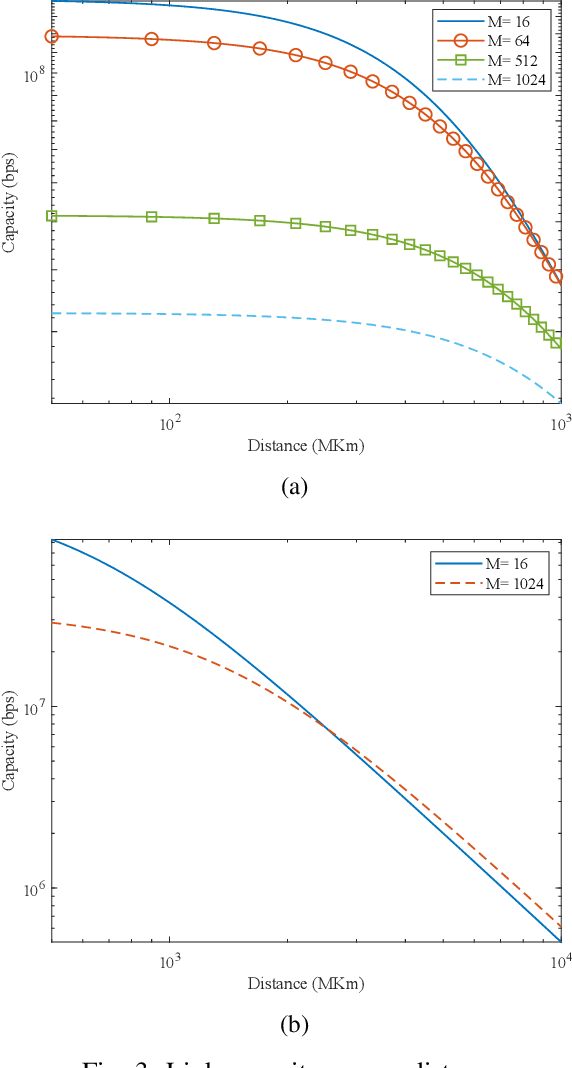
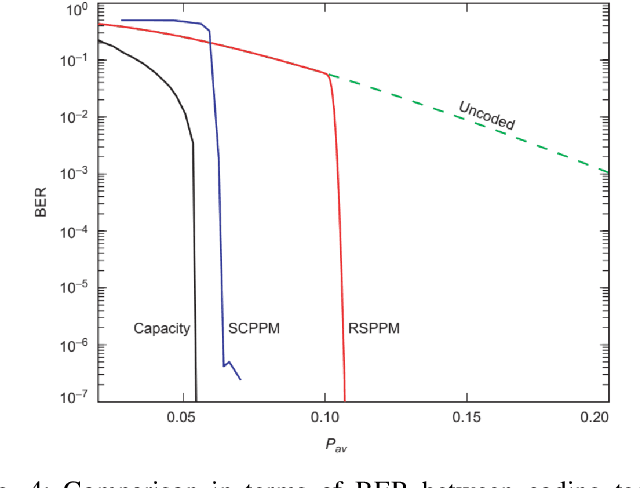
Abstract:With a large number of deep space (DS) missions anticipated by the end of this decade, reliable and high-capacity DS communications systems are needed more than ever. Nevertheless, existing DS communications technologies are far from meeting such a goal. Improving current DS communications systems does not only require system engineering leadership but also, very crucially, an investigation of potential emerging technologies that overcome the unique challenges of ultra-long DS communications links. To the best of our knowledge, there has not been any comprehensive surveys of DS communications technologies over the last decade.Fee-space optical (FSO) technology is an emerging DS technology, proven to acquire lower communications systems size, weight and power (SWaP) and achieve a very high capacity compared to its counterpart radio frequency (RF) technology, the current used DS technology. In this survey, we discuss the pros and cons of deep space optical communications (DSOC). Furthermore, we review the modulation, coding, and detection, receiver, and protocols schemes and technologies for DSOC. We provide, for the very first time, thoughtful discussions about implementing orbital angular momentum (OAM) and quantum communications (QC)for DS. We elaborate on how these technologies among other field advances, including interplanetary network, and RF/FSO systems improve reliability, capacity, and security and address related implementation challenges and potential solutions. This paper provides a holistic survey in DSOC technologies gathering 200+ fragmented literature and including novel perspectives aiming to setting the stage for more developments in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge