Nadia Adem
Connecting the Universe: Challenges, Mitigation, Advances, and Link Engineering
Feb 19, 2023Abstract:With the large number of deep space (DS) missions anticipated by the end of this decade, reliable-high capacity DS communication systems are needed more than ever. Nevertheless, existing DS communication technologies are far from meeting such a goal. Improving current systems does not only demand a system engineering leadership, but more crucially a well investigation in the potentials of emerging technologies in overcoming the challenges of the unique-ultra long DS communication channel. This project starts with a survey that highlights current technologies, trends, and advancements, investigates potentials, and identify challenges, and in essence, provide perspectives and propose solutions. It focuses on free-space optical (FSO) communication as a potential technology that can overcome the shortcomings of current radio frequency (RF)-based communication systems. To the best of our knowledge, in addition, it provides for the very first time a thoughtful discussion about implementing orbital angular momentum (OAM) for DS, identifies major related challenges, and proposes some novel solutions. Furthermore, we discuss DS modulations and coding schemes, as well as emerging receiver technologies and communication protocols. We also elaborate on how all of these technologies guarantee reliability, improve efficiency, offer capacity boosts, and enhance security in the unique DS environment. In addition to that, an extended study on the design and performance analysis of deep space optical communication (DSOC) is included, with the most suggested modulation for such a link being pulse position modulation (PPM) and a focus on the communication between Earth and the planet Mars, which is an important destination for space exploration.
How Well Sensing Integrates with Communications in MmWave Wi-Fi?
Feb 16, 2023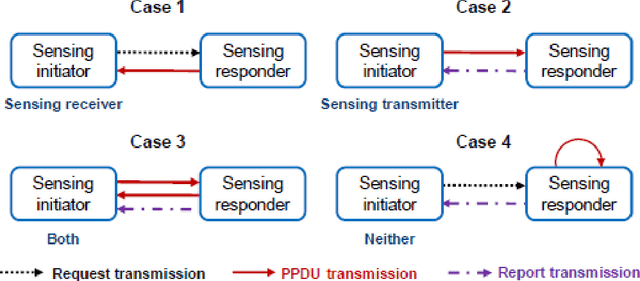
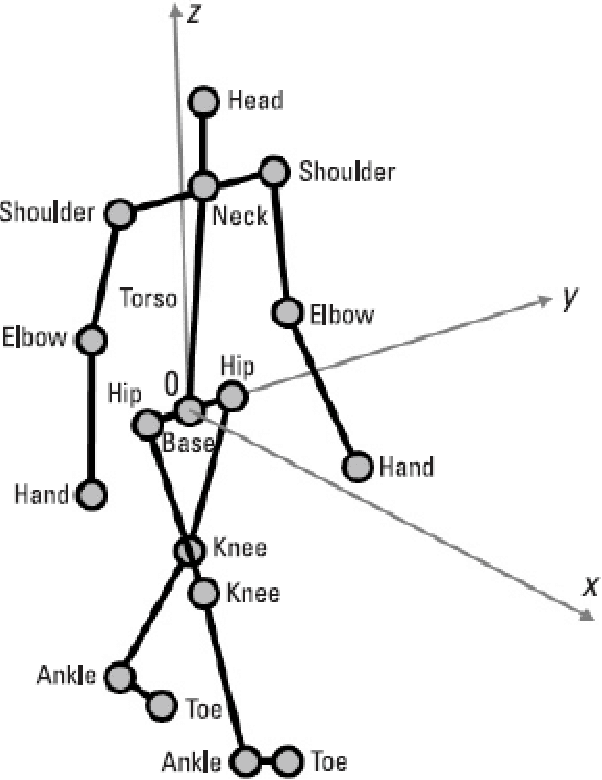

Abstract:The development of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems has recently gained interest for its ability to offer a variety of services including resources sharing and new applications, for example, localization, tracking, and health care related. While the sensing capabilities are offered through many technologies, rending to their wide deployments and the high frequency spectrum they provide and high range resolution, its accessibility through the Wi-Fi networks IEEE 802.11ad and 802.11ay has been getting the interest of research and industry. Even though there is a dedicated standardization body, namely the 802.11bf task group, working on enhancing the Wi-Fi sensing performance, investigations are needed to evaluate the effectiveness of various sensing techniques. In this project, we, in addition to surveying related literature, we evaluate the sensing performance of the millimeter wave (mmWave) Wi-Fi systems by simulating a scenario of a human target using Matlab simulation tools. In this analysis, we processed channel estimation data using the short time Fourier transform (STFT). Furthermore, using a channel variation threshold method, we evaluated the performance while reducing feedback. Our findings indicate that using STFT window overlap can provide good tracking results, and that the reduction in feedback measurements using 0.05 and 0.1 threshold levels reduces feedback measurements by 48% and 77%, respectively, without significantly degrading performance.
Why Should and How Can Quantum Technologies Be Leveraged at National Levels?
Dec 11, 2022Abstract:Quantum technologies (QT) promise to change the landscape of technologies disruptively in diverse industries. For this reason, many nations around the globe are investing to emerge within the global quantum ecosystem through initiating national programs and international partnerships. Nonetheless, some other countries are still running behind and yet their governments need to take series actions to help their private and public sectors adapt to the looming changes, considering the new regulations required and the huge influence that QT will present in the near future. In this opinion piece, we provide, for the best of our knowledge, the first generally applicable, yet comprehensive and brief, framework for leveraging the emerging quantum technologies to facilitate the establishment of national initiatives properly. The insights presented in this article were driven based on investigating various approaches, initiatives, and roadmaps adopted globally and meeting with local and regional leaders, professionals, and governmental officials. Furthermore, taken into account socioeconomic and institutional dimensions of the Libyan society, we project the framework for the Libyan nation. This opinion piece is intended to inspire researchers, technical industrial experts, stakeholders, and governmental bodies to find roles they need to play to bring QT forward.
How Can Optical Communications Shape the Future of Deep Space Communications? A Survey
Dec 07, 2022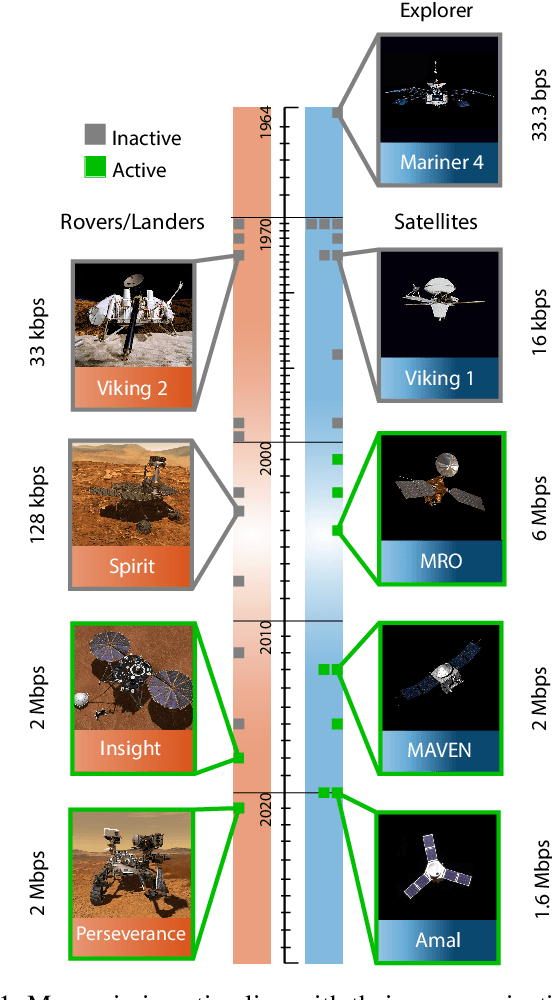
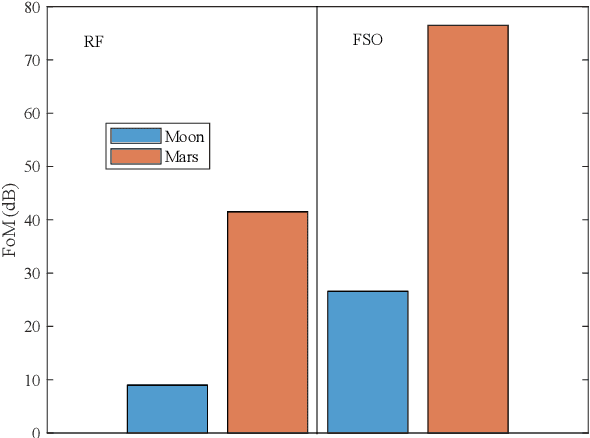
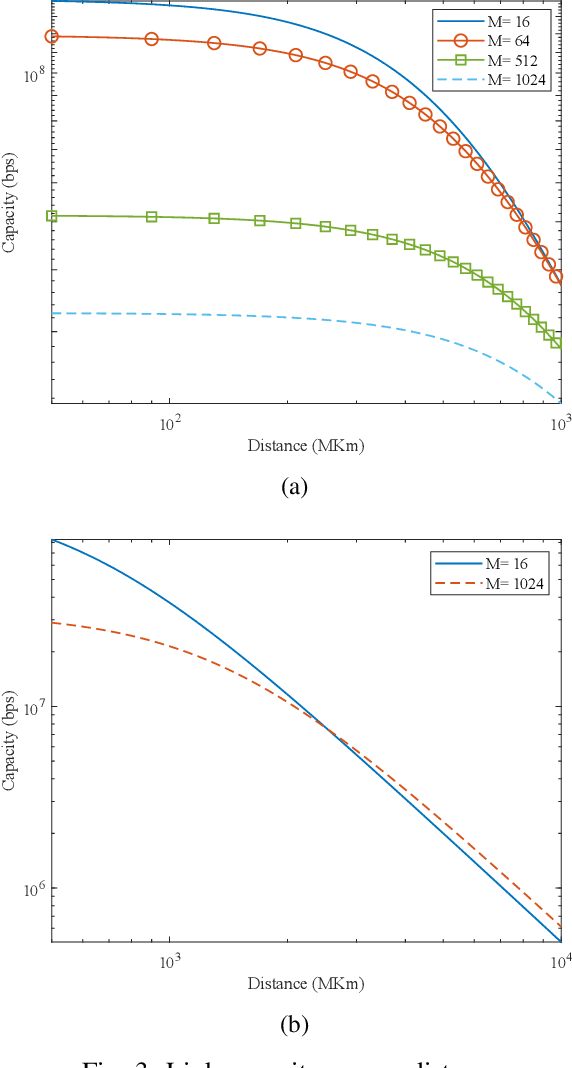
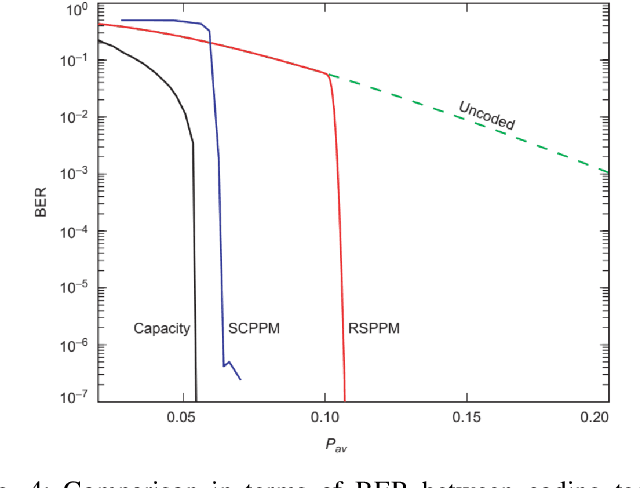
Abstract:With a large number of deep space (DS) missions anticipated by the end of this decade, reliable and high-capacity DS communications systems are needed more than ever. Nevertheless, existing DS communications technologies are far from meeting such a goal. Improving current DS communications systems does not only require system engineering leadership but also, very crucially, an investigation of potential emerging technologies that overcome the unique challenges of ultra-long DS communications links. To the best of our knowledge, there has not been any comprehensive surveys of DS communications technologies over the last decade.Fee-space optical (FSO) technology is an emerging DS technology, proven to acquire lower communications systems size, weight and power (SWaP) and achieve a very high capacity compared to its counterpart radio frequency (RF) technology, the current used DS technology. In this survey, we discuss the pros and cons of deep space optical communications (DSOC). Furthermore, we review the modulation, coding, and detection, receiver, and protocols schemes and technologies for DSOC. We provide, for the very first time, thoughtful discussions about implementing orbital angular momentum (OAM) and quantum communications (QC)for DS. We elaborate on how these technologies among other field advances, including interplanetary network, and RF/FSO systems improve reliability, capacity, and security and address related implementation challenges and potential solutions. This paper provides a holistic survey in DSOC technologies gathering 200+ fragmented literature and including novel perspectives aiming to setting the stage for more developments in the field.
ProSky: NEAT Meets NOMA-mmWave in the Sky of 6G
Oct 13, 2022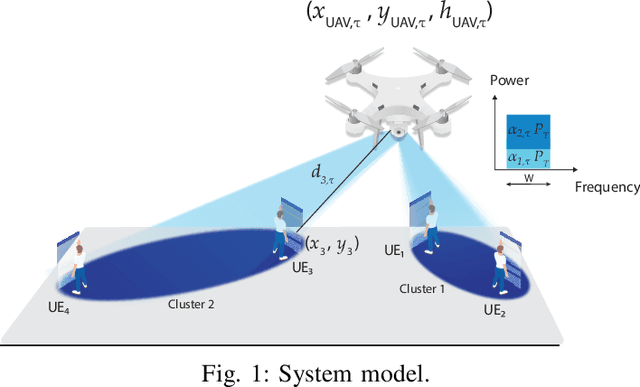
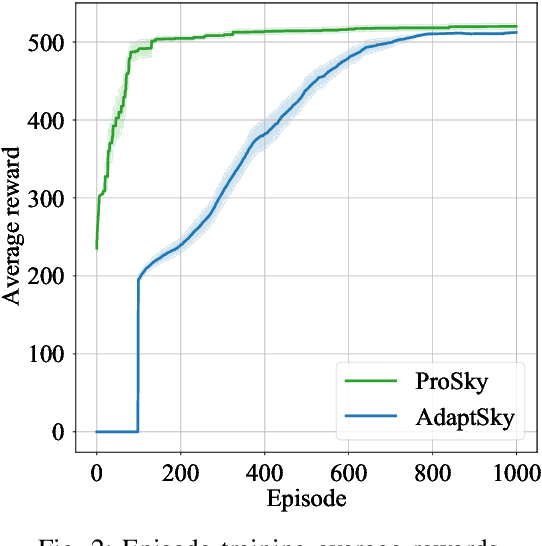
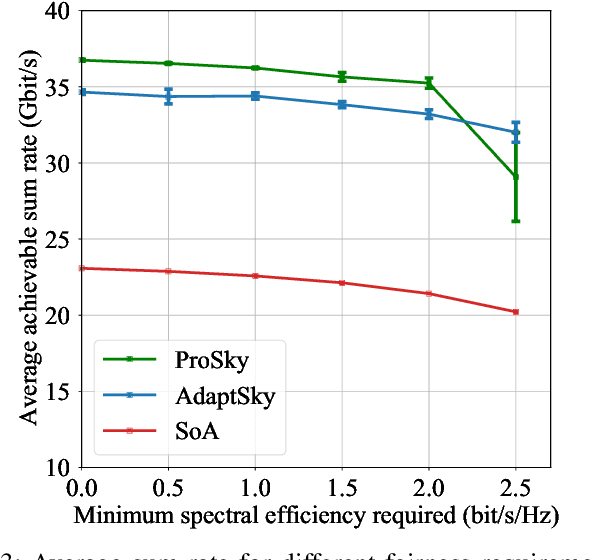
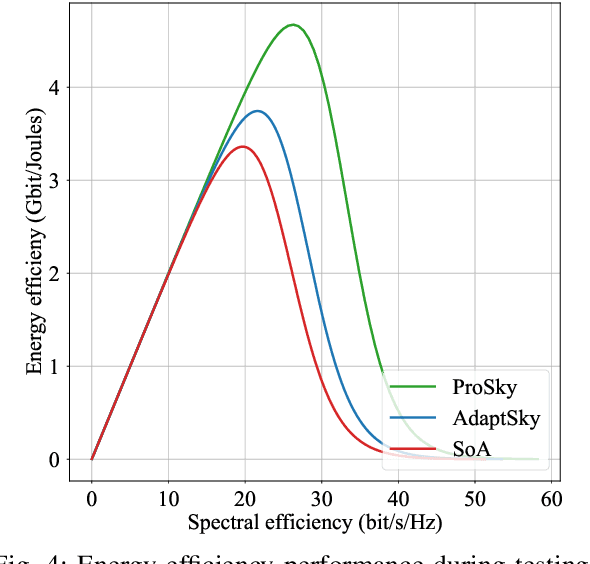
Abstract:Rendering to their abilities to provide ubiquitous connectivity, flexibly and cost effectively, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have been getting more and more research attention. To take the UAVs' performance to the next level, however, they need to be merged with some other technologies like non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and millimeter wave (mmWave), which both promise high spectral efficiency (SE). As managing UAVs efficiently may not be possible using model-based techniques, another key innovative technology that UAVs will inevitably need to leverage is artificial intelligence (AI). Designing an AI-based technique that adaptively allocates radio resources and places UAVs in 3D space to meet certain communication objectives, however, is a tough row to hoe. In this paper, we propose a neuroevolution of augmenting topologies NEAT framework, referred to as ProSky, to manage NOMA-mmWave-UAV networks. ProSky exhibits a remarkable performance improvement over a model-based method. Moreover, ProSky learns 5.3 times faster than and outperforms, in both SE and energy efficiency EE while being reasonably fair, a deep reinforcement learning DRL based scheme. The ProSky source code is accessible to use here: https://github.com/Fouzibenfaid/ProSky
Channel Estimation Based on Machine Learning Paradigm for Spatial Modulation OFDM
Sep 15, 2021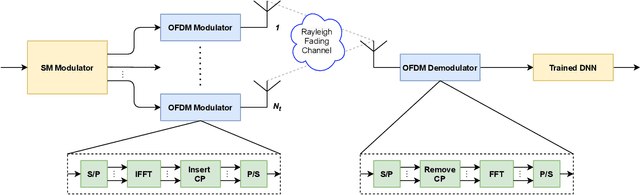
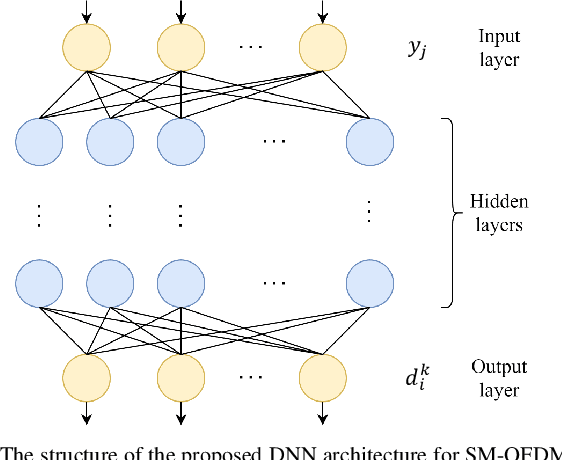
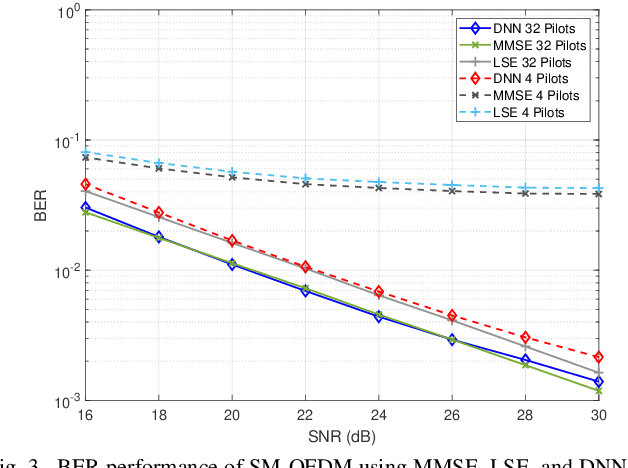
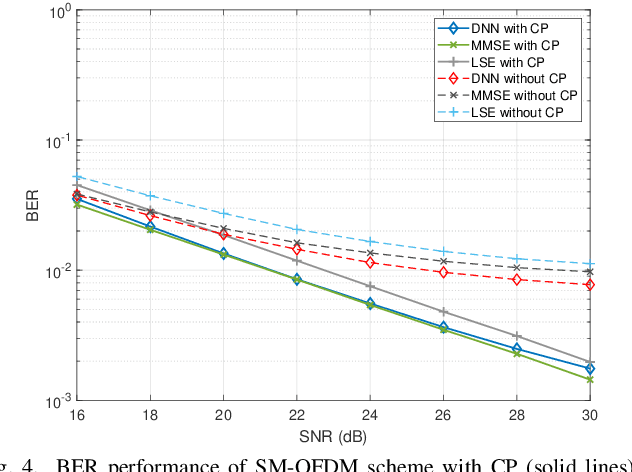
Abstract:In this paper, deep neural network (DNN) is integrated with spatial modulation-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (SM-OFDM) technique for end-to-end data detection over Rayleigh fading channel. This proposed system directly demodulates the received symbols, leaving the channel estimation done only implicitly. Furthermore, an ensemble network is also proposed for this system. Simulation results show that the proposed DNN detection scheme has a significant advantage over classical methods when the pilot overhead and cyclic prefix (CP) are reduced, owing to its ability to learn and adjust to complicated channel conditions. Finally, the ensemble network is shown to improve the generalization of the proposed scheme, while also showing a slight improvement in its performance.
How Crucial Is It for 6G Networks to Be Autonomous?
Jul 09, 2021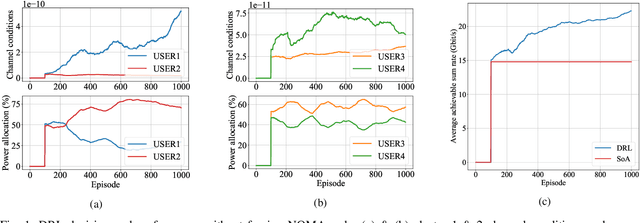
Abstract:The sixth generation (6G), unlike any of the previous generations, is envisioned by 2030 to connect everything. Moreover, in addition to the new use cases, 6G is expected to support, it will need to provide a superior performance over 5G. The global connectivity, large network dimensions, users heterogeneity, extremely low-power consumption, high throughput, ultrahigh reliability, efficient network operation and maintenance, and low-latency requirements to be met by future networks inevitably necessitate the autonomy of 6G. Intelligence, facilitated mainly by the advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, is a key to achieve autonomy. In this paper, we provide a bird's-eye view of 6G, its vision, progress, and objectives. Furthermore, we present some technologies that would be mainly enabling intelligent globally connected world. In addition to discussing the role of AI for future wireless communications, we, unlike any other review papers, provide our original results which give early evidence for the viability of achieving 6G networks autonomy through leveraging AI advances. Furthermore, we, very importantly, identify 6G implementation challenges and key innovative techniques that promise to solve them. This article serves as a starting point for learners to acquire more knowledge about 6G and also for researchers to promote more development to the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge