Taissir Y. Elganimi
Sparsity Realization in User-Side Multilayer RIS
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:User-side reconfigurable intelligent surface (US-RIS)-aided communication has recently emerged as a promising solution to overcome the high hardware cost and physical size limitations of large-scale user side antenna arrays. This letter proposes, for the first time, a framework that realizes sparsity in multilayer US-RIS using two strategies, namely element-wise sparsity and geometric sparsity. The element-wise approach distributes a limited number of active elements irregularly across multiple layers, thereby exploiting additional spatial degrees of freedom and boosting the achievable rate. For further performance enhancement, a novel foldable RIS architecture leveraging geometric sparsity is proposed, achieving additional gains by optimizing the folding topology of its multilayer structure. Simulation results show that the proposed sparse architectures provide consistently higher achievable rates than existing designs.
STAR-RIS-Aided Secure Communications:Analytical Insights and Performance Comparison
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (STAR-RISs) have emerged as a promising technology for enabling full-space signal manipulation and enhancing wireless network coverage and capacity. In this article, we present a comprehensive analytical comparison of STAR-RIS-assisted systems with single-input single-output (SISO), conventional RISs, and decode-and-forward (DF) relaying schemes, including both half-duplex (HD) and full-duplex (FD) modes. Closed-form expressions are derived for the achievable secrecy rates of STAR-RIS-aided communications under both the absence and presence of eavesdroppers. Unlike most existing works, the direct source destination link is incorporated in all considered schemes, and optimal transmit power allocation is investigated for HD and FD-DF relaying. Furthermore, we provide the conditions under which STAR-RIS outperforms HD- and FD-DF relaying and quantify the minimum number of STAR-RIS elements required to achieve superior rates. The impacts of key system parameters including transmit power, number of elements, reflection-to-transmission power ratio, element-splitting factor, and deployment positions on both achievable and secrecy performance are investigated. The results reveal that STAR-RIS systems can achieve superior rates and secrecy rates compared to all benchmark schemes.
Novel Selection Schemes for Multi-RIS-Assisted Fluid Antenna Systems
Apr 28, 2025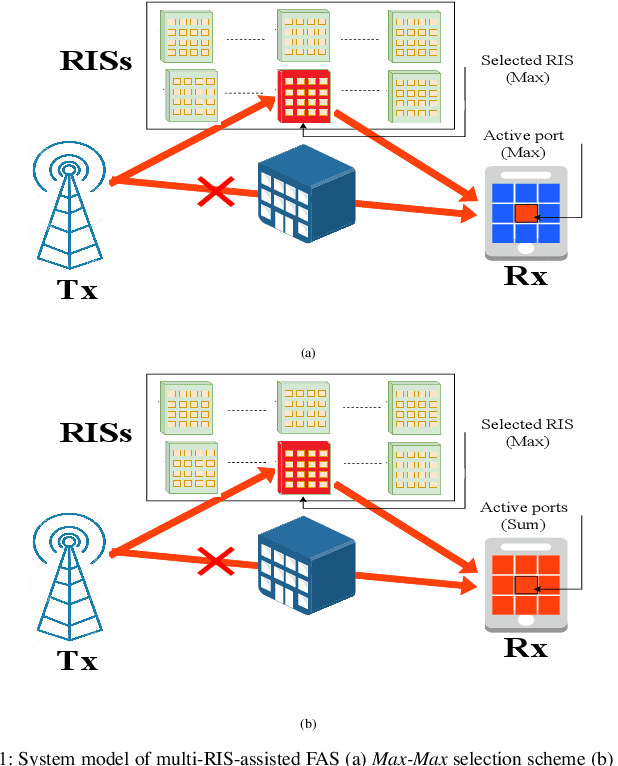
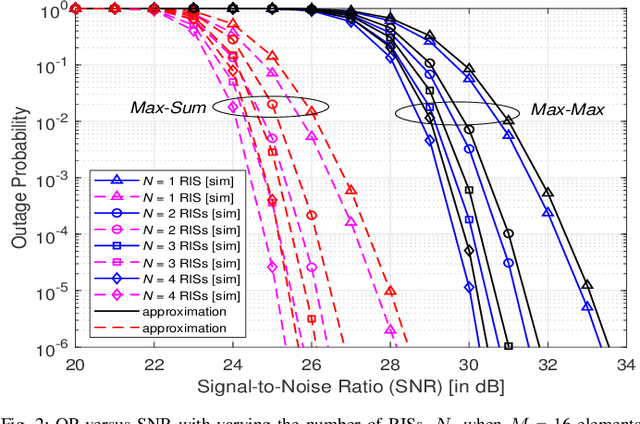
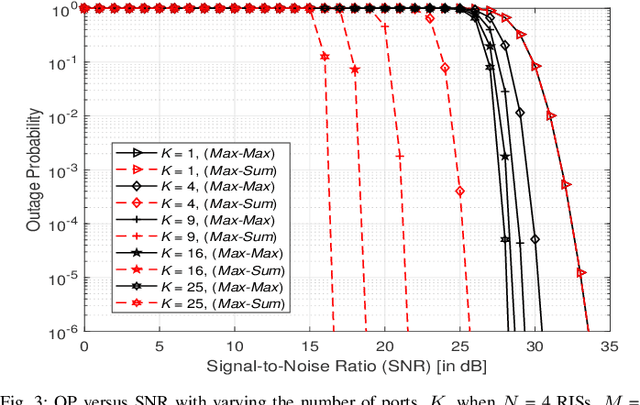
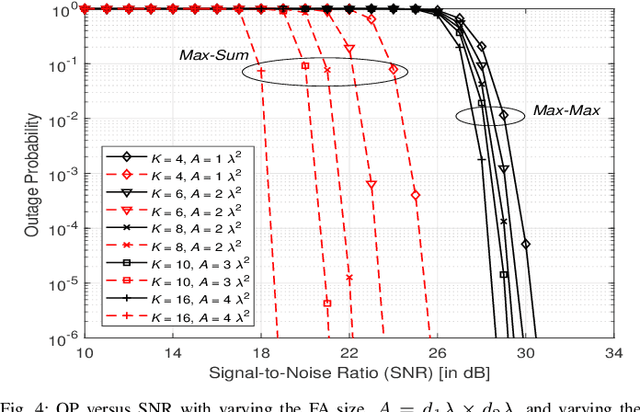
Abstract:This paper investigates the performance of a multi-reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted fluid antenna system (FAS). In this system, a single-antenna transmitter communicates with a receiver equipped with a planar FAS through multiple RISs in the absence of a direct link. To enhance the system performance, we propose two novel selection schemes: \textit{Max-Max} and \textit{Max-Sum}. In particular, the \textit{Max-Max} scheme selects the best combination of a single RIS and a single fluid antenna (FA) port that offers the maximum signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at the receiver. On the other hand, the \textit{Max-Sum} scheme selects one RIS while activating all FA ports providing the highest overall SNR. We conduct a detailed performance analysis of the proposed system under Nakagami-$m$ fading channels. First, we derive the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the SNR for both selection schemes. The derived CDF is then used to obtain approximate theoretical expressions for the outage probability (OP) and the delay outage rate (DOR). Next, a high-SNR asymptotic analysis is carried out to provide further insights into the system performance in terms of diversity and coding gains. Finally, the analytical results are validated through extensive Monte Carlo simulations, demonstrating their accuracy and providing a comprehensive understanding of the system's performance.
Error Performance Analysis of UAV-Mounted RIS for NOMA Systems with Practical Constraints
May 26, 2024Abstract:Uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs) have attracted recent attention for sixth-generation (6G) networks due to their low cost and flexible deployment. In order to maximize the ever-increasing data rates, spectral efficiency, and wider coverage, technologies such as reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) are adapted with UAVs (UAV-RIS NOMA). However, the error performance of UAV-RIS NOMA has not been considered, yet. In this letter, we investigate the error probability of UAV-RIS NOMA systems. We also consider the practical constraints of hardware impairments (HWI) at the transceivers, inter-cell interference (ICI), and imperfect successive interference cancellation (SIC). The analytical derivations are validated by Monte-Carlo simulations. Our results demonstrate that our proposed system achieves higher performance gain (more than 5 dB with increasing the number of RIS elements) with less error probability compared to UAVs without RIS. Moreover, it is found that the HWI, ICI, and imperfect SIC have shown a negative impact on the system performance.
IRS-Assisted Millimeter-wave Massive MIMO with Transmit Antenna Selection for IoT Networks
Dec 12, 2022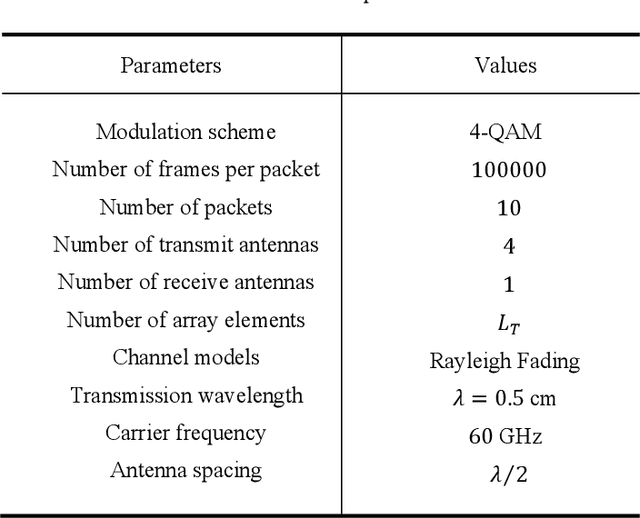
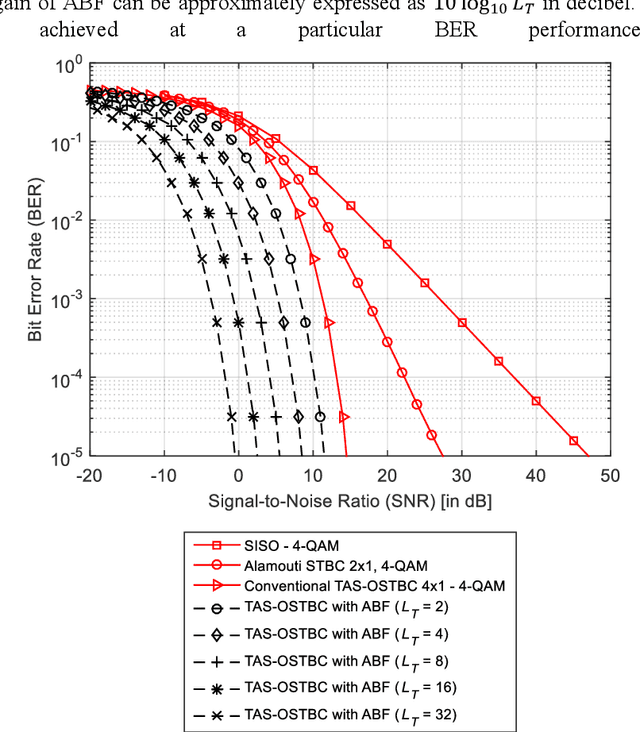
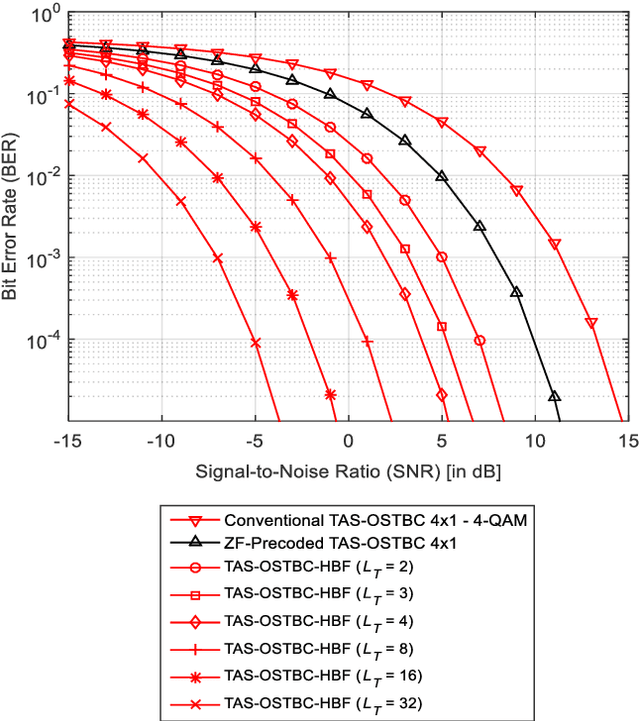
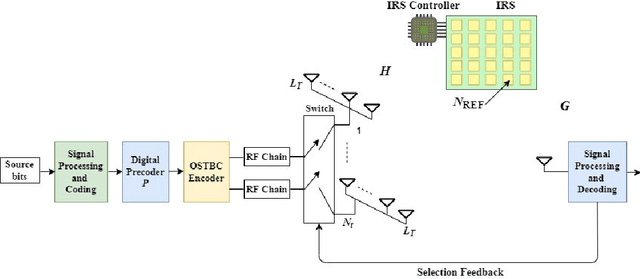
Abstract:An intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted millimeter-wave (mmWave) massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO) system with transmit antenna selection (TAS) using orthogonal space-time block codes (OSTBC) scheme is proposed in this paper. This system combines TAS and IRS with hybrid analog-digital beamforming (HBF) for 60 GHz mmWave communications in order to exploit the benefits of TAS, OSTBC, analog beamforming (ABF), and transmit digital precoding techniques. The proposed system, however, benefits from the transmit diversity gain of OSTBC scheme as well as from the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) gains of both the beamformer and the IRS technology. The simulation results demonstrate that TAS-OSTBC system with zero-forcing precoding technique outperforms the conventional TAS system with OSTBC scheme. Furthermore, the bit error rate (BER) performance significantly im-proves as the number of antenna array elements increases due to providing a beamforming gain. In addition, increasing the number of reflecting elements further enhances the error performance. It is also found from the simulation results that the TAS-OSTBC system with hybrid precoding has better BER performance than that of TAS-OSTBC with ABF, and IRS-assisted systems significantly outperform the conventional systems without the IRS technology. This makes the proposed IRS-assisted system an appealing solution for internet-of-things (IoT) networks.
Channel Estimation Based on Machine Learning Paradigm for Spatial Modulation OFDM
Sep 15, 2021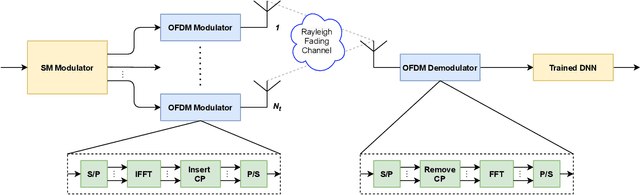
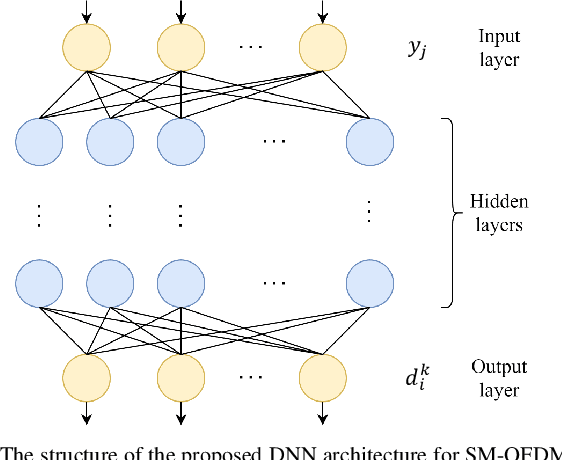
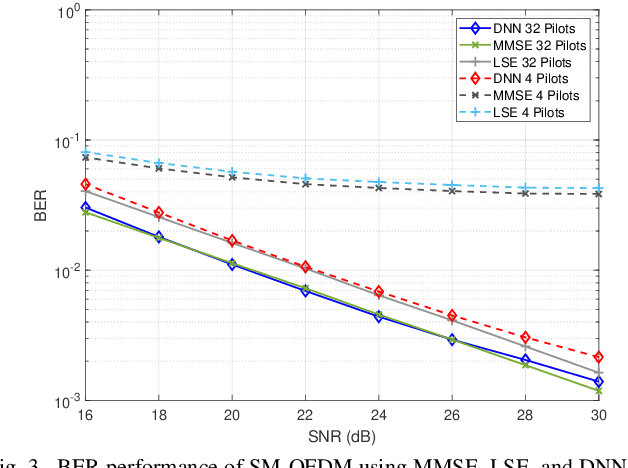
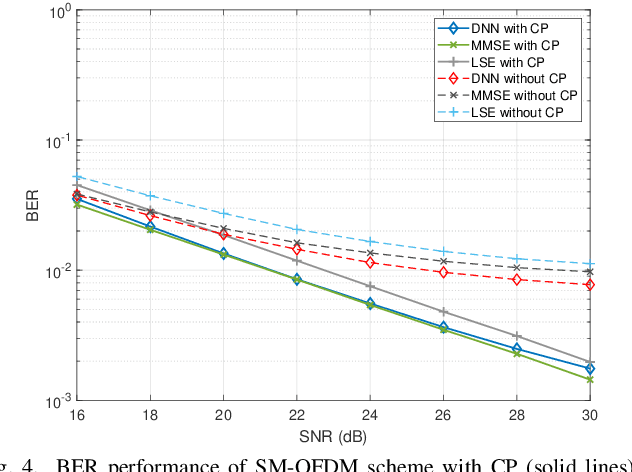
Abstract:In this paper, deep neural network (DNN) is integrated with spatial modulation-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (SM-OFDM) technique for end-to-end data detection over Rayleigh fading channel. This proposed system directly demodulates the received symbols, leaving the channel estimation done only implicitly. Furthermore, an ensemble network is also proposed for this system. Simulation results show that the proposed DNN detection scheme has a significant advantage over classical methods when the pilot overhead and cyclic prefix (CP) are reduced, owing to its ability to learn and adjust to complicated channel conditions. Finally, the ensemble network is shown to improve the generalization of the proposed scheme, while also showing a slight improvement in its performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge