Mohammad Rahmati
Amirkabir University of Technology
LiDAR-Camera Fusion for Video Panoptic Segmentation without Video Training
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:Panoptic segmentation, which combines instance and semantic segmentation, has gained a lot of attention in autonomous vehicles, due to its comprehensive representation of the scene. This task can be applied for cameras and LiDAR sensors, but there has been a limited focus on combining both sensors to enhance image panoptic segmentation (PS). Although previous research has acknowledged the benefit of 3D data on camera-based scene perception, no specific study has explored the influence of 3D data on image and video panoptic segmentation (VPS).This work seeks to introduce a feature fusion module that enhances PS and VPS by fusing LiDAR and image data for autonomous vehicles. We also illustrate that, in addition to this fusion, our proposed model, which utilizes two simple modifications, can further deliver even more high-quality VPS without being trained on video data. The results demonstrate a substantial improvement in both the image and video panoptic segmentation evaluation metrics by up to 5 points.
SegLoc: Visual Self-supervised Learning Scheme for Dense Prediction Tasks of Security Inspection X-ray Images
Oct 21, 2023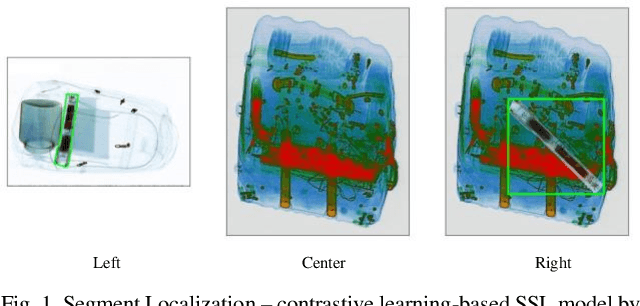

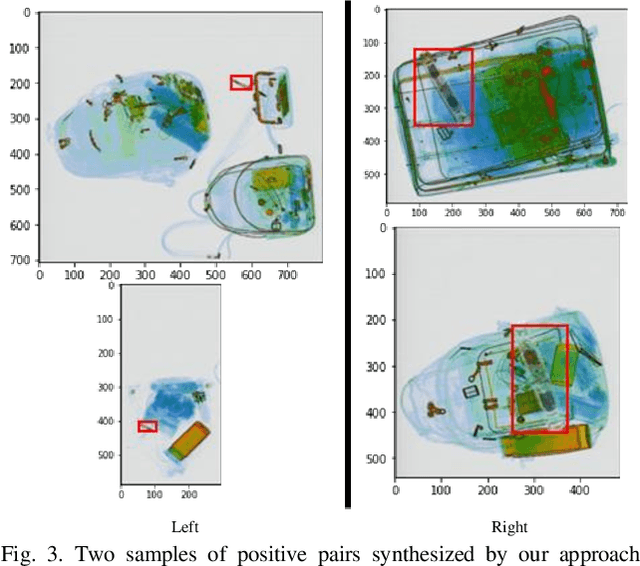
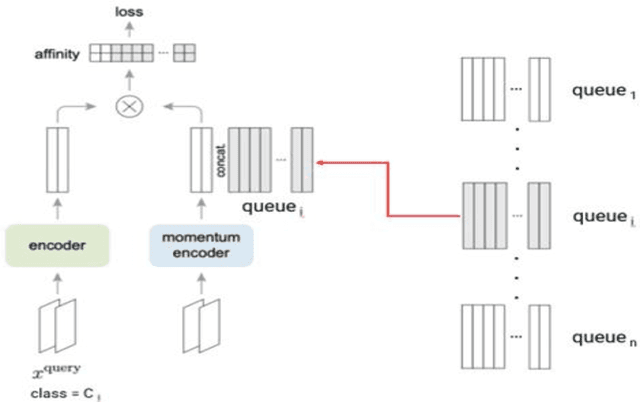
Abstract:Lately, remarkable advancements of artificial intelligence have been attributed to the integration of self-supervised learning (SSL) scheme. Despite impressive achievements within natural language processing (NLP), SSL in computer vision has not been able to stay on track comparatively. Recently, integration of contrastive learning on top of existing visual SSL models has established considerable progress, thereby being able to outperform supervised counterparts. Nevertheless, the improvements were mostly limited to classification tasks; moreover, few studies have evaluated visual SSL models in real-world scenarios, while the majority considered datasets containing class-wise portrait images, notably ImageNet. Thus, here, we have considered dense prediction tasks on security inspection x-ray images to evaluate our proposed model Segmentation Localization (SegLoc). Based upon the model Instance Localization (InsLoc), our model has managed to address one of the most challenging downsides of contrastive learning, i.e., false negative pairs of query embeddings. To do so, our pre-training dataset is synthesized by cutting, transforming, then pasting labeled segments, as foregrounds, from an already existing labeled dataset (PIDray) onto instances, as backgrounds, of an unlabeled dataset (SIXray;) further, we fully harness the labels through integration of the notion, one queue per class, into MoCo-v2 memory bank, avoiding false negative pairs. Regarding the task in question, our approach has outperformed random initialization method by 3% to 6%, while having underperformed supervised initialization, in AR and AP metrics at different IoU values for 20 to 30 pre-training epochs.
On Continuity of Robust and Accurate Classifiers
Sep 29, 2023



Abstract:The reliability of a learning model is key to the successful deployment of machine learning in various applications. Creating a robust model, particularly one unaffected by adversarial attacks, requires a comprehensive understanding of the adversarial examples phenomenon. However, it is difficult to describe the phenomenon due to the complicated nature of the problems in machine learning. It has been shown that adversarial training can improve the robustness of the hypothesis. However, this improvement comes at the cost of decreased performance on natural samples. Hence, it has been suggested that robustness and accuracy of a hypothesis are at odds with each other. In this paper, we put forth the alternative proposal that it is the continuity of a hypothesis that is incompatible with its robustness and accuracy. In other words, a continuous function cannot effectively learn the optimal robust hypothesis. To this end, we will introduce a framework for a rigorous study of harmonic and holomorphic hypothesis in learning theory terms and provide empirical evidence that continuous hypotheses does not perform as well as discontinuous hypotheses in some common machine learning tasks. From a practical point of view, our results suggests that a robust and accurate learning rule would train different continuous hypotheses for different regions of the domain. From a theoretical perspective, our analysis explains the adversarial examples phenomenon as a conflict between the continuity of a sequence of functions and its uniform convergence to a discontinuous function.
Regularized Complete Cycle Consistent GAN for Anomaly Detection
Apr 16, 2023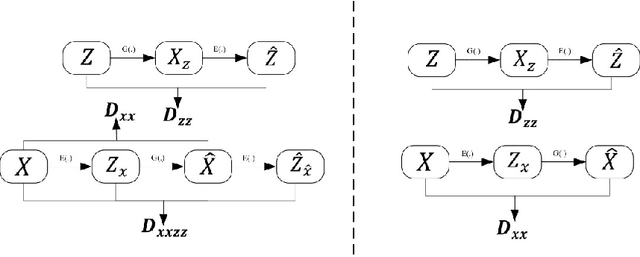
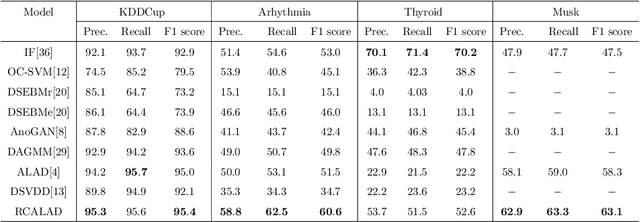
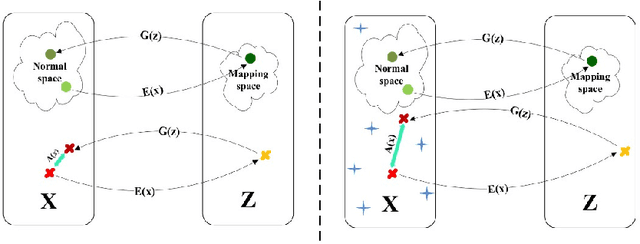

Abstract:This study presents an adversarial method for anomaly detection in real-world applications, leveraging the power of generative adversarial neural networks (GANs) through cycle consistency in reconstruction error. Previous methods suffer from the high variance between class-wise accuracy which leads to not being applicable for all types of anomalies. The proposed method named RCALAD tries to solve this problem by introducing a novel discriminator to the structure, which results in a more efficient training process. Additionally, RCALAD employs a supplementary distribution in the input space to steer reconstructions toward the normal data distribution, effectively separating anomalous samples from their reconstructions and facilitating more accurate anomaly detection. To further enhance the performance of the model, two novel anomaly scores are introduced. The proposed model has been thoroughly evaluated through extensive experiments on six various datasets, yielding results that demonstrate its superiority over existing state-of-the-art models. The code is readily available to the research community at https://github.com/zahraDehghanian97/RCALAD.
An Analytic Framework for Robust Training of Artificial Neural Networks
May 26, 2022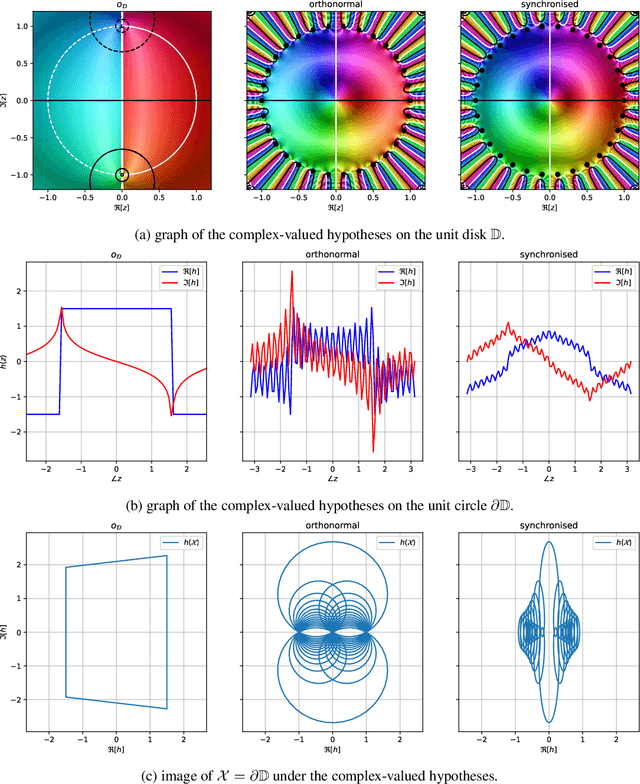
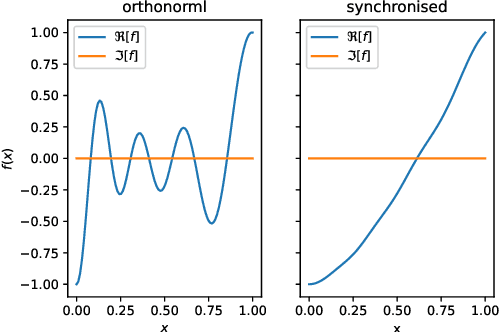
Abstract:The reliability of a learning model is key to the successful deployment of machine learning in various industries. Creating a robust model, particularly one unaffected by adversarial attacks, requires a comprehensive understanding of the adversarial examples phenomenon. However, it is difficult to describe the phenomenon due to the complicated nature of the problems in machine learning. Consequently, many studies investigate the phenomenon by proposing a simplified model of how adversarial examples occur and validate it by predicting some aspect of the phenomenon. While these studies cover many different characteristics of the adversarial examples, they have not reached a holistic approach to the geometric and analytic modeling of the phenomenon. This paper propose a formal framework to study the phenomenon in learning theory and make use of complex analysis and holomorphicity to offer a robust learning rule for artificial neural networks. With the help of complex analysis, we can effortlessly move between geometric and analytic perspectives of the phenomenon and offer further insights on the phenomenon by revealing its connection with harmonic functions. Using our model, we can explain some of the most intriguing characteristics of adversarial examples, including transferability of adversarial examples, and pave the way for novel approaches to mitigate the effects of the phenomenon.
Triple Motion Estimation and Frame Interpolation based on Adaptive Threshold for Frame Rate Up-Conversion
Mar 05, 2022
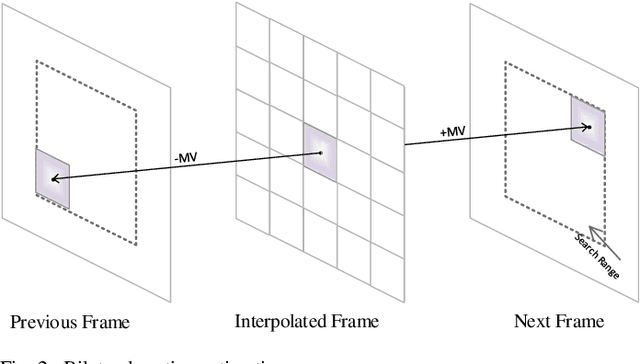

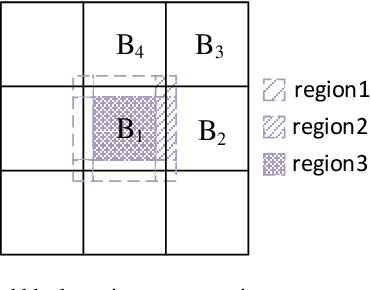
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel motion-compensated frame rate up-conversion (MC-FRUC) algorithm. The proposed algorithm creates interpolated frames by first estimating motion vectors using unilateral (jointing forward and backward) and bilateral motion estimation. Then motion vectors are combined based on adaptive threshold, in order to creates high-quality interpolated frames and reduce block artifacts. Since motion-compensated frame interpolation along unilateral motion trajectories yields holes, a new algorithm is introduced to resolve this problem. The experimental results show that the quality of the interpolated frames using the proposed algorithm is much higher than the existing algorithms.
Identity-Preserving Pose-Robust Face Hallucination Through Face Subspace Prior
Nov 20, 2021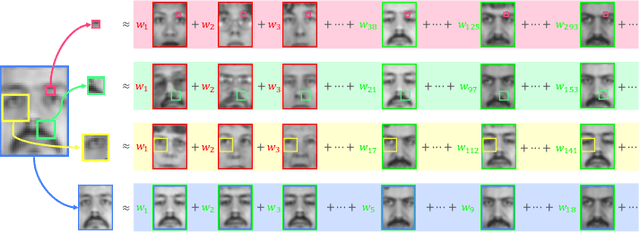


Abstract:Over the past few decades, numerous attempts have been made to address the problem of recovering a high-resolution (HR) facial image from its corresponding low-resolution (LR) counterpart, a task commonly referred to as face hallucination. Despite the impressive performance achieved by position-patch and deep learning-based methods, most of these techniques are still unable to recover identity-specific features of faces. The former group of algorithms often produces blurry and oversmoothed outputs particularly in the presence of higher levels of degradation, whereas the latter generates faces which sometimes by no means resemble the individuals in the input images. In this paper, a novel face super-resolution approach will be introduced, in which the hallucinated face is forced to lie in a subspace spanned by the available training faces. Therefore, in contrast to the majority of existing face hallucination techniques and thanks to this face subspace prior, the reconstruction is performed in favor of recovering person-specific facial features, rather than merely increasing image quantitative scores. Furthermore, inspired by recent advances in the area of 3D face reconstruction, an efficient 3D dictionary alignment scheme is also presented, through which the algorithm becomes capable of dealing with low-resolution faces taken in uncontrolled conditions. In extensive experiments carried out on several well-known face datasets, the proposed algorithm shows remarkable performance by generating detailed and close to ground truth results which outperform the state-of-the-art face hallucination algorithms by significant margins both in quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
Xp-GAN: Unsupervised Multi-object Controllable Video Generation
Nov 19, 2021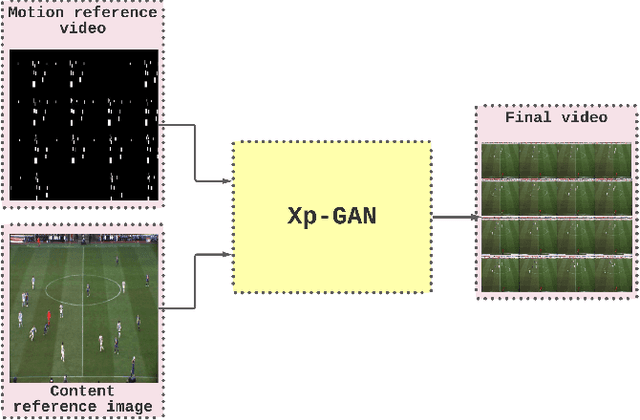

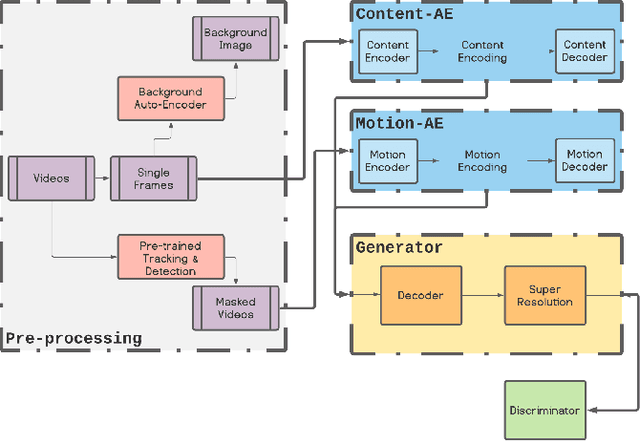
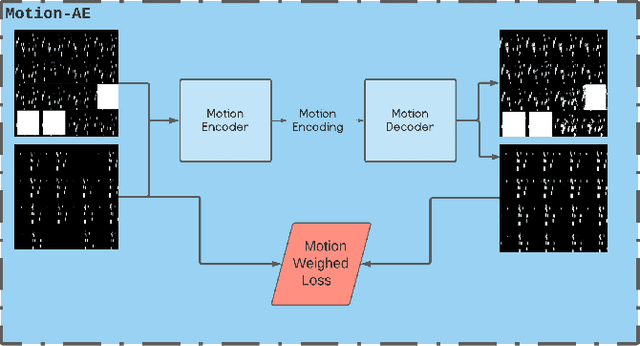
Abstract:Video Generation is a relatively new and yet popular subject in machine learning due to its vast variety of potential applications and its numerous challenges. Current methods in Video Generation provide the user with little or no control over the exact specification of how the objects in the generate video are to be moved and located at each frame, that is, the user can't explicitly control how each object in the video should move. In this paper we propose a novel method that allows the user to move any number of objects of a single initial frame just by drawing bounding boxes over those objects and then moving those boxes in the desired path. Our model utilizes two Autoencoders to fully decompose the motion and content information in a video and achieves results comparable to well-known baseline and state of the art methods.
Towards Explaining Adversarial Examples Phenomenon in Artificial Neural Networks
Jul 22, 2021
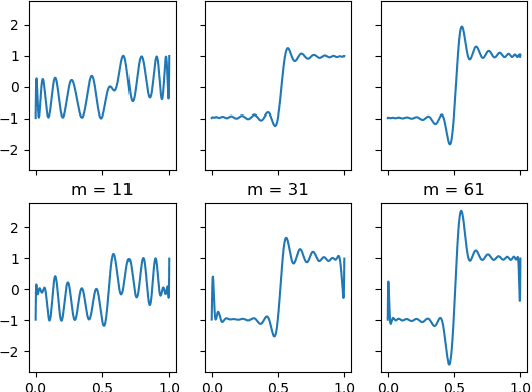
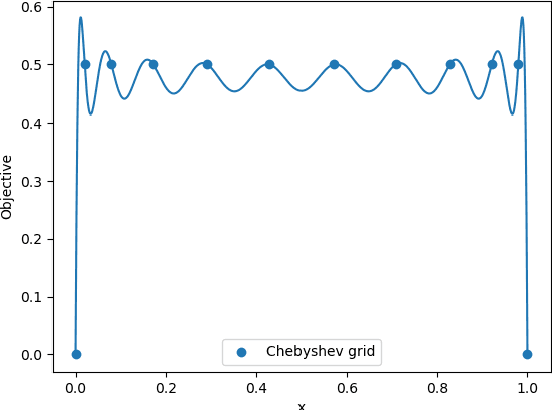
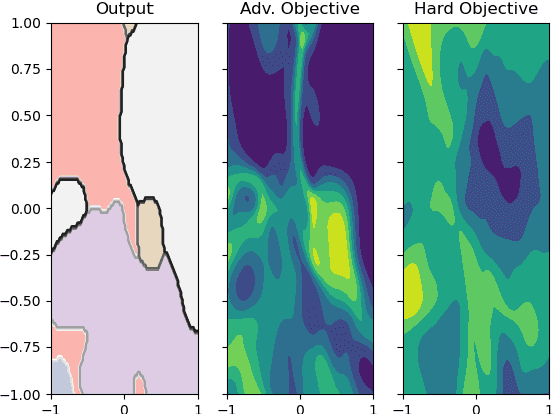
Abstract:In this paper, we study the adversarial examples existence and adversarial training from the standpoint of convergence and provide evidence that pointwise convergence in ANNs can explain these observations. The main contribution of our proposal is that it relates the objective of the evasion attacks and adversarial training with concepts already defined in learning theory. Also, we extend and unify some of the other proposals in the literature and provide alternative explanations on the observations made in those proposals. Through different experiments, we demonstrate that the framework is valuable in the study of the phenomenon and is applicable to real-world problems.
Maximum Entropy Weighted Independent Set Pooling for Graph Neural Networks
Jul 03, 2021
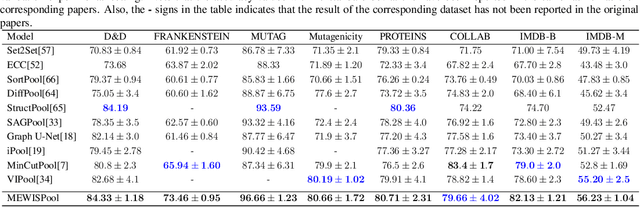
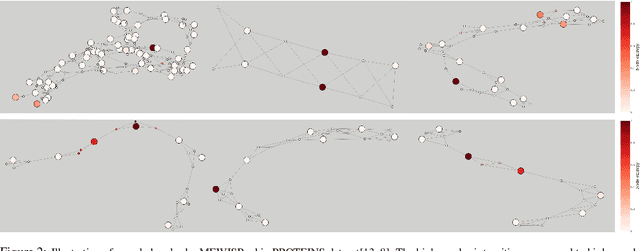
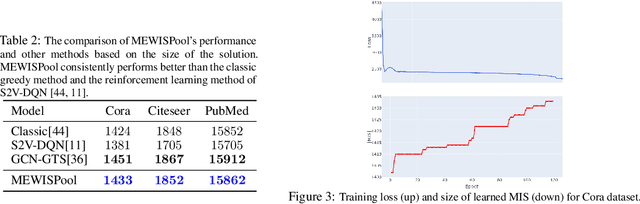
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel pooling layer for graph neural networks based on maximizing the mutual information between the pooled graph and the input graph. Since the maximum mutual information is difficult to compute, we employ the Shannon capacity of a graph as an inductive bias to our pooling method. More precisely, we show that the input graph to the pooling layer can be viewed as a representation of a noisy communication channel. For such a channel, sending the symbols belonging to an independent set of the graph yields a reliable and error-free transmission of information. We show that reaching the maximum mutual information is equivalent to finding a maximum weight independent set of the graph where the weights convey entropy contents. Through this communication theoretic standpoint, we provide a distinct perspective for posing the problem of graph pooling as maximizing the information transmission rate across a noisy communication channel, implemented by a graph neural network. We evaluate our method, referred to as Maximum Entropy Weighted Independent Set Pooling (MEWISPool), on graph classification tasks and the combinatorial optimization problem of the maximum independent set. Empirical results demonstrate that our method achieves the state-of-the-art and competitive results on graph classification tasks and the maximum independent set problem in several benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge