Maryam Amirmazlaghani
Beyond Imperfections: A Conditional Inpainting Approach for End-to-End Artifact Removal in VTON and Pose Transfer
Oct 05, 2024



Abstract:Artifacts often degrade the visual quality of virtual try-on (VTON) and pose transfer applications, impacting user experience. This study introduces a novel conditional inpainting technique designed to detect and remove such distortions, improving image aesthetics. Our work is the first to present an end-to-end framework addressing this specific issue, and we developed a specialized dataset of artifacts in VTON and pose transfer tasks, complete with masks highlighting the affected areas. Experimental results show that our method not only effectively removes artifacts but also significantly enhances the visual quality of the final images, setting a new benchmark in computer vision and image processing.
Regularized Complete Cycle Consistent GAN for Anomaly Detection
Apr 16, 2023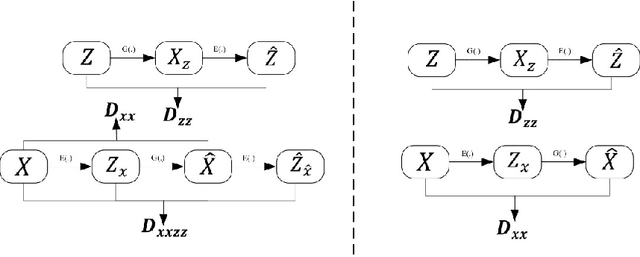
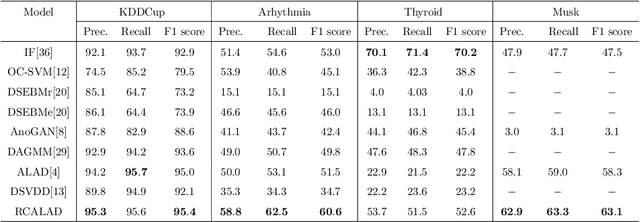
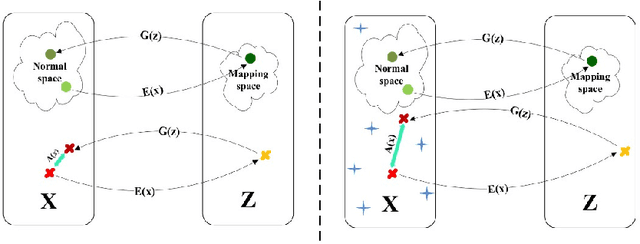

Abstract:This study presents an adversarial method for anomaly detection in real-world applications, leveraging the power of generative adversarial neural networks (GANs) through cycle consistency in reconstruction error. Previous methods suffer from the high variance between class-wise accuracy which leads to not being applicable for all types of anomalies. The proposed method named RCALAD tries to solve this problem by introducing a novel discriminator to the structure, which results in a more efficient training process. Additionally, RCALAD employs a supplementary distribution in the input space to steer reconstructions toward the normal data distribution, effectively separating anomalous samples from their reconstructions and facilitating more accurate anomaly detection. To further enhance the performance of the model, two novel anomaly scores are introduced. The proposed model has been thoroughly evaluated through extensive experiments on six various datasets, yielding results that demonstrate its superiority over existing state-of-the-art models. The code is readily available to the research community at https://github.com/zahraDehghanian97/RCALAD.
Layer-wise Regularized Adversarial Training using Layers Sustainability Analysis (LSA) framework
Feb 15, 2022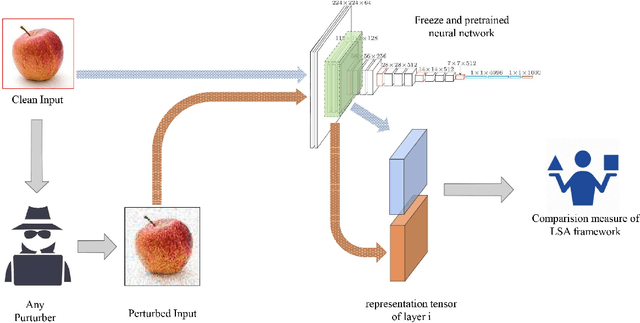
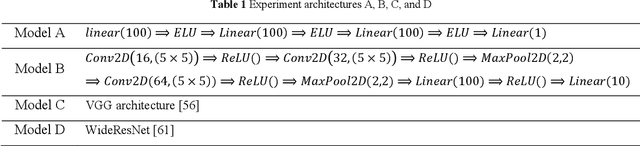
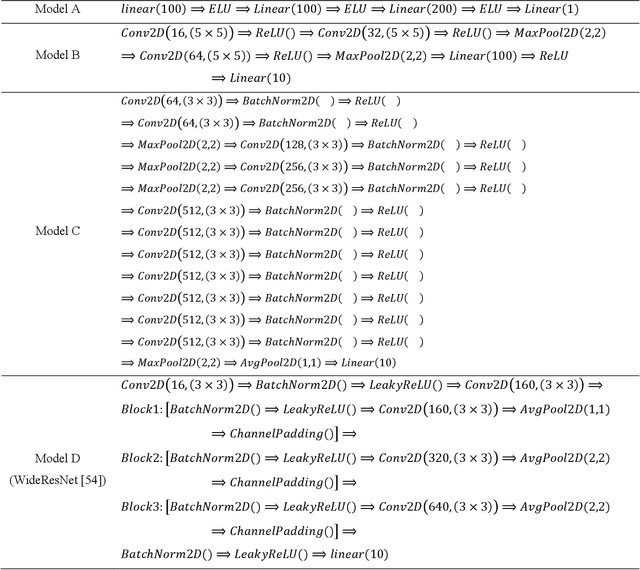
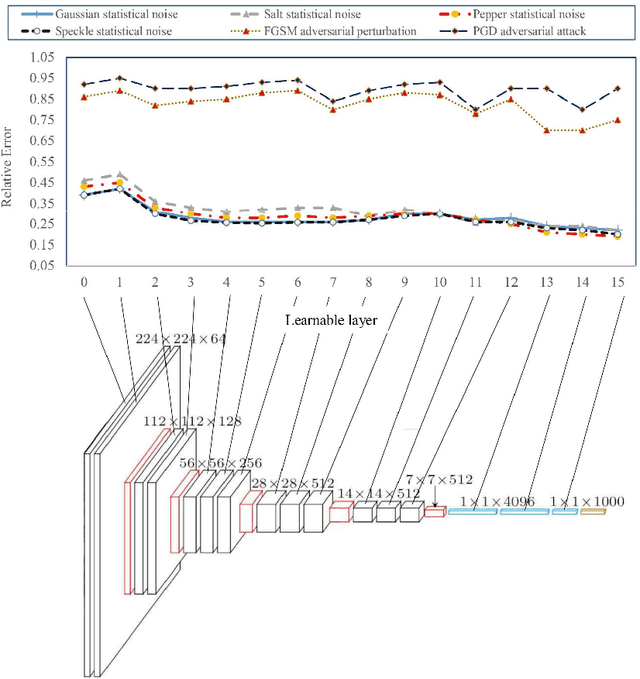
Abstract:Deep neural network models are used today in various applications of artificial intelligence, the strengthening of which, in the face of adversarial attacks is of particular importance. An appropriate solution to adversarial attacks is adversarial training, which reaches a trade-off between robustness and generalization. This paper introduces a novel framework (Layer Sustainability Analysis (LSA)) for the analysis of layer vulnerability in an arbitrary neural network in the scenario of adversarial attacks. LSA can be a helpful toolkit to assess deep neural networks and to extend the adversarial training approaches towards improving the sustainability of model layers via layer monitoring and analysis. The LSA framework identifies a list of Most Vulnerable Layers (MVL list) of the given network. The relative error, as a comparison measure, is used to evaluate representation sustainability of each layer against adversarial inputs. The proposed approach for obtaining robust neural networks to fend off adversarial attacks is based on a layer-wise regularization (LR) over LSA proposal(s) for adversarial training (AT); i.e. the AT-LR procedure. AT-LR could be used with any benchmark adversarial attack to reduce the vulnerability of network layers and to improve conventional adversarial training approaches. The proposed idea performs well theoretically and experimentally for state-of-the-art multilayer perceptron and convolutional neural network architectures. Compared with the AT-LR and its corresponding base adversarial training, the classification accuracy of more significant perturbations increased by 16.35%, 21.79%, and 10.730% on Moon, MNIST, and CIFAR-10 benchmark datasets, respectively. The LSA framework is available and published at https://github.com/khalooei/LSA.
Color Texture Image Retrieval Based on Copula Multivariate Modeling in the Shearlet Domain
Aug 03, 2020
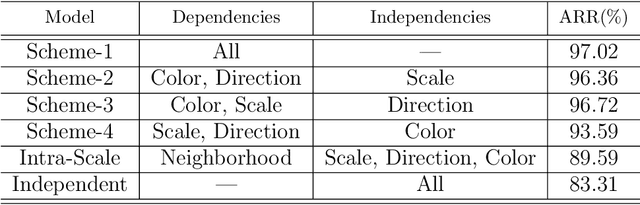
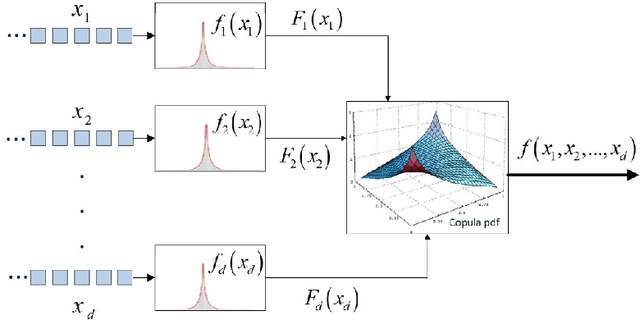
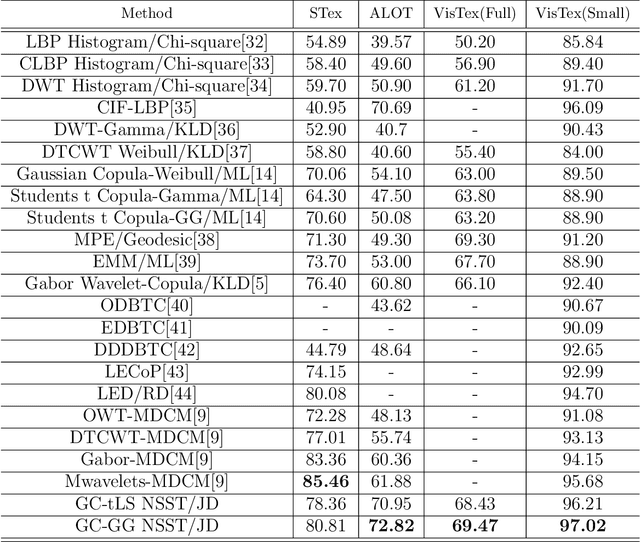
Abstract:In this paper, a color texture image retrieval framework is proposed based on Shearlet domain modeling using Copula multivariate model. In the proposed framework, Gaussian Copula is used to model the dependencies between different sub-bands of the Non Subsample Shearlet Transform (NSST) and non-Gaussian models are used for marginal modeling of the coefficients. Six different schemes are proposed for modeling NSST coefficients based on the four types of neighboring defined; moreover, Kullback Leibler Divergence(KLD) close form is calculated in different situations for the two Gaussian Copula and non Gaussian functions in order to investigate the similarities in the proposed retrieval framework. The Jeffery divergence (JD) criterion, which is a symmetrical version of KLD, is used for investigating similarities in the proposed framework. We have implemented our experiments on four texture image retrieval benchmark datasets, the results of which show the superiority of the proposed framework over the existing state-of-the-art methods. In addition, the retrieval time of the proposed framework is also analyzed in the two steps of feature extraction and similarity matching, which also shows that the proposed framework enjoys an appropriate retrieval time.
A Novel Distributed Approximate Nearest Neighbor Method for Real-time Face Recognition
May 12, 2020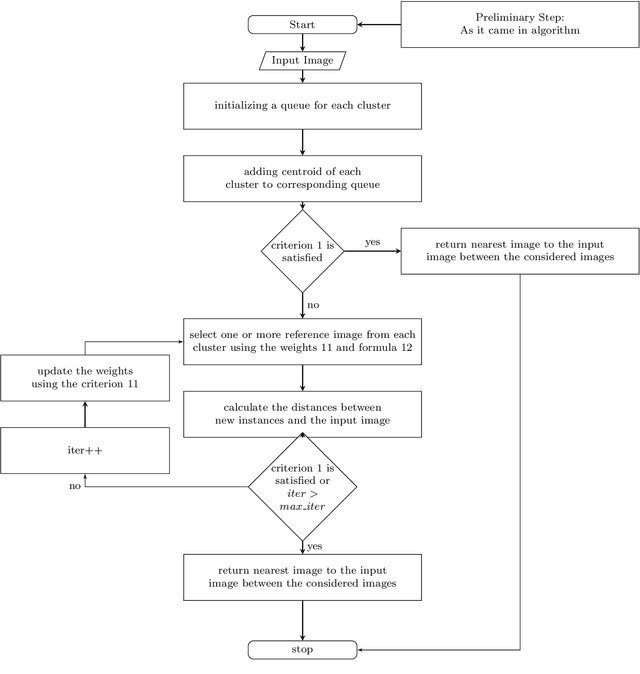

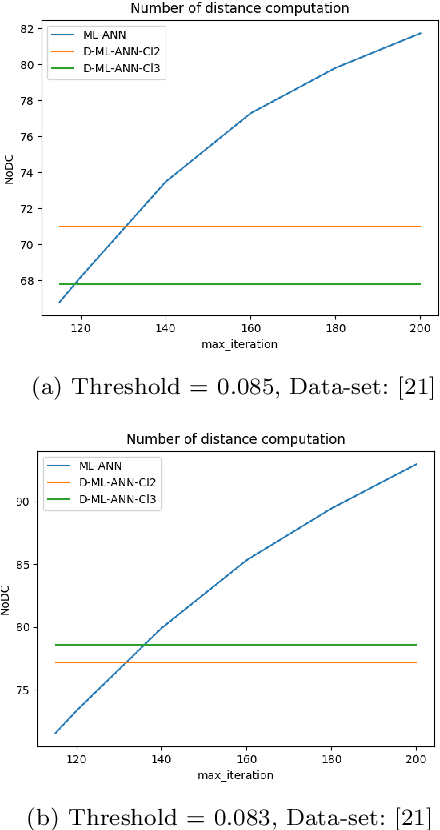
Abstract:Nowadays face recognition and more generally, image recognition have many applications in the modern world and are widely used in our daily tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel distributed approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) method for real-time face recognition with a big data-set that involves a lot of classes. The proposed approach is based on using a clustering method to separate the data-set into different clusters, and specifying the importance of each cluster by defining cluster weights. Reference instances are selected from each cluster based on the cluster weights and by using a maximum likelihood approach. This process leads to a more informed selection of instances, and so enhances the performance of the algorithm. Experimental results confirm the efficiency of the proposed method and its out-performance in terms of accuracy and processing time.
Reconstruction of Gene Regulatory Networks usingMultiple Datasets
Dec 19, 2019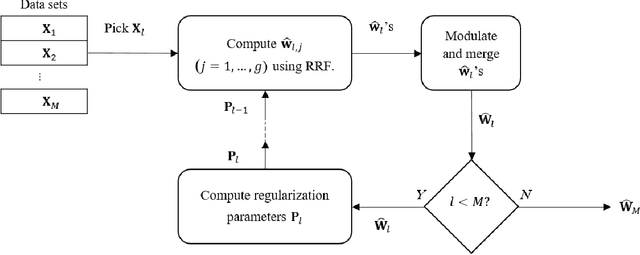

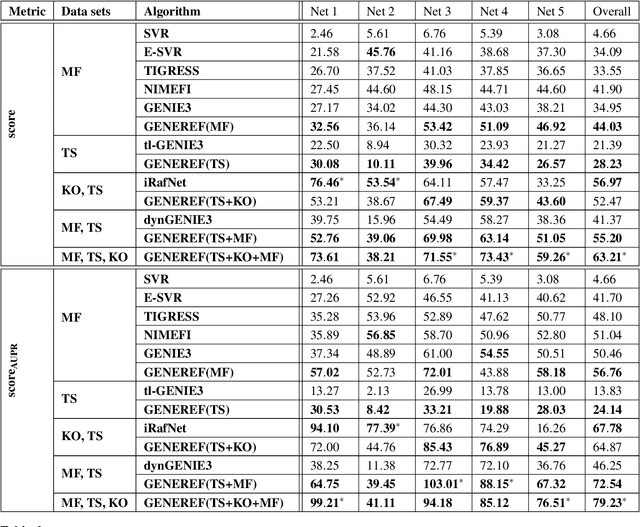
Abstract:Motivation: Laboratory gene regulatory data for a species are sporadic. Despite the abundance of gene regulatory network algorithms that employ single data sets, few algorithms can combine the vast but disperse sources of data and extract the potential information. With a motivation to compensate for this shortage, we developed an algorithm called GENEREF that can accumulate information from multiple types of data sets in an iterative manner, with each iteration boosting the performance of the prediction results. Results: The algorithm is examined extensively on data extracted from the quintuple DREAM4 networks. Many single-dataset algorithms and one multi-dataset algorithm were compared to test the performance of the algorithm. Results show that GENEREF surpasses non-ensemble state-of-the-art multi-perturbation algorithms on the selected networks and is competitive to present multiple-dataset algorithms. Specifically, it outperforms dynGENIE3 and is on par with iRafNet. Also, we argued that a scoring method solely based on the AUPR criterion would be more trustworthy than the traditional score. Availability: The Python implementation along with the data sets and results can be downloaded from \url{github.com/msaremi/GENEREF}
Unsupervised Hypergraph Feature Selection via a Novel Point-Weighting Framework and Low-Rank Representation
Oct 03, 2018
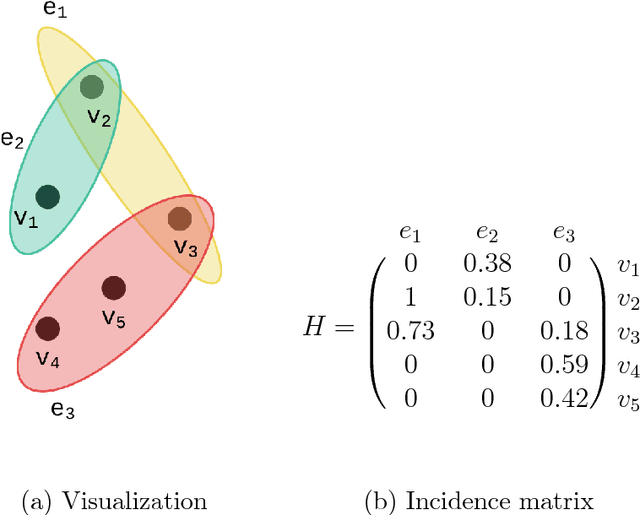
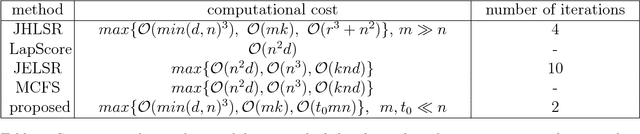
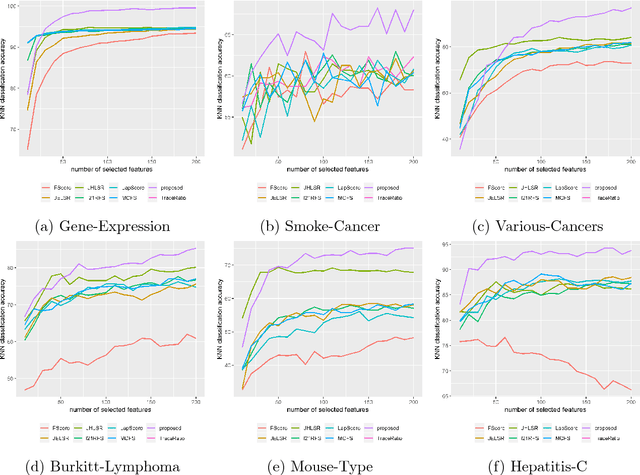
Abstract:Feature selection methods are widely used in order to solve the 'curse of dimensionality' problem. Many proposed feature selection frameworks, treat all data points equally; neglecting their different representation power and importance. In this paper, we propose an unsupervised hypergraph feature selection method via a novel point-weighting framework and low-rank representation that captures the importance of different data points. We introduce a novel soft hypergraph with low complexity to model data. Then, we formulate the feature selection as an optimization problem to preserve local relationships and also global structure of data. Our approach for global structure preservation helps the framework overcome the problem of unavailability of data labels in unsupervised learning. The proposed feature selection method treats with different data points based on their importance in defining data structure and representation power. Moreover, since the robustness of feature selection methods against noise and outlier is of great importance, we adopt low-rank representation in our model. Also, we provide an efficient algorithm to solve the proposed optimization problem. The computational cost of the proposed algorithm is lower than many state-of-the-art methods which is of high importance in feature selection tasks. We conducted comprehensive experiments with various evaluation methods on different benchmark data sets. These experiments indicate significant improvement, compared with state-of-the-art feature selection methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge