Mingyan Zhou
Developing Trajectory Planning with Behavioral Cloning and Proximal Policy Optimization for Path-Tracking and Static Obstacle Nudging
Sep 09, 2024



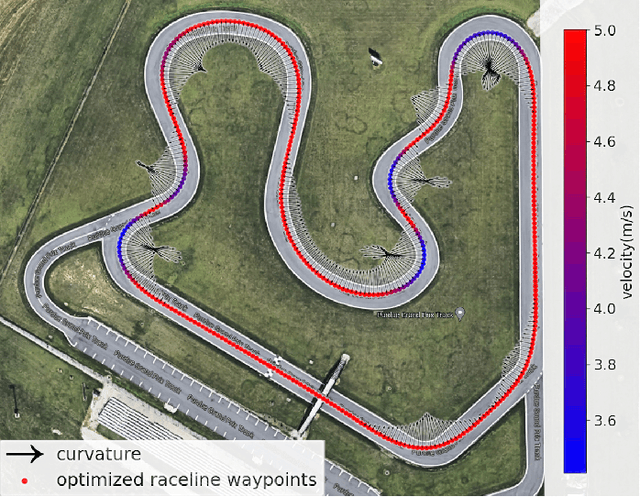
Abstract:End-to-end approaches with Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Imitation Learning (IL) have gained increasing popularity in autonomous driving. However, they do not involve explicit reasoning like classic robotics workflow, nor planning with horizons, leading strategies implicit and myopic. In this paper, we introduce our trajectory planning method that uses Behavioral Cloning (BC) for path-tracking and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) bootstrapped by BC for static obstacle nudging. It outputs lateral offset values to adjust the given reference trajectory, and performs modified path for different controllers. Our experimental results show that the algorithm can do path-tracking that mimics the expert performance, and avoiding collision to fixed obstacles by trial and errors. This method makes a good attempt at planning with learning-based methods in trajectory planning problems of autonomous driving.
AV4EV: Open-Source Modular Autonomous Electric Vehicle Platform to Make Mobility Research Accessible
Dec 01, 2023


Abstract:When academic researchers develop and validate autonomous driving algorithms, there is a challenge in balancing high-performance capabilities with the cost and complexity of the vehicle platform. Much of today's research on autonomous vehicles (AV) is limited to experimentation on expensive commercial vehicles that require large teams with diverse skills to retrofit the vehicles and test them in dedicated testing facilities. Testing the limits of safety and performance on such vehicles is costly and hazardous. It is also outside the reach of most academic departments and research groups. On the other hand, scaled-down 1/10th-1/16th scale vehicle platforms are more affordable but have limited similitude in dynamics, control, and drivability. To address this issue, we present the design of a one-third-scale autonomous electric go-kart platform with open-source mechatronics design along with fully-functional autonomous driving software. The platform's multi-modal driving system is capable of manual, autonomous, and teleoperation driving modes. It also features a flexible sensing suite for development and deployment of algorithms across perception, localization, planning, and control. This development serves as a bridge between full-scale vehicles and reduced-scale cars while accelerating cost-effective algorithmic advancements in autonomous systems research. Our experimental results demonstrate the AV4EV platform's capabilities and ease-of-use for developing new AV algorithms. All materials are available at AV4EV.org to stimulate collaborative efforts within the AV and electric vehicle (EV) communities.
A Benchmark Comparison of Imitation Learning-based Control Policies for Autonomous Racing
Sep 29, 2022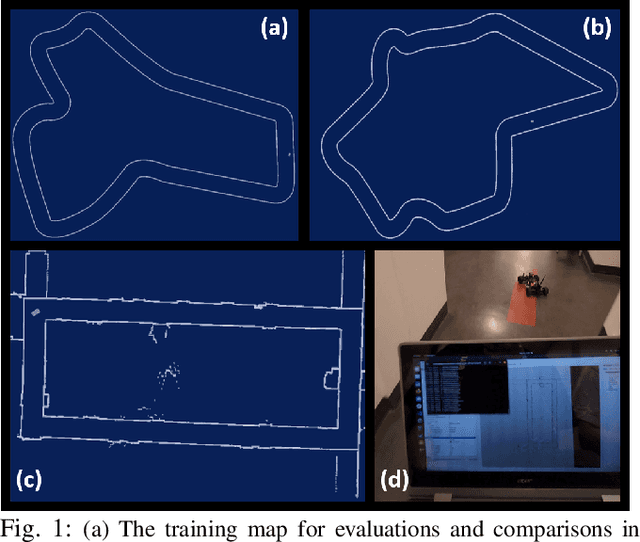
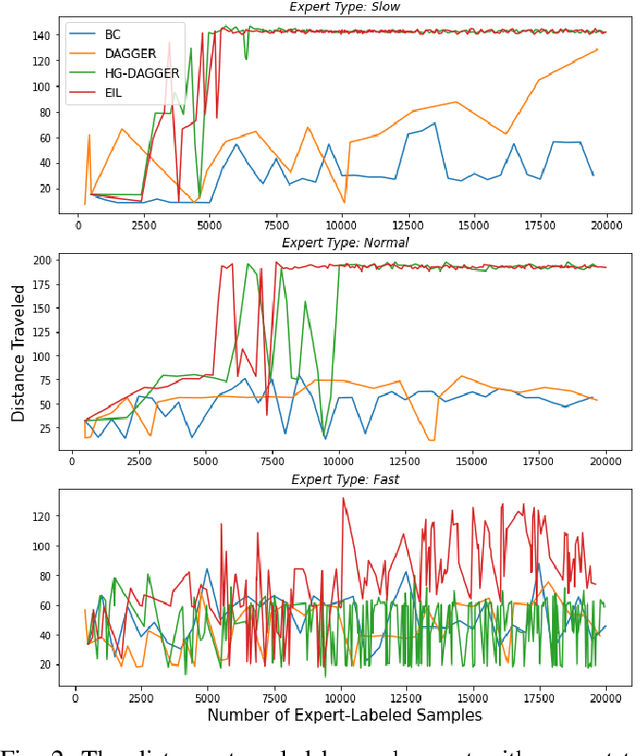
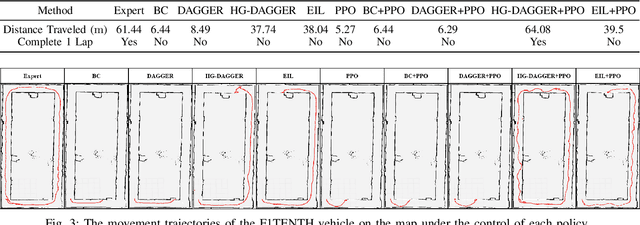
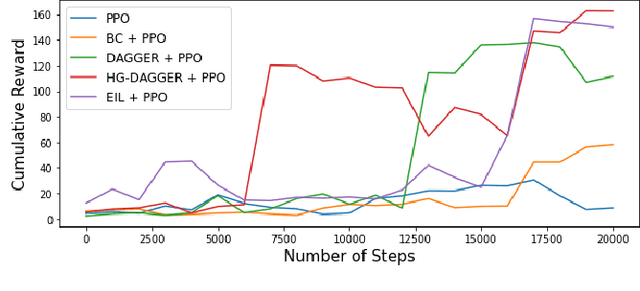
Abstract:Autonomous racing with scaled race cars has gained increasing attention as an effective approach for developing perception, planning and control algorithms for safe autonomous driving at the limits of the vehicle's handling. To train agile control policies for autonomous racing, learning-based approaches largely utilize reinforcement learning, albeit with mixed results. In this study, we benchmark a variety of imitation learning policies for racing vehicles that are applied directly or for bootstrapping reinforcement learning both in simulation and on scaled real-world environments. We show that interactive imitation learning techniques outperform traditional imitation learning methods and can greatly improve the performance of reinforcement learning policies by bootstrapping thanks to its better sample efficiency. Our benchmarks provide a foundation for future research on autonomous racing using Imitation Learning and Reinforcement Learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge