Milind Naphade
T1: A Tool-Oriented Conversational Dataset for Multi-Turn Agentic Planning
May 22, 2025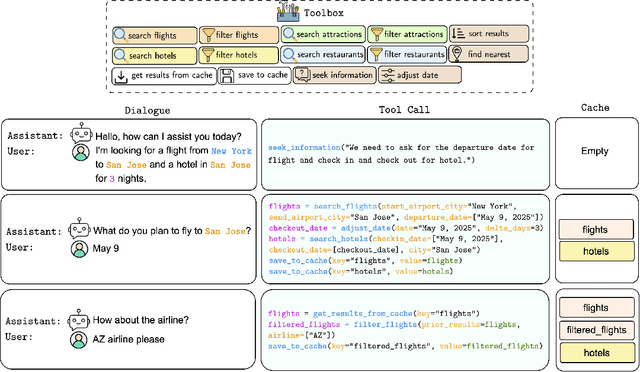
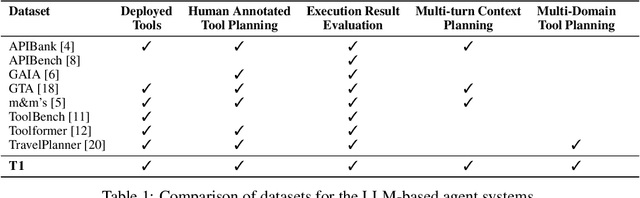

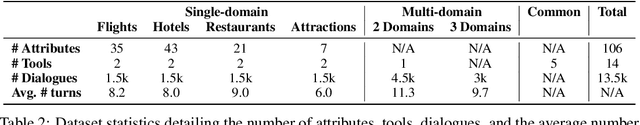
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities as intelligent agents capable of solving complex problems. However, effective planning in scenarios involving dependencies between API or tool calls-particularly in multi-turn conversations-remains a significant challenge. To address this, we introduce T1, a tool-augmented, multi-domain, multi-turn conversational dataset specifically designed to capture and manage inter-tool dependencies across diverse domains. T1 enables rigorous evaluation of agents' ability to coordinate tool use across nine distinct domains (4 single domain and 5 multi-domain) with the help of an integrated caching mechanism for both short- and long-term memory, while supporting dynamic replanning-such as deciding whether to recompute or reuse cached results. Beyond facilitating research on tool use and planning, T1 also serves as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of open-source language models. We present results powered by T1-Agent, highlighting their ability to plan and reason in complex, tool-dependent scenarios.
The 7th AI City Challenge
Apr 15, 2023
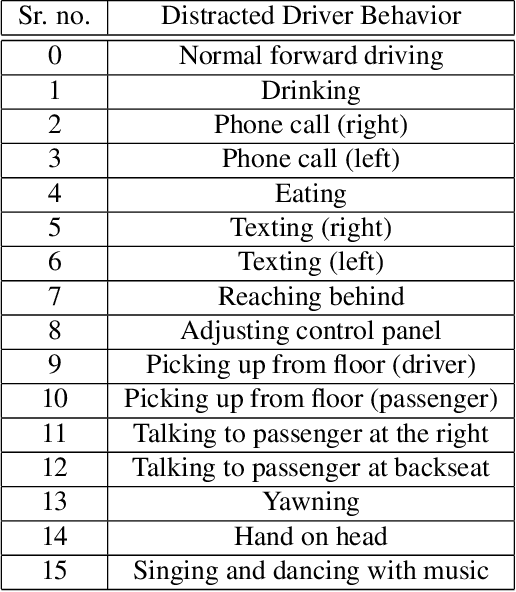

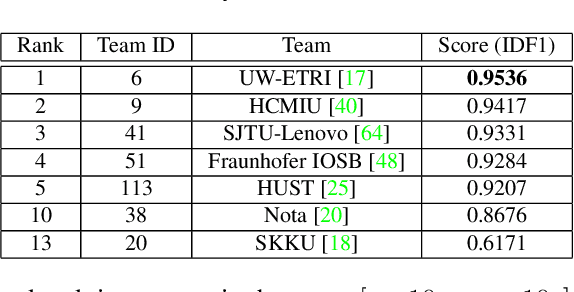
Abstract:The AI City Challenge's seventh edition emphasizes two domains at the intersection of computer vision and artificial intelligence - retail business and Intelligent Traffic Systems (ITS) - that have considerable untapped potential. The 2023 challenge had five tracks, which drew a record-breaking number of participation requests from 508 teams across 46 countries. Track 1 was a brand new track that focused on multi-target multi-camera (MTMC) people tracking, where teams trained and evaluated using both real and highly realistic synthetic data. Track 2 centered around natural-language-based vehicle track retrieval. Track 3 required teams to classify driver actions in naturalistic driving analysis. Track 4 aimed to develop an automated checkout system for retail stores using a single view camera. Track 5, another new addition, tasked teams with detecting violations of the helmet rule for motorcyclists. Two leader boards were released for submissions based on different methods: a public leader board for the contest where external private data wasn't allowed and a general leader board for all results submitted. The participating teams' top performances established strong baselines and even outperformed the state-of-the-art in the proposed challenge tracks.
The 6th AI City Challenge
Apr 21, 2022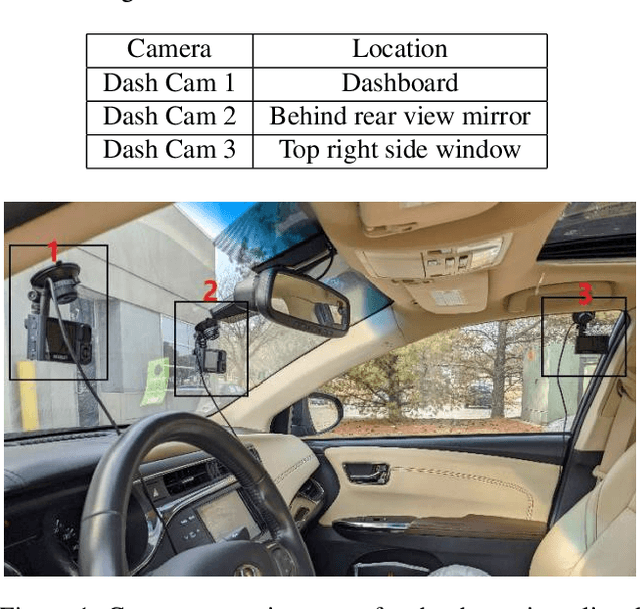
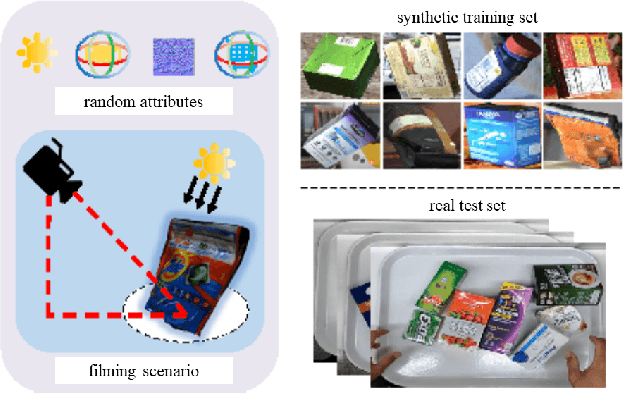
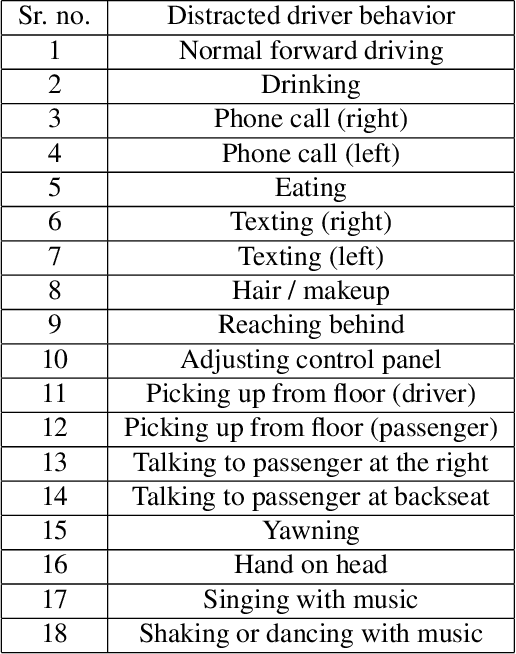
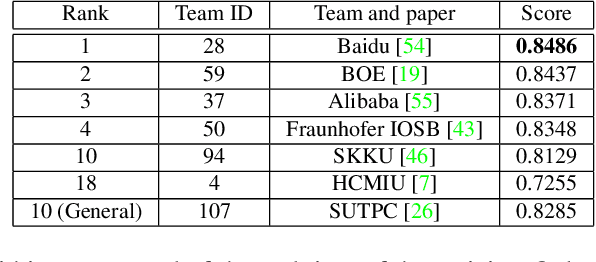
Abstract:The 6th edition of the AI City Challenge specifically focuses on problems in two domains where there is tremendous unlocked potential at the intersection of computer vision and artificial intelligence: Intelligent Traffic Systems (ITS), and brick and mortar retail businesses. The four challenge tracks of the 2022 AI City Challenge received participation requests from 254 teams across 27 countries. Track 1 addressed city-scale multi-target multi-camera (MTMC) vehicle tracking. Track 2 addressed natural-language-based vehicle track retrieval. Track 3 was a brand new track for naturalistic driving analysis, where the data were captured by several cameras mounted inside the vehicle focusing on driver safety, and the task was to classify driver actions. Track 4 was another new track aiming to achieve retail store automated checkout using only a single view camera. We released two leader boards for submissions based on different methods, including a public leader board for the contest, where no use of external data is allowed, and a general leader board for all submitted results. The top performance of participating teams established strong baselines and even outperformed the state-of-the-art in the proposed challenge tracks.
The 5th AI City Challenge
May 24, 2021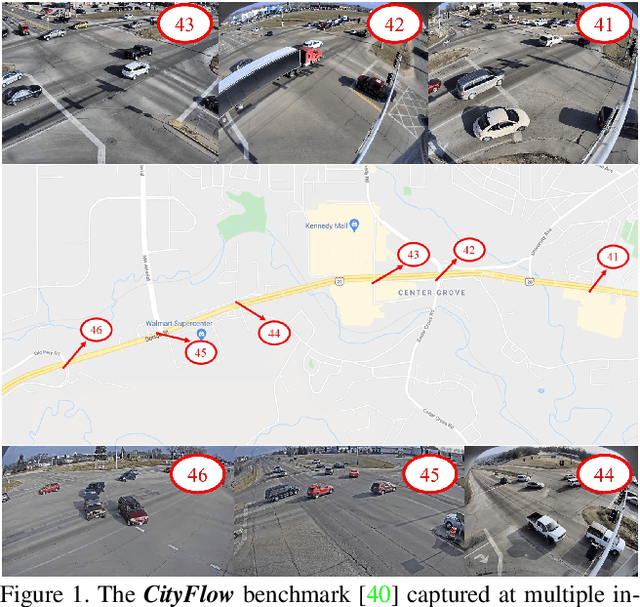
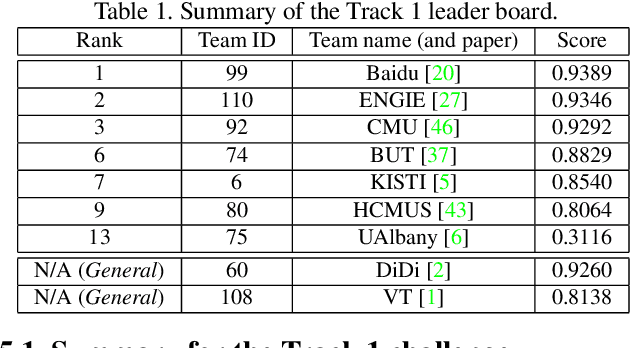
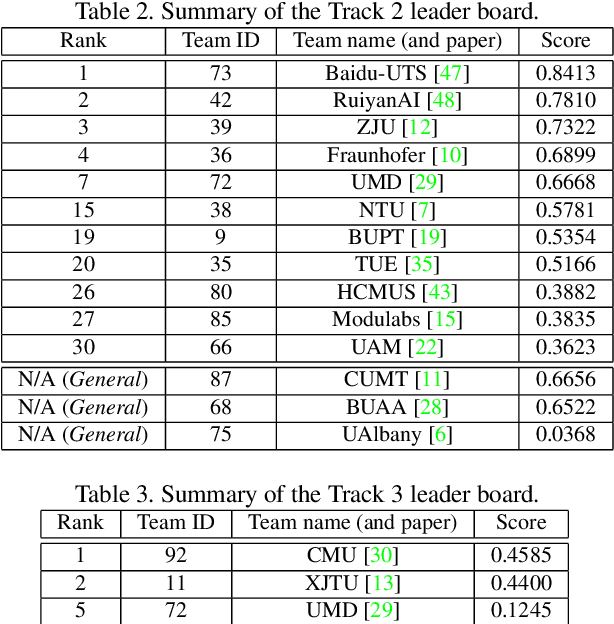
Abstract:The AI City Challenge was created with two goals in mind: (1) pushing the boundaries of research and development in intelligent video analysis for smarter cities use cases, and (2) assessing tasks where the level of performance is enough to cause real-world adoption. Transportation is a segment ripe for such adoption. The fifth AI City Challenge attracted 305 participating teams across 38 countries, who leveraged city-scale real traffic data and high-quality synthetic data to compete in five challenge tracks. Track 1 addressed video-based automatic vehicle counting, where the evaluation being conducted on both algorithmic effectiveness and computational efficiency. Track 2 addressed city-scale vehicle re-identification with augmented synthetic data to substantially increase the training set for the task. Track 3 addressed city-scale multi-target multi-camera vehicle tracking. Track 4 addressed traffic anomaly detection. Track 5 was a new track addressing vehicle retrieval using natural language descriptions. The evaluation system shows a general leader board of all submitted results, and a public leader board of results limited to the contest participation rules, where teams are not allowed to use external data in their work. The public leader board shows results more close to real-world situations where annotated data is limited. Results show the promise of AI in Smarter Transportation. State-of-the-art performance for some tasks shows that these technologies are ready for adoption in real-world systems.
PAMTRI: Pose-Aware Multi-Task Learning for Vehicle Re-Identification Using Highly Randomized Synthetic Data
May 02, 2020



Abstract:In comparison with person re-identification (ReID), which has been widely studied in the research community, vehicle ReID has received less attention. Vehicle ReID is challenging due to 1) high intra-class variability (caused by the dependency of shape and appearance on viewpoint), and 2) small inter-class variability (caused by the similarity in shape and appearance between vehicles produced by different manufacturers). To address these challenges, we propose a Pose-Aware Multi-Task Re-Identification (PAMTRI) framework. This approach includes two innovations compared with previous methods. First, it overcomes viewpoint-dependency by explicitly reasoning about vehicle pose and shape via keypoints, heatmaps and segments from pose estimation. Second, it jointly classifies semantic vehicle attributes (colors and types) while performing ReID, through multi-task learning with the embedded pose representations. Since manually labeling images with detailed pose and attribute information is prohibitive, we create a large-scale highly randomized synthetic dataset with automatically annotated vehicle attributes for training. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of each proposed component, showing that PAMTRI achieves significant improvement over state-of-the-art on two mainstream vehicle ReID benchmarks: VeRi and CityFlow-ReID. Code and models are available at https://github.com/NVlabs/PAMTRI.
The 4th AI City Challenge
Apr 30, 2020



Abstract:The AI City Challenge was created to accelerate intelligent video analysis that helps make cities smarter and safer. Transportation is one of the largest segments that can benefit from actionable insights derived from data captured by sensors, where computer vision and deep learning have shown promise in achieving large-scale practical deployment. The 4th annual edition of the AI City Challenge has attracted 315 participating teams across 37 countries, who leveraged city-scale real traffic data and high-quality synthetic data to compete in four challenge tracks. Track 1 addressed video-based automatic vehicle counting, where the evaluation is conducted on both algorithmic effectiveness and computational efficiency. Track 2 addressed city-scale vehicle re-identification with augmented synthetic data to substantially increase the training set for the task. Track 3 addressed city-scale multi-target multi-camera vehicle tracking. Track 4 addressed traffic anomaly detection. The evaluation system shows two leader boards, in which a general leader board shows all submitted results, and a public leader board shows results limited to our contest participation rules, that teams are not allowed to use external data in their work. The public leader board shows results more close to real-world situations where annotated data are limited. Our results show promise that AI technology can enable smarter and safer transportation systems.
Simulating Content Consistent Vehicle Datasets with Attribute Descent
Dec 18, 2019



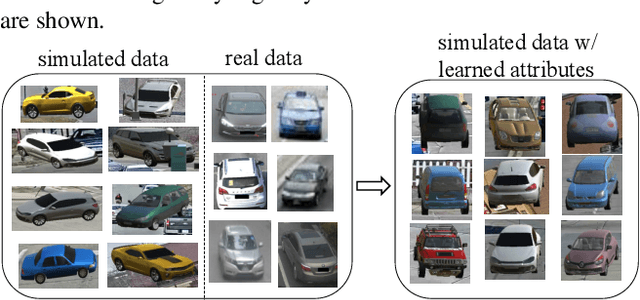
Abstract:We simulate data using a graphic engine to augment real-world datasets, with application to vehicle re-identification (re-ID). In order for data augmentation to be effective, the simulated data should be similar to the real data in key attributes like illumination and viewpoint. We introduce a large-scale synthetic dataset VehicleX. Created in Unity, it contains 1,209 vehicles of various models in 3D with fully editable attributes. We propose an attribute descent approach to let VehicleX approximate the attributes in real-world datasets. Specifically, we manipulate each attribute in VehicleX, aiming to minimize the discrepancy between VehicleX and real data in terms of the Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID). This attribute descent algorithm allows content-level domain adaptation (DA), which has advantages over existing DA methods working on the pixel level or feature level. We mix adapted VehicleX data with three vehicle re-ID datasets individually, and observe consistent improvement when the proposed attribute descent is applied. With the augmented datasets, we report competitive accuracy compared with state-of-the-art results. The VehicleX engine and code of this paper will be released.
CityFlow: A City-Scale Benchmark for Multi-Target Multi-Camera Vehicle Tracking and Re-Identification
Apr 05, 2019



Abstract:Urban traffic optimization using traffic cameras as sensors is driving the need to advance state-of-the-art multi-target multi-camera (MTMC) tracking. This work introduces CityFlow, a city-scale traffic camera dataset consisting of more than 3 hours of synchronized HD videos from 40 cameras across 10 intersections, with the longest distance between two simultaneous cameras being 2.5 km. To the best of our knowledge, CityFlow is the largest-scale dataset in terms of spatial coverage and the number of cameras/videos in an urban environment. The dataset contains more than 200K annotated bounding boxes covering a wide range of scenes, viewing angles, vehicle models, and urban traffic flow conditions. Camera geometry and calibration information are provided to aid spatio-temporal analysis. In addition, a subset of the benchmark is made available for the task of image-based vehicle re-identification (ReID). We conducted an extensive experimental evaluation of baselines/state-of-the-art approaches in MTMC tracking, multi-target single-camera (MTSC) tracking, object detection, and image-based ReID on this dataset, analyzing the impact of different network architectures, loss functions, spatio-temporal models and their combinations on task effectiveness. An evaluation server is launched with the release of our benchmark at the 2019 AI City Challenge (https://www.aicitychallenge.org/) that allows researchers to compare the performance of their newest techniques. We expect this dataset to catalyze research in this field, propel the state-of-the-art forward, and lead to deployed traffic optimization(s) in the real world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge