Mikihiro Tanaka
Chronologically Accurate Retrieval for Temporal Grounding of Motion-Language Models
Jul 22, 2024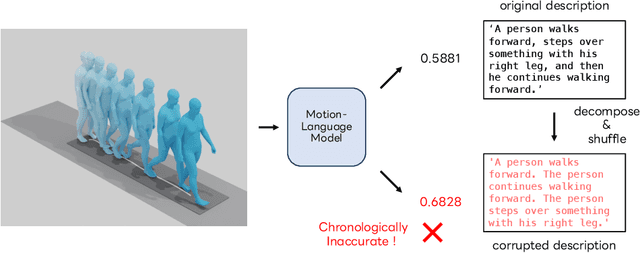
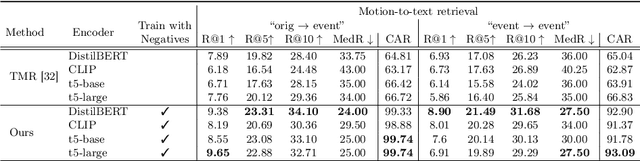
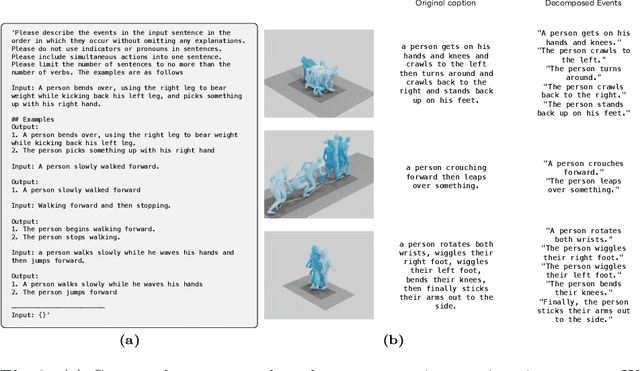
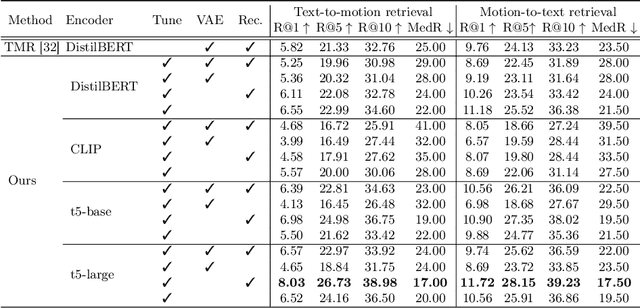
Abstract:With the release of large-scale motion datasets with textual annotations, the task of establishing a robust latent space for language and 3D human motion has recently witnessed a surge of interest. Methods have been proposed to convert human motion and texts into features to achieve accurate correspondence between them. Despite these efforts to align language and motion representations, we claim that the temporal element is often overlooked, especially for compound actions, resulting in chronological inaccuracies. To shed light on the temporal alignment in motion-language latent spaces, we propose Chronologically Accurate Retrieval (CAR) to evaluate the chronological understanding of the models. We decompose textual descriptions into events, and prepare negative text samples by shuffling the order of events in compound action descriptions. We then design a simple task for motion-language models to retrieve the more likely text from the ground truth and its chronologically shuffled version. CAR reveals many cases where current motion-language models fail to distinguish the event chronology of human motion, despite their impressive performance in terms of conventional evaluation metrics. To achieve better temporal alignment between text and motion, we further propose to use these texts with shuffled sequence of events as negative samples during training to reinforce the motion-language models. We conduct experiments on text-motion retrieval and text-to-motion generation using the reinforced motion-language models, which demonstrate improved performance over conventional approaches, indicating the necessity to consider temporal elements in motion-language alignment.
Exploring Vision Transformers for 3D Human Motion-Language Models with Motion Patches
May 08, 2024



Abstract:To build a cross-modal latent space between 3D human motion and language, acquiring large-scale and high-quality human motion data is crucial. However, unlike the abundance of image data, the scarcity of motion data has limited the performance of existing motion-language models. To counter this, we introduce "motion patches", a new representation of motion sequences, and propose using Vision Transformers (ViT) as motion encoders via transfer learning, aiming to extract useful knowledge from the image domain and apply it to the motion domain. These motion patches, created by dividing and sorting skeleton joints based on body parts in motion sequences, are robust to varying skeleton structures, and can be regarded as color image patches in ViT. We find that transfer learning with pre-trained weights of ViT obtained through training with 2D image data can boost the performance of motion analysis, presenting a promising direction for addressing the issue of limited motion data. Our extensive experiments show that the proposed motion patches, used jointly with ViT, achieve state-of-the-art performance in the benchmarks of text-to-motion retrieval, and other novel challenging tasks, such as cross-skeleton recognition, zero-shot motion classification, and human interaction recognition, which are currently impeded by the lack of data.
Leveraging Image-Text Similarity and Caption Modification for the DataComp Challenge: Filtering Track and BYOD Track
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:Large web crawl datasets have already played an important role in learning multimodal features with high generalization capabilities. However, there are still very limited studies investigating the details or improvements of data design. Recently, a DataComp challenge has been designed to propose the best training data with the fixed models. This paper presents our solution to both filtering track and BYOD track of the DataComp challenge. Our solution adopts large multimodal models CLIP and BLIP-2 to filter and modify web crawl data, and utilize external datasets along with a bag of tricks to improve the data quality. Experiments show our solution significantly outperforms DataComp baselines (filtering track: 6.6% improvement, BYOD track: 48.5% improvement).
Captioning Images with Novel Objects via Online Vocabulary Expansion
Mar 06, 2020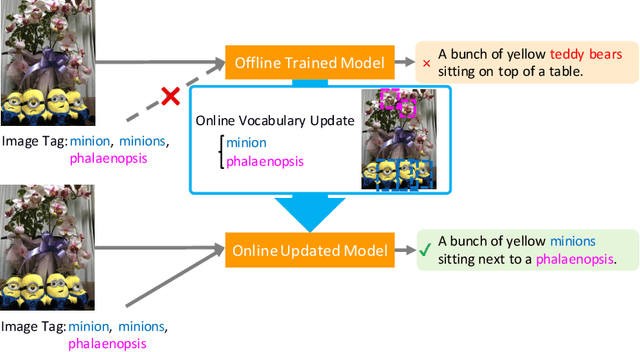



Abstract:In this study, we introduce a low cost method for generating descriptions from images containing novel objects. Generally, constructing a model, which can explain images with novel objects, is costly because of the following: (1) collecting a large amount of data for each category, and (2) retraining the entire system. If humans see a small number of novel objects, they are able to estimate their properties by associating their appearance with known objects. Accordingly, we propose a method that can explain images with novel objects without retraining using the word embeddings of the objects estimated from only a small number of image features of the objects. The method can be integrated with general image-captioning models. The experimental results show the effectiveness of our approach.
Towards Human-Friendly Referring Expression Generation
Nov 29, 2018



Abstract:This paper addresses the generation of referring expressions that not only refer to objects correctly but also ease human comprehension. As the composition of an image becomes more complicated and a target becomes relatively less salient, identifying referred objects comes more difficult. However, the existing studies regarded all sentences that refer to objects correctly as equally good, ignoring whether they are easily understood by humans. If the target is not salient, humans utilize relationships with the salient contexts around it to help listeners to comprehend it better. To derive these information from human annotations, our model is designed to extract information from the inside and outside of the target. Moreover, we regard that sentences that are easily understood are those that are comprehended correctly and quickly by humans. We optimized it by using the time required to locate the referred objects by humans and their accuracies. To evaluate our system, we created a new referring expression dataset whose images were acquired from Grand Theft Auto V (GTA V), limiting targets to persons. Our proposed method outperformed previous methods both on machine evaluation and on crowd-sourced human evaluation. The source code and dataset will be available soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge