Peifei Zhu
Watermark-embedded Adversarial Examples for Copyright Protection against Diffusion Models
Apr 19, 2024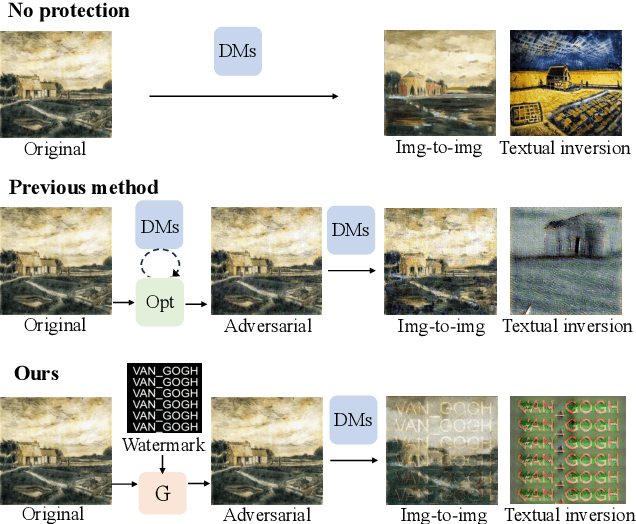
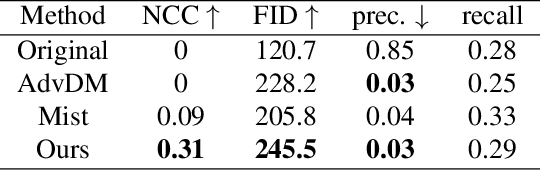
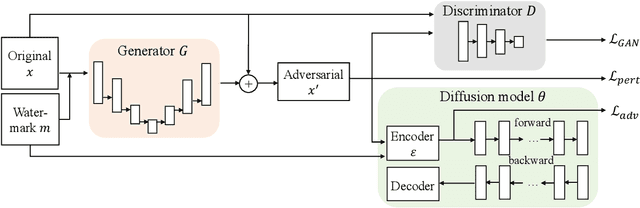

Abstract:Diffusion Models (DMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in various image-generation tasks. However, there are growing concerns that DMs could be used to imitate unauthorized creations and thus raise copyright issues. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework that embeds personal watermarks in the generation of adversarial examples. Such examples can force DMs to generate images with visible watermarks and prevent DMs from imitating unauthorized images. We construct a generator based on conditional adversarial networks and design three losses (adversarial loss, GAN loss, and perturbation loss) to generate adversarial examples that have subtle perturbation but can effectively attack DMs to prevent copyright violations. Training a generator for a personal watermark by our method only requires 5-10 samples within 2-3 minutes, and once the generator is trained, it can generate adversarial examples with that watermark significantly fast (0.2s per image). We conduct extensive experiments in various conditional image-generation scenarios. Compared to existing methods that generate images with chaotic textures, our method adds visible watermarks on the generated images, which is a more straightforward way to indicate copyright violations. We also observe that our adversarial examples exhibit good transferability across unknown generative models. Therefore, this work provides a simple yet powerful way to protect copyright from DM-based imitation.
Image Generation and Learning Strategy for Deep Document Forgery Detection
Nov 07, 2023Abstract:In recent years, document processing has flourished and brought numerous benefits. However, there has been a significant rise in reported cases of forged document images. Specifically, recent advancements in deep neural network (DNN) methods for generative tasks may amplify the threat of document forgery. Traditional approaches for forged document images created by prevalent copy-move methods are unsuitable against those created by DNN-based methods, as we have verified. To address this issue, we construct a training dataset of document forgery images, named FD-VIED, by emulating possible attacks, such as text addition, removal, and replacement with recent DNN-methods. Additionally, we introduce an effective pre-training approach through self-supervised learning with both natural images and document images. In our experiments, we demonstrate that our approach enhances detection performance.
Leveraging Image-Text Similarity and Caption Modification for the DataComp Challenge: Filtering Track and BYOD Track
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:Large web crawl datasets have already played an important role in learning multimodal features with high generalization capabilities. However, there are still very limited studies investigating the details or improvements of data design. Recently, a DataComp challenge has been designed to propose the best training data with the fixed models. This paper presents our solution to both filtering track and BYOD track of the DataComp challenge. Our solution adopts large multimodal models CLIP and BLIP-2 to filter and modify web crawl data, and utilize external datasets along with a bag of tricks to improve the data quality. Experiments show our solution significantly outperforms DataComp baselines (filtering track: 6.6% improvement, BYOD track: 48.5% improvement).
3rd Place Solution to Meta AI Video Similarity Challenge
Apr 24, 2023Abstract:This paper presents our 3rd place solution in both Descriptor Track and Matching Track of the Meta AI Video Similarity Challenge (VSC2022), a competition aimed at detecting video copies. Our approach builds upon existing image copy detection techniques and incorporates several strategies to exploit on the properties of video data, resulting in a simple yet powerful solution. By employing our proposed method, we achieved substantial improvements in accuracy compared to the baseline results (Descriptor Track: 41% improvement, Matching Track: 76% improvement). Our code is publicly available here: https://github.com/line/Meta-AI-Video-Similarity-Challenge-3rd-Place-Solution
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge