Yamato Okamoto
CREPE: Coordinate-Aware End-to-End Document Parser
May 01, 2024



Abstract:In this study, we formulate an OCR-free sequence generation model for visual document understanding (VDU). Our model not only parses text from document images but also extracts the spatial coordinates of the text based on the multi-head architecture. Named as Coordinate-aware End-to-end Document Parser (CREPE), our method uniquely integrates these capabilities by introducing a special token for OCR text, and token-triggered coordinate decoding. We also proposed a weakly-supervised framework for cost-efficient training, requiring only parsing annotations without high-cost coordinate annotations. Our experimental evaluations demonstrate CREPE's state-of-the-art performances on document parsing tasks. Beyond that, CREPE's adaptability is further highlighted by its successful usage in other document understanding tasks such as layout analysis, document visual question answering, and so one. CREPE's abilities including OCR and semantic parsing not only mitigate error propagation issues in existing OCR-dependent methods, it also significantly enhance the functionality of sequence generation models, ushering in a new era for document understanding studies.
The Effects of Short Video-Sharing Services on Video Copy Detection
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:The short video-sharing services that allow users to post 10-30 second videos (e.g., YouTube Shorts and TikTok) have attracted a lot of attention in recent years. However, conventional video copy detection (VCD) methods mainly focus on general video-sharing services (e.g., YouTube and Bilibili), and the effects of short video-sharing services on video copy detection are still unclear. Considering that illegally copied videos in short video-sharing services have service-distinctive characteristics, especially in those time lengths, the pros and cons of VCD in those services are required to be analyzed. In this paper, we examine the effects of short video-sharing services on VCD by constructing a dataset that has short video-sharing service characteristics. Our novel dataset is automatically constructed from the publicly available dataset to have reference videos and fixed short-time-length query videos, and such automation procedures assure the reproducibility and data privacy preservation of this paper. From the experimental results focusing on segment-level and video-level situations, we can see that three effects: "Segment-level VCD in short video-sharing services is more difficult than those in general video-sharing services", "Video-level VCD in short video-sharing services is easier than those in general video-sharing services", "The video alignment component mainly suppress the detection performance in short video-sharing services".
Image Generation and Learning Strategy for Deep Document Forgery Detection
Nov 07, 2023Abstract:In recent years, document processing has flourished and brought numerous benefits. However, there has been a significant rise in reported cases of forged document images. Specifically, recent advancements in deep neural network (DNN) methods for generative tasks may amplify the threat of document forgery. Traditional approaches for forged document images created by prevalent copy-move methods are unsuitable against those created by DNN-based methods, as we have verified. To address this issue, we construct a training dataset of document forgery images, named FD-VIED, by emulating possible attacks, such as text addition, removal, and replacement with recent DNN-methods. Additionally, we introduce an effective pre-training approach through self-supervised learning with both natural images and document images. In our experiments, we demonstrate that our approach enhances detection performance.
Constructing Image-Text Pair Dataset from Books
Oct 03, 2023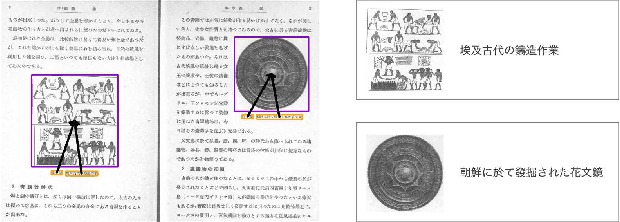
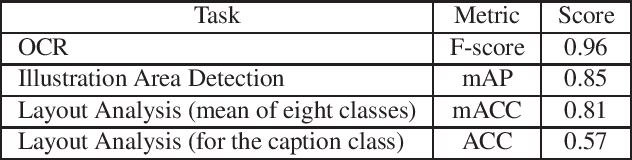
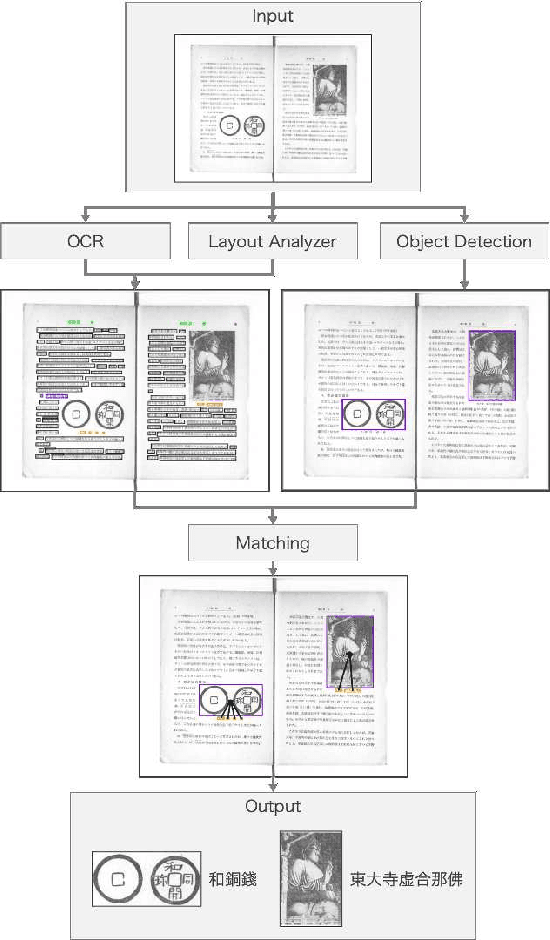

Abstract:Digital archiving is becoming widespread owing to its effectiveness in protecting valuable books and providing knowledge to many people electronically. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to leverage digital archives for machine learning. If we can fully utilize such digitized data, machine learning has the potential to uncover unknown insights and ultimately acquire knowledge autonomously, just like humans read books. As a first step, we design a dataset construction pipeline comprising an optical character reader (OCR), an object detector, and a layout analyzer for the autonomous extraction of image-text pairs. In our experiments, we apply our pipeline on old photo books to construct an image-text pair dataset, showing its effectiveness in image-text retrieval and insight extraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge