Rintaro Yanagi
Zero-shot Composed Image Retrieval Considering Query-target Relationship Leveraging Masked Image-text Pairs
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes a novel zero-shot composed image retrieval (CIR) method considering the query-target relationship by masked image-text pairs. The objective of CIR is to retrieve the target image using a query image and a query text. Existing methods use a textual inversion network to convert the query image into a pseudo word to compose the image and text and use a pre-trained visual-language model to realize the retrieval. However, they do not consider the query-target relationship to train the textual inversion network to acquire information for retrieval. In this paper, we propose a novel zero-shot CIR method that is trained end-to-end using masked image-text pairs. By exploiting the abundant image-text pairs that are convenient to obtain with a masking strategy for learning the query-target relationship, it is expected that accurate zero-shot CIR using a retrieval-focused textual inversion network can be realized. Experimental results show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
The Effects of Short Video-Sharing Services on Video Copy Detection
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:The short video-sharing services that allow users to post 10-30 second videos (e.g., YouTube Shorts and TikTok) have attracted a lot of attention in recent years. However, conventional video copy detection (VCD) methods mainly focus on general video-sharing services (e.g., YouTube and Bilibili), and the effects of short video-sharing services on video copy detection are still unclear. Considering that illegally copied videos in short video-sharing services have service-distinctive characteristics, especially in those time lengths, the pros and cons of VCD in those services are required to be analyzed. In this paper, we examine the effects of short video-sharing services on VCD by constructing a dataset that has short video-sharing service characteristics. Our novel dataset is automatically constructed from the publicly available dataset to have reference videos and fixed short-time-length query videos, and such automation procedures assure the reproducibility and data privacy preservation of this paper. From the experimental results focusing on segment-level and video-level situations, we can see that three effects: "Segment-level VCD in short video-sharing services is more difficult than those in general video-sharing services", "Video-level VCD in short video-sharing services is easier than those in general video-sharing services", "The video alignment component mainly suppress the detection performance in short video-sharing services".
Edge-Selective Feature Weaving for Point Cloud Matching
Feb 08, 2022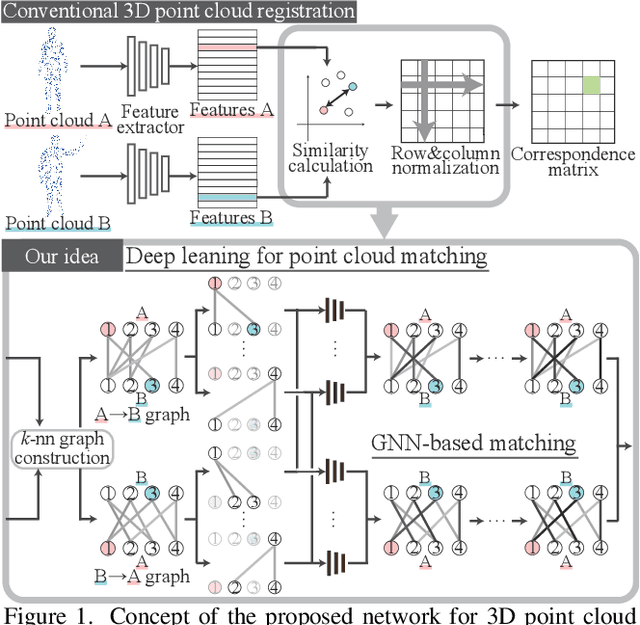
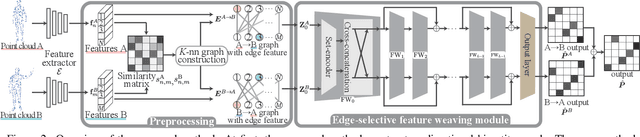
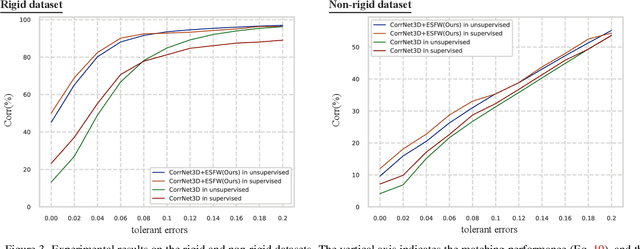

Abstract:This paper tackles the problem of accurately matching the points of two 3D point clouds. Most conventional methods improve their performance by extracting representative features from each point via deep-learning-based algorithms. On the other hand, the correspondence calculation between the extracted features has not been examined in depth, and non-trainable algorithms (e.g. the Sinkhorn algorithm) are frequently applied. As a result, the extracted features may be forcibly fitted to a non-trainable algorithm. Furthermore, the extracted features frequently contain stochastically unavoidable errors, which degrades the matching accuracy. In this paper, instead of using a non-trainable algorithm, we propose a differentiable matching network that can be jointly optimized with the feature extraction procedure. Our network first constructs graphs with edges connecting the points of each point cloud and then extracts discriminative edge features by using two main components: a shared set-encoder and an edge-selective cross-concatenation. These components enable us to symmetrically consider two point clouds and to extract discriminative edge features, respectively. By using the extracted discriminative edge features, our network can accurately calculate the correspondence between points. Our experimental results show that the proposed network can significantly improve the performance of point cloud matching. Our code is available at https://github.com/yanarin/ESFW
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge