Mengyuan Zhao
NUV-DoA: NUV Prior-based Bayesian Sparse Reconstruction with Spatial Filtering for Super-Resolution DoA Estimation
Sep 13, 2023Abstract:Achieving high-resolution Direction of Arrival (DoA) recovery typically requires high Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) and a sufficiently large number of snapshots. This paper presents NUV-DoA algorithm, that augments Bayesian sparse reconstruction with spatial filtering for super-resolution DoA estimation. By modeling each direction on the azimuth's grid with the sparsity-promoting normal with unknown variance (NUV) prior, the non-convex optimization problem is reduced to iteratively reweighted least-squares under Gaussian distribution, where the mean of the snapshots is a sufficient statistic. This approach not only simplifies our solution but also accurately detects the DoAs. We utilize a hierarchical approach for interference cancellation in multi-source scenarios. Empirical evaluations show the superiority of NUV-DoA, especially in low SNRs, compared to alternative DoA estimators.
Linguistic-Enhanced Transformer with CTC Embedding for Speech Recognition
Oct 25, 2022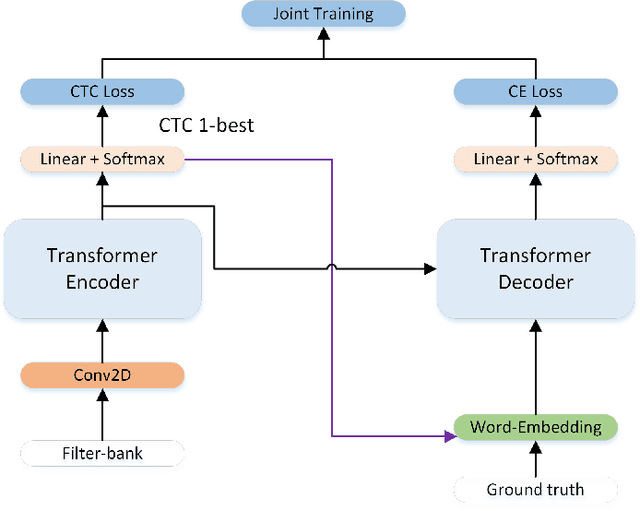
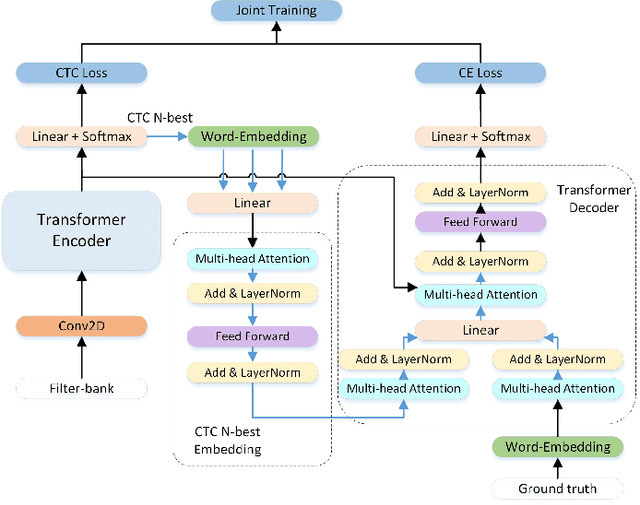
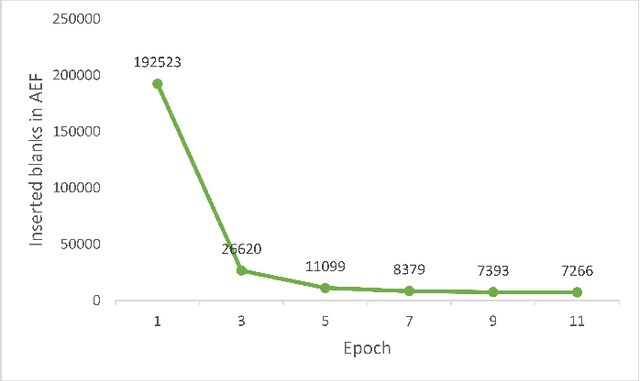
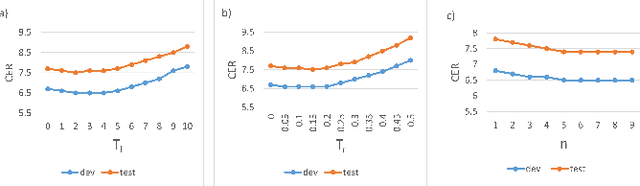
Abstract:The recent emergence of joint CTC-Attention model shows significant improvement in automatic speech recognition (ASR). The improvement largely lies in the modeling of linguistic information by decoder. The decoder joint-optimized with an acoustic encoder renders the language model from ground-truth sequences in an auto-regressive manner during training. However, the training corpus of the decoder is limited to the speech transcriptions, which is far less than the corpus needed to train an acceptable language model. This leads to poor robustness of decoder. To alleviate this problem, we propose linguistic-enhanced transformer, which introduces refined CTC information to decoder during training process, so that the decoder can be more robust. Our experiments on AISHELL-1 speech corpus show that the character error rate (CER) is relatively reduced by up to 7%. We also find that in joint CTC-Attention ASR model, decoder is more sensitive to linguistic information than acoustic information.
Enhancing Keyphrase Extraction from Academic Articles with their Reference Information
Nov 30, 2021
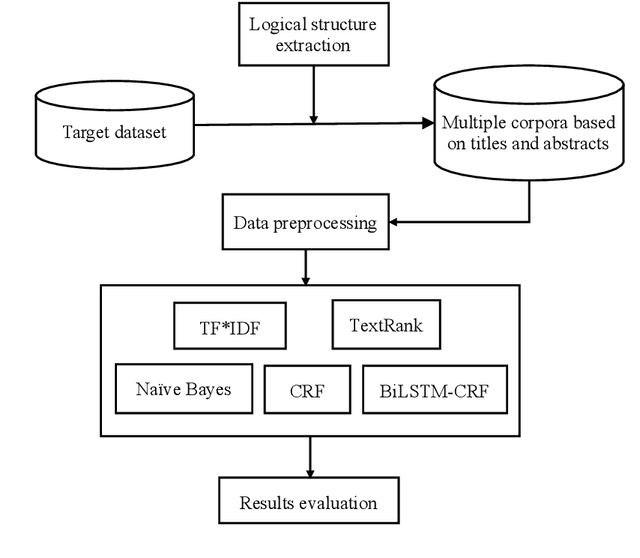
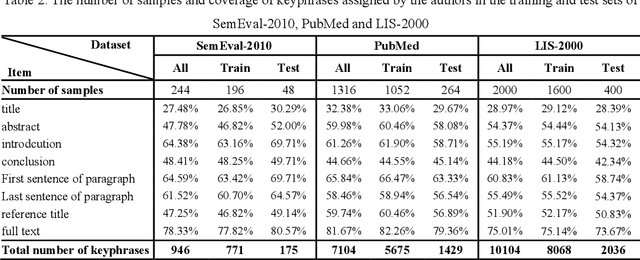
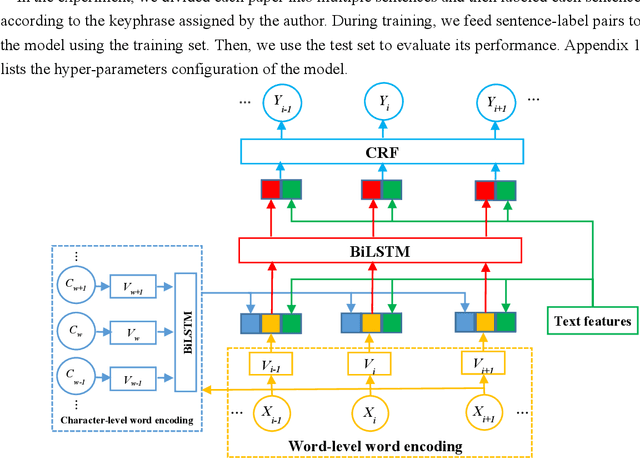
Abstract:With the development of Internet technology, the phenomenon of information overload is becoming more and more obvious. It takes a lot of time for users to obtain the information they need. However, keyphrases that summarize document information highly are helpful for users to quickly obtain and understand documents. For academic resources, most existing studies extract keyphrases through the title and abstract of papers. We find that title information in references also contains author-assigned keyphrases. Therefore, this article uses reference information and applies two typical methods of unsupervised extraction methods (TF*IDF and TextRank), two representative traditional supervised learning algorithms (Na\"ive Bayes and Conditional Random Field) and a supervised deep learning model (BiLSTM-CRF), to analyze the specific performance of reference information on keyphrase extraction. It is expected to improve the quality of keyphrase recognition from the perspective of expanding the source text. The experimental results show that reference information can increase precision, recall, and F1 of automatic keyphrase extraction to a certain extent. This indicates the usefulness of reference information on keyphrase extraction of academic papers and provides a new idea for the following research on automatic keyphrase extraction.
Knowledge Graph-enhanced Sampling for Conversational Recommender System
Oct 13, 2021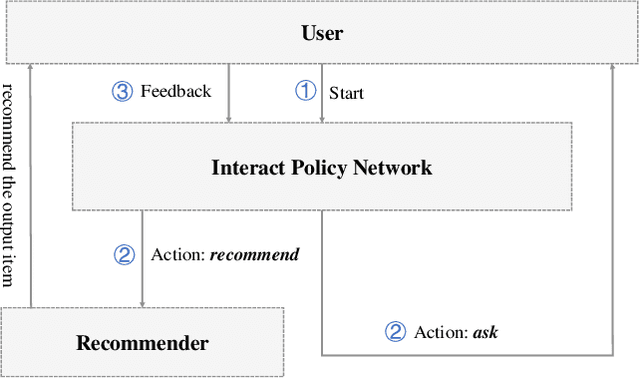
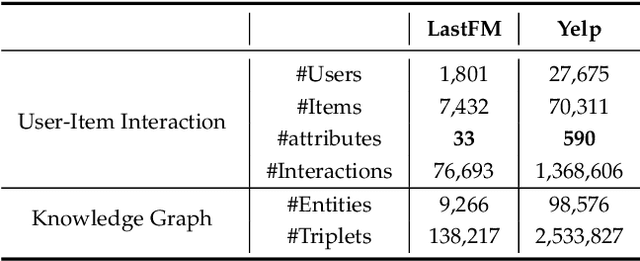
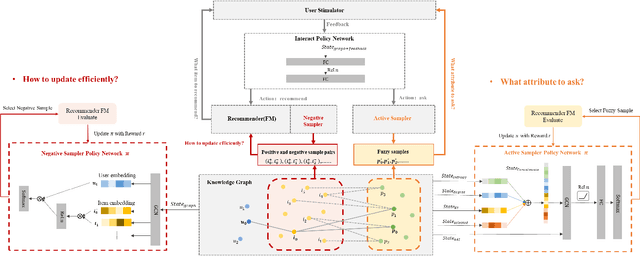
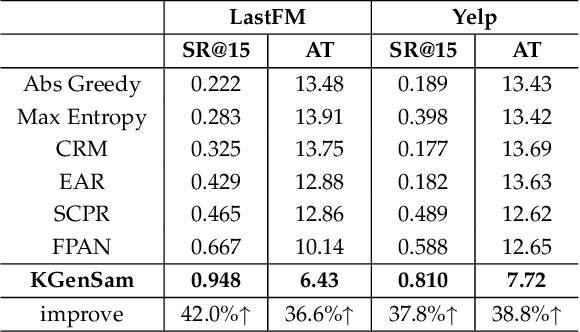
Abstract:The traditional recommendation systems mainly use offline user data to train offline models, and then recommend items for online users, thus suffering from the unreliable estimation of user preferences based on sparse and noisy historical data. Conversational Recommendation System (CRS) uses the interactive form of the dialogue systems to solve the intrinsic problems of traditional recommendation systems. However, due to the lack of contextual information modeling, the existing CRS models are unable to deal with the exploitation and exploration (E&E) problem well, resulting in the heavy burden on users. To address the aforementioned issue, this work proposes a contextual information enhancement model tailored for CRS, called Knowledge Graph-enhanced Sampling (KGenSam). KGenSam integrates the dynamic graph of user interaction data with the external knowledge into one heterogeneous Knowledge Graph (KG) as the contextual information environment. Then, two samplers are designed to enhance knowledge by sampling fuzzy samples with high uncertainty for obtaining user preferences and reliable negative samples for updating recommender to achieve efficient acquisition of user preferences and model updating, and thus provide a powerful solution for CRS to deal with E&E problem. Experimental results on two real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of KGenSam with significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge