Marthie Grobler
Resurrecting Trust in Facial Recognition: Mitigating Backdoor Attacks in Face Recognition to Prevent Potential Privacy Breaches
Feb 18, 2022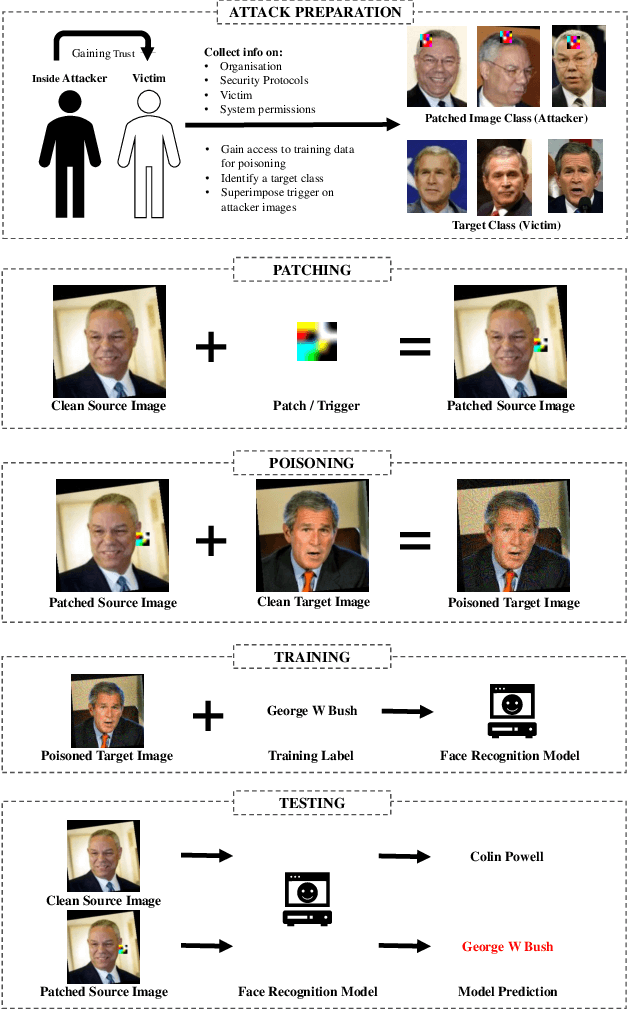
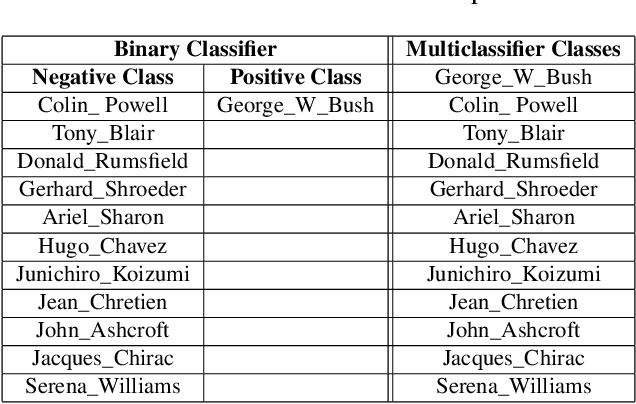
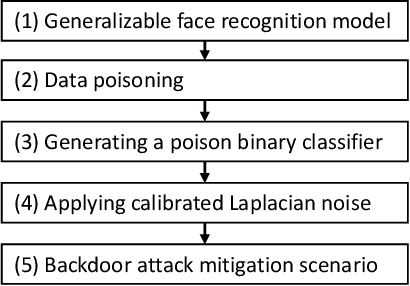
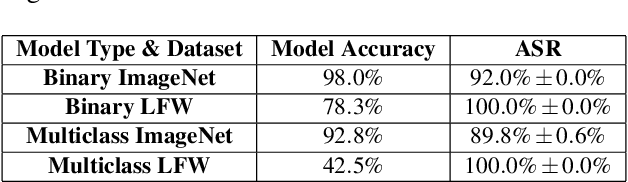
Abstract:Biometric data, such as face images, are often associated with sensitive information (e.g medical, financial, personal government records). Hence, a data breach in a system storing such information can have devastating consequences. Deep learning is widely utilized for face recognition (FR); however, such models are vulnerable to backdoor attacks executed by malicious parties. Backdoor attacks cause a model to misclassify a particular class as a target class during recognition. This vulnerability can allow adversaries to gain access to highly sensitive data protected by biometric authentication measures or allow the malicious party to masquerade as an individual with higher system permissions. Such breaches pose a serious privacy threat. Previous methods integrate noise addition mechanisms into face recognition models to mitigate this issue and improve the robustness of classification against backdoor attacks. However, this can drastically affect model accuracy. We propose a novel and generalizable approach (named BA-BAM: Biometric Authentication - Backdoor Attack Mitigation), that aims to prevent backdoor attacks on face authentication deep learning models through transfer learning and selective image perturbation. The empirical evidence shows that BA-BAM is highly robust and incurs a maximal accuracy drop of 2.4%, while reducing the attack success rate to a maximum of 20%. Comparisons with existing approaches show that BA-BAM provides a more practical backdoor mitigation approach for face recognition.
Robust Training Using Natural Transformation
May 10, 2021
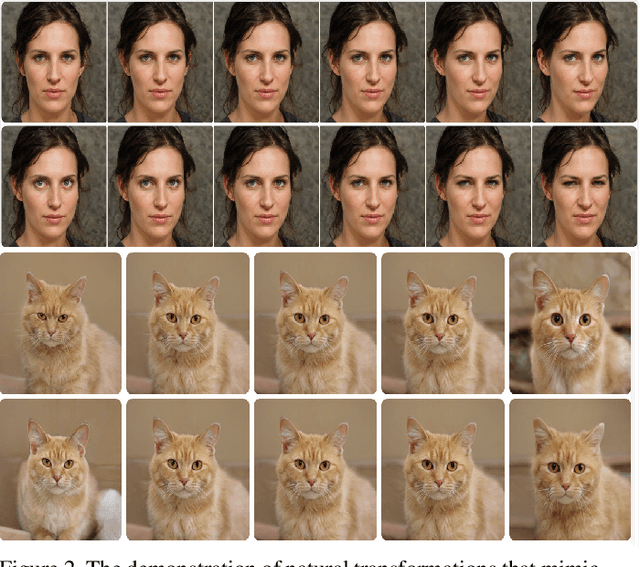
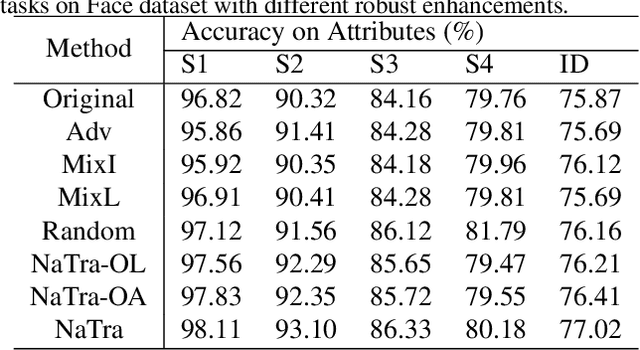

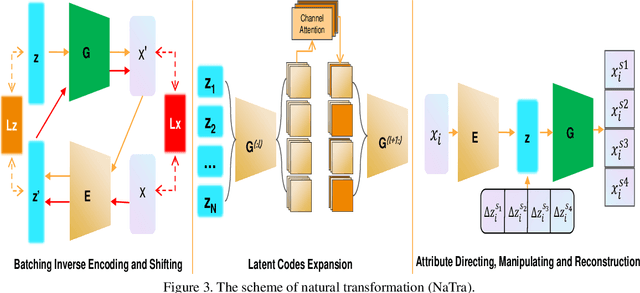
Abstract:Previous robustness approaches for deep learning models such as data augmentation techniques via data transformation or adversarial training cannot capture real-world variations that preserve the semantics of the input, such as a change in lighting conditions. To bridge this gap, we present NaTra, an adversarial training scheme that is designed to improve the robustness of image classification algorithms. We target attributes of the input images that are independent of the class identification, and manipulate those attributes to mimic real-world natural transformations (NaTra) of the inputs, which are then used to augment the training dataset of the image classifier. Specifically, we apply \textit{Batch Inverse Encoding and Shifting} to map a batch of given images to corresponding disentangled latent codes of well-trained generative models. \textit{Latent Codes Expansion} is used to boost image reconstruction quality through the incorporation of extended feature maps. \textit{Unsupervised Attribute Directing and Manipulation} enables identification of the latent directions that correspond to specific attribute changes, and then produce interpretable manipulations of those attributes, thereby generating natural transformations to the input data. We demonstrate the efficacy of our scheme by utilizing the disentangled latent representations derived from well-trained GANs to mimic transformations of an image that are similar to real-world natural variations (such as lighting conditions or hairstyle), and train models to be invariant to these natural transformations. Extensive experiments show that our method improves generalization of classification models and increases its robustness to various real-world distortions
OCTOPUS: Overcoming Performance andPrivatization Bottlenecks in Distributed Learning
May 03, 2021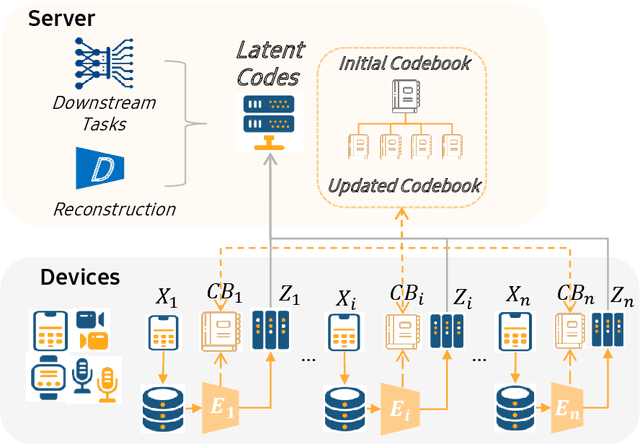

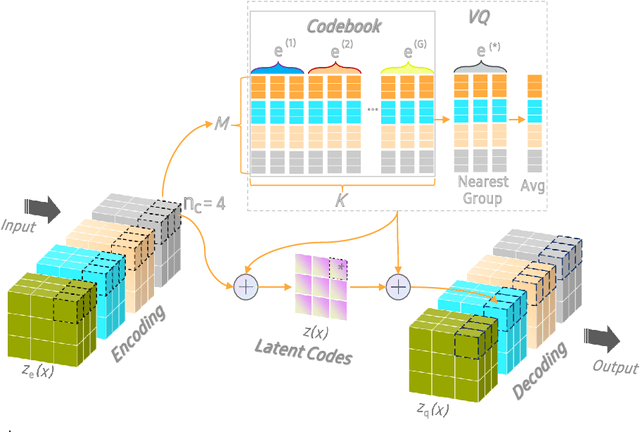
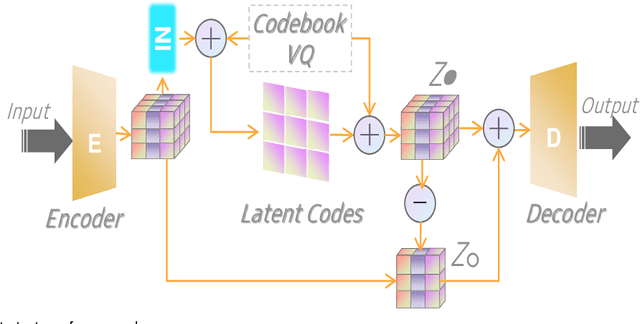
Abstract:The diversity and quantity of the data warehousing, gathering data from distributed devices such as mobile phones, can enhance machine learning algorithms' success and robustness. Federated learning enables distributed participants to collaboratively learn a commonly-shared model while holding data locally. However, it is also faced with expensive communication and limitations due to the heterogeneity of distributed data sources and lack of access to global data. In this paper, we investigate a practical distributed learning scenario where multiple downstream tasks (e.g., classifiers) could be learned from dynamically-updated and non-iid distributed data sources, efficiently and providing local privatization. We introduce a new distributed learning scheme to address communication overhead via latent compression, leveraging global data while providing local privatization of local data without additional cost due to encryption or perturbation. This scheme divides the learning into (1) informative feature encoding, extracting and transmitting the latent space compressed representation features of local data at each node to address communication overhead; (2) downstream tasks centralized at the server using the encoded codes gathered from each node to address computing and storage overhead. Besides, a disentanglement strategy is applied to address the privatization of sensitive components of local data. Extensive experiments are conducted on image and speech datasets. The results demonstrate that downstream tasks on the compact latent representations can achieve comparable accuracy to centralized learning with the privatization of local data.
Adversarial Defense by Latent Style Transformations
Jun 17, 2020


Abstract:Machine learning models have demonstrated vulnerability to adversarial attacks, more specifically misclassification of adversarial examples. In this paper, we investigate an attack-agnostic defense against adversarial attacks on high-resolution images by detecting suspicious inputs. The intuition behind our approach is that the essential characteristics of a normal image are generally consistent with non-essential style transformations, e.g., slightly changing the facial expression of human portraits. In contrast, adversarial examples are generally sensitive to such transformations. In our approach to detect adversarial instances, we propose an in\underline{V}ertible \underline{A}utoencoder based on the \underline{S}tyleGAN2 generator via \underline{A}dversarial training (VASA) to inverse images to disentangled latent codes that reveal hierarchical styles. We then build a set of edited copies with non-essential style transformations by performing latent shifting and reconstruction, based on the correspondences between latent codes and style transformations. The classification-based consistency of these edited copies is used to distinguish adversarial instances.
Defending Adversarial Attacks via Semantic Feature Manipulation
Feb 03, 2020



Abstract:Machine learning models have demonstrated vulnerability to adversarial attacks, more specifically misclassification of adversarial examples. In this paper, we propose a one-off and attack-agnostic Feature Manipulation (FM)-Defense to detect and purify adversarial examples in an interpretable and efficient manner. The intuition is that the classification result of a normal image is generally resistant to non-significant intrinsic feature changes, e.g., varying thickness of handwritten digits. In contrast, adversarial examples are sensitive to such changes since the perturbation lacks transferability. To enable manipulation of features, a combo-variational autoencoder is applied to learn disentangled latent codes that reveal semantic features. The resistance to classification change over the morphs, derived by varying and reconstructing latent codes, is used to detect suspicious inputs. Further, combo-VAE is enhanced to purify the adversarial examples with good quality by considering both class-shared and class-unique features. We empirically demonstrate the effectiveness of detection and the quality of purified instance. Our experiments on three datasets show that FM-Defense can detect nearly $100\%$ of adversarial examples produced by different state-of-the-art adversarial attacks. It achieves more than $99\%$ overall purification accuracy on the suspicious instances that close the manifold of normal examples.
OIAD: One-for-all Image Anomaly Detection with Disentanglement Learning
Jan 18, 2020



Abstract:Anomaly detection aims to recognize samples with anomalous and unusual patterns with respect to a set of normal data, which is significant for numerous domain applications, e.g. in industrial inspection, medical imaging, and security enforcement. There are two key research challenges associated with existing anomaly detention approaches: (1) many of them perform well on low-dimensional problems however the performance on high-dimensional instances is limited, such as images; (2) many of them depend on often still rely on traditional supervised approaches and manual engineering of features, while the topic has not been fully explored yet using modern deep learning approaches, even when the well-label samples are limited. In this paper, we propose a One-for-all Image Anomaly Detection system (OIAD) based on disentangled learning using only clean samples. Our key insight is that the impact of small perturbation on the latent representation can be bounded for normal samples while anomaly images are usually outside such bounded intervals, called structure consistency. We implement this idea and evaluate its performance for anomaly detention. Our experiments with three datasets show that OIAD can detect over $90\%$ of anomalies while maintaining a high low false alarm rate. It can also detect suspicious samples from samples labeled as clean, coincided with what humans would deem unusual.
Backdoor Attacks against Transfer Learning with Pre-trained Deep Learning Models
Jan 10, 2020
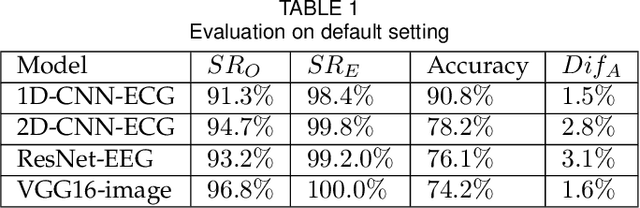
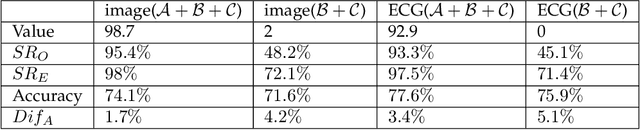

Abstract:Transfer learning, that transfer the learned knowledge of pre-trained Teacher models over large datasets via fine-tuning, provides an effective solution for feasibly and fast customize accurate Student models. Many pre-trained Teacher models are publicly available and maintained by public platforms, increasing their vulnerability to backdoor attacks. In this paper, we demonstrate a backdoor threat to transfer learning tasks on both image and time-series data leveraging the knowledge of publicly accessible Teacher models, aimed at defeating three commonly-adopted defenses: pruning-based, retraining-based and input pre-processing-based defenses. Specifically, (A) ranking-based selection mechanism to speed up the backdoor trigger generation and perturbation process while defeating pruning-based and/or retraining-based defenses. (B) autoencoder-powered trigger generation is proposed to produce a robust trigger that can defeat the input pre-processing-based defense, while guaranteeing that selected neuron(s) can be significantly activated. (C) defense-aware retraining to generate the manipulated model using reverse-engineered model inputs. We use the real-world image and bioelectric signal analytics applications to demonstrate the power of our attack and conduct a comprehensive empirical analysis of the possible factors that affect the attack. The efficiency/effectiveness and feasibility/easiness of such attacks are validated by empirically evaluating the state-of-the-art image, Electroencephalography (EEG) and Electrocardiography (ECG) learning systems.
Generating Semantic Adversarial Examples via Feature Manipulation
Jan 06, 2020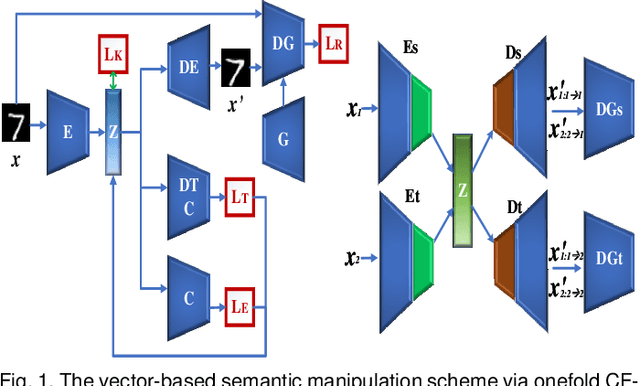



Abstract:The vulnerability of deep neural networks to adversarial attacks has been widely demonstrated (e.g., adversarial example attacks). Traditional attacks perform unstructured pixel-wise perturbation to fool the classifier. An alternative approach is to have perturbations in the latent space. However, such perturbations are hard to control due to the lack of interpretability and disentanglement. In this paper, we propose a more practical adversarial attack by designing structured perturbation with semantic meanings. Our proposed technique manipulates the semantic attributes of images via the disentangled latent codes. The intuition behind our technique is that images in similar domains have some commonly shared but theme-independent semantic attributes, e.g. thickness of lines in handwritten digits, that can be bidirectionally mapped to disentangled latent codes. We generate adversarial perturbation by manipulating a single or a combination of these latent codes and propose two unsupervised semantic manipulation approaches: vector-based disentangled representation and feature map-based disentangled representation, in terms of the complexity of the latent codes and smoothness of the reconstructed images. We conduct extensive experimental evaluations on real-world image data to demonstrate the power of our attacks for black-box classifiers. We further demonstrate the existence of a universal, image-agnostic semantic adversarial example.
Security and Performance Considerations in ROS 2: A Balancing Act
Sep 24, 2018

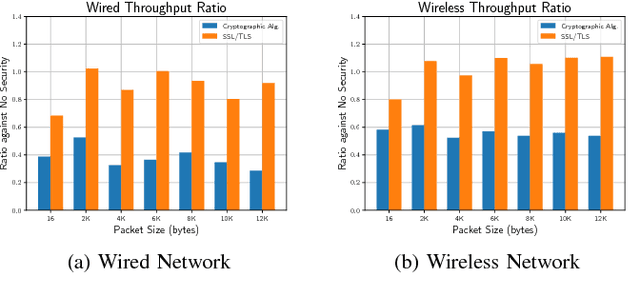
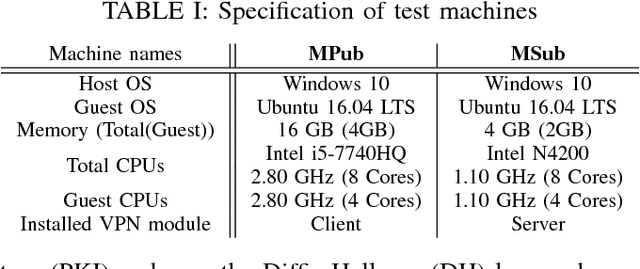
Abstract:Robot Operating System (ROS) 2 is a ground-up re-design of ROS 1 to support performance critical cyber-physical systems (CPSs) using the Data Distribution Service (DDS) middleware. Accordingly, the security of ROS 2 is highly reliant on the security of its DDS communication protocol. However, finding a balance between the performance and security is non-trivial task. Inappropriate security implementations may cause not only significant loss on performance of the system, but also security failures in the system. In this paper, we provide an analysis of the DDS security protocol as well as an overview on how to find the balance between performance and security. To accomplish this, we evaluate the latency and throughput of the communication protocols of ROS 2 in both wired and wireless networks, and measure the efficiency loss caused by the enabling of security protocols such as Virtual Private Network (VPN) and DDS security protocol in ROS 2 in both network setups. The result can be directly used by robotics developers to find the optimal and balanced settings of ROS 2 applications. Additionally, we analyzed the security specification of DDS using existing security standards and tested the implementation of the DDS protocol by performing static analysis. The results of this work can be used to enhance the security of ROS 2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge