Manuel Lagunas
SplatVoxel: History-Aware Novel View Streaming without Temporal Training
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:We study the problem of novel view streaming from sparse-view videos, which aims to generate a continuous sequence of high-quality, temporally consistent novel views as new input frames arrive. However, existing novel view synthesis methods struggle with temporal coherence and visual fidelity, leading to flickering and inconsistency. To address these challenges, we introduce history-awareness, leveraging previous frames to reconstruct the scene and improve quality and stability. We propose a hybrid splat-voxel feed-forward scene reconstruction approach that combines Gaussian Splatting to propagate information over time, with a hierarchical voxel grid for temporal fusion. Gaussian primitives are efficiently warped over time using a motion graph that extends 2D tracking models to 3D motion, while a sparse voxel transformer integrates new temporal observations in an error-aware manner. Crucially, our method does not require training on multi-view video datasets, which are currently limited in size and diversity, and can be directly applied to sparse-view video streams in a history-aware manner at inference time. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in both static and streaming scene reconstruction, effectively reducing temporal artifacts and visual artifacts while running at interactive rates (15 fps with 350ms delay) on a single H100 GPU. Project Page: https://19reborn.github.io/SplatVoxel/
Transfer Learning for Fine-grained Classification Using Semi-supervised Learning and Visual Transformers
May 17, 2023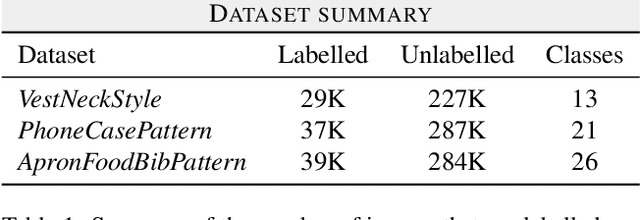

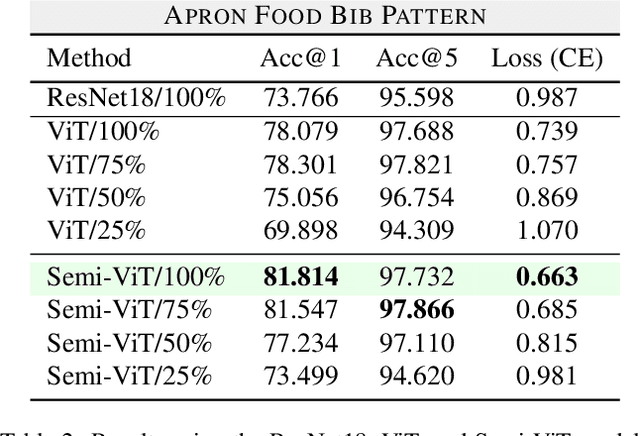
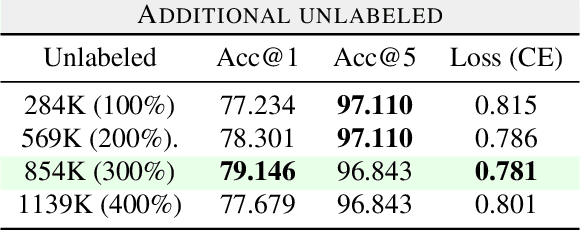
Abstract:Fine-grained classification is a challenging task that involves identifying subtle differences between objects within the same category. This task is particularly challenging in scenarios where data is scarce. Visual transformers (ViT) have recently emerged as a powerful tool for image classification, due to their ability to learn highly expressive representations of visual data using self-attention mechanisms. In this work, we explore Semi-ViT, a ViT model fine tuned using semi-supervised learning techniques, suitable for situations where we have lack of annotated data. This is particularly common in e-commerce, where images are readily available but labels are noisy, nonexistent, or expensive to obtain. Our results demonstrate that Semi-ViT outperforms traditional convolutional neural networks (CNN) and ViTs, even when fine-tuned with limited annotated data. These findings indicate that Semi-ViTs hold significant promise for applications that require precise and fine-grained classification of visual data.
Single-image Full-body Human Relighting
Jul 15, 2021
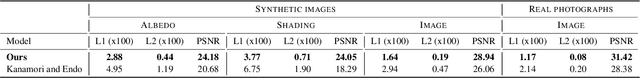

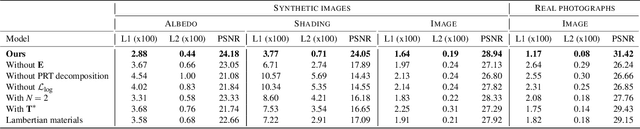
Abstract:We present a single-image data-driven method to automatically relight images with full-body humans in them. Our framework is based on a realistic scene decomposition leveraging precomputed radiance transfer (PRT) and spherical harmonics (SH) lighting. In contrast to previous work, we lift the assumptions on Lambertian materials and explicitly model diffuse and specular reflectance in our data. Moreover, we introduce an additional light-dependent residual term that accounts for errors in the PRT-based image reconstruction. We propose a new deep learning architecture, tailored to the decomposition performed in PRT, that is trained using a combination of L1, logarithmic, and rendering losses. Our model outperforms the state of the art for full-body human relighting both with synthetic images and photographs.
* 11 pages, 12 figures
The joint role of geometry and illumination on material recognition
Feb 04, 2021


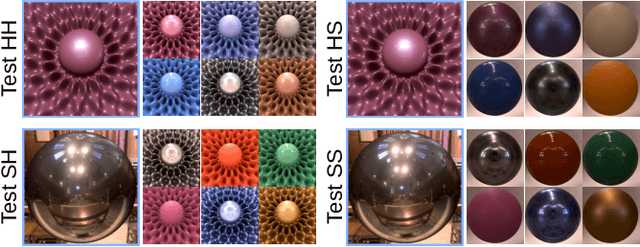
Abstract:Observing and recognizing materials is a fundamental part of our daily life. Under typical viewing conditions, we are capable of effortlessly identifying the objects that surround us and recognizing the materials they are made of. Nevertheless, understanding the underlying perceptual processes that take place to accurately discern the visual properties of an object is a long-standing problem. In this work, we perform a comprehensive and systematic analysis of how the interplay of geometry, illumination, and their spatial frequencies affects human performance on material recognition tasks. We carry out large-scale behavioral experiments where participants are asked to recognize different reference materials among a pool of candidate samples. In the different experiments, we carefully sample the information in the frequency domain of the stimuli. From our analysis, we find significant first-order interactions between the geometry and the illumination, of both the reference and the candidates. In addition, we observe that simple image statistics and higher-order image histograms do not correlate with human performance. Therefore, we perform a high-level comparison of highly non-linear statistics by training a deep neural network on material recognition tasks. Our results show that such models can accurately classify materials, which suggests that they are capable of defining a meaningful representation of material appearance from labeled proximal image data. Last, we find preliminary evidence that these highly non-linear models and humans may use similar high-level factors for material recognition tasks.
* 15 pages, 16 figures, Accepted to the Journal of Vision, 2021
A Similarity Measure for Material Appearance
May 04, 2019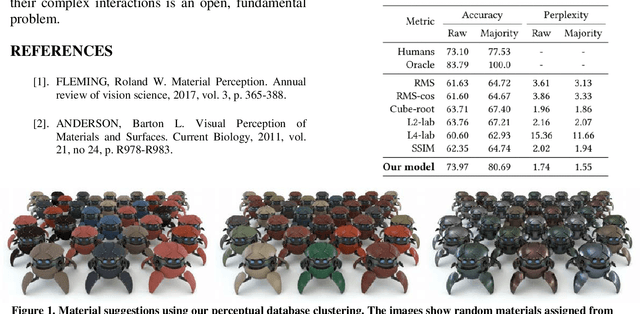
Abstract:We present a model to measure the similarity in appearance between different materials, which correlates with human similarity judgments. We first create a database of 9,000 rendered images depicting objects with varying materials, shape and illumination. We then gather data on perceived similarity from crowdsourced experiments; our analysis of over 114,840 answers suggests that indeed a shared perception of appearance similarity exists. We feed this data to a deep learning architecture with a novel loss function, which learns a feature space for materials that correlates with such perceived appearance similarity. Our evaluation shows that our model outperforms existing metrics. Last, we demonstrate several applications enabled by our metric, including appearance-based search for material suggestions, database visualization, clustering and summarization, and gamut mapping.
* 12 pages, 17 figures
Learning icons appearance similarity
Feb 01, 2019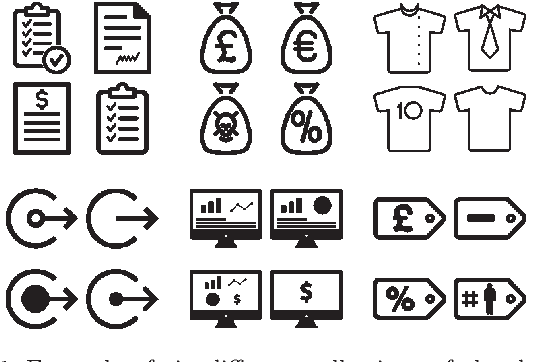
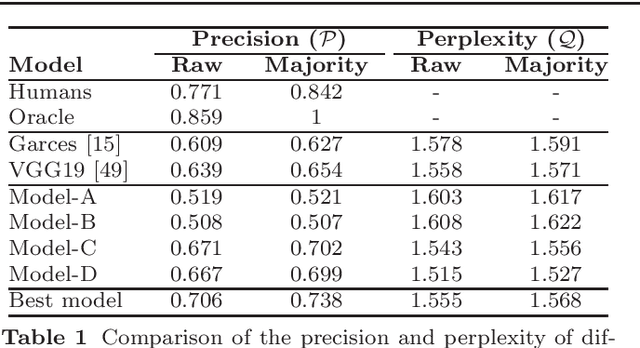
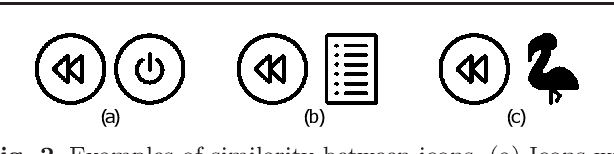

Abstract:Selecting an optimal set of icons is a crucial step in the pipeline of visual design to structure and navigate through content. However, designing the icons sets is usually a difficult task for which expert knowledge is required. In this work, to ease the process of icon set selection to the users, we propose a similarity metric which captures the properties of style and visual identity. We train a Siamese Neural Network with an online dataset of icons organized in visually coherent collections that are used to adaptively sample training data and optimize the training process. As the dataset contains noise, we further collect human-rated information on the perception of icon's similarity which will be used for evaluating and testing the proposed model. We present several results and applications based on searches, kernel visualizations and optimized set proposals that can be helpful for designers and non-expert users while exploring large collections of icons.
* 12 pages, 11 figures
Transfer Learning for Illustration Classification
May 23, 2018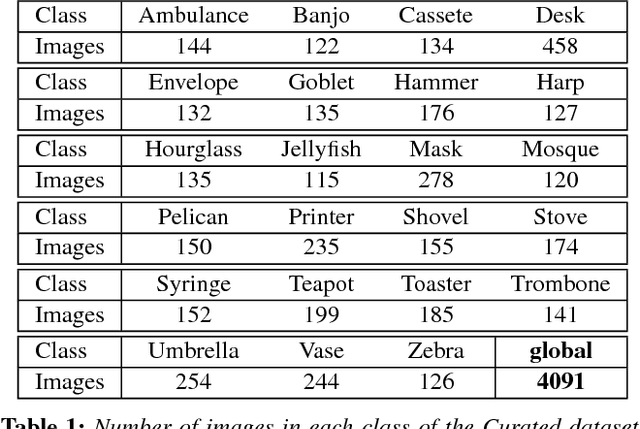
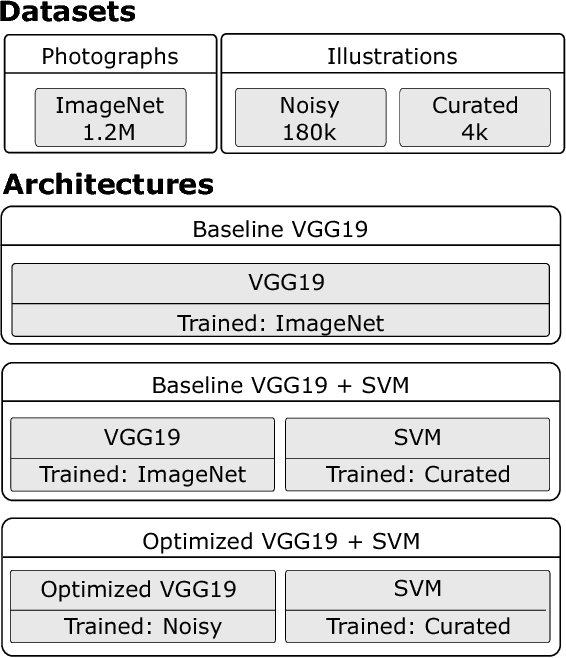
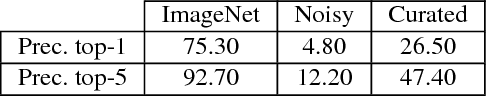
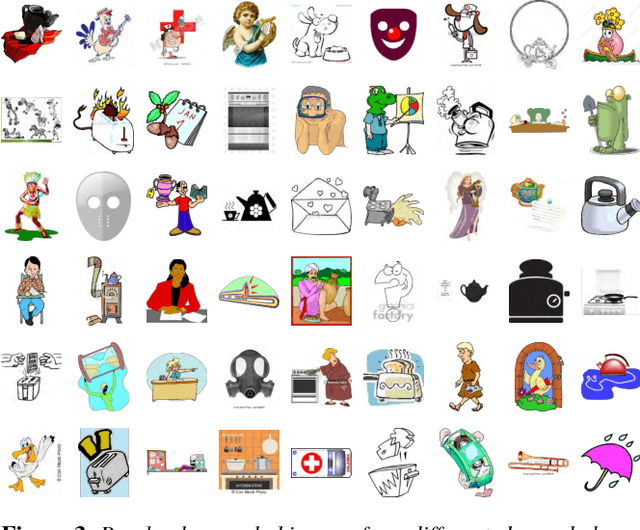
Abstract:The field of image classification has shown an outstanding success thanks to the development of deep learning techniques. Despite the great performance obtained, most of the work has focused on natural images ignoring other domains like artistic depictions. In this paper, we use transfer learning techniques to propose a new classification network with better performance in illustration images. Starting from the deep convolutional network VGG19, pre-trained with natural images, we propose two novel models which learn object representations in the new domain. Our optimized network will learn new low-level features of the images (colours, edges, textures) while keeping the knowledge of the objects and shapes that it already learned from the ImageNet dataset. Thus, requiring much less data for the training. We propose a novel dataset of illustration images labelled by content where our optimized architecture achieves $\textbf{86.61\%}$ of top-1 and $\textbf{97.21\%}$ of top-5 precision. We additionally demonstrate that our model is still able to recognize objects in photographs.
* 9 pages, 8 figures, 4 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge