Mahmood Fathy
A Survey on Multi-Objective Neural Architecture Search
Jul 18, 2023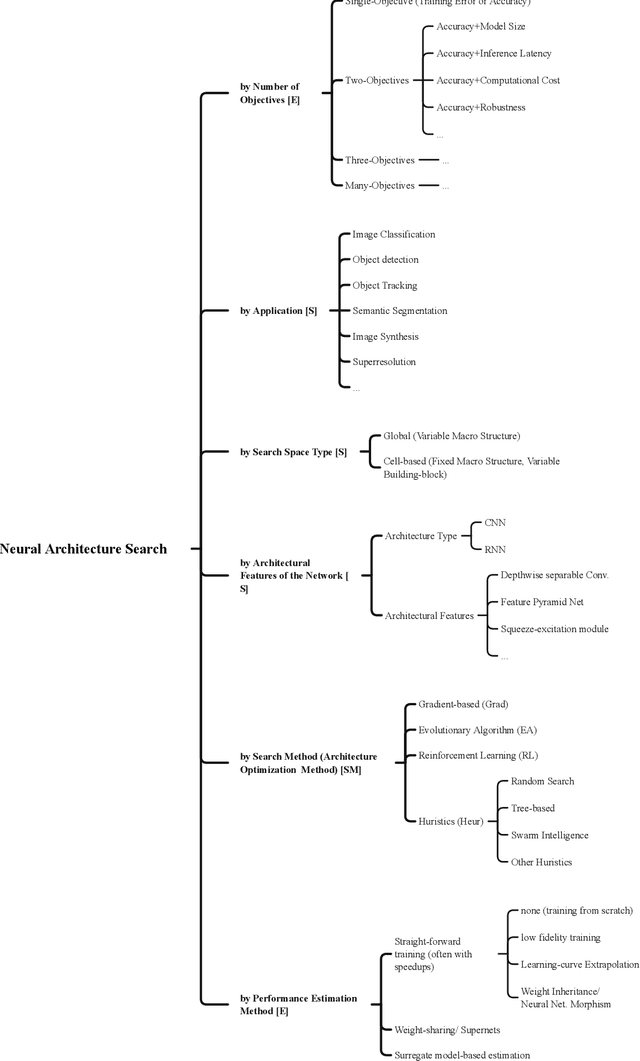
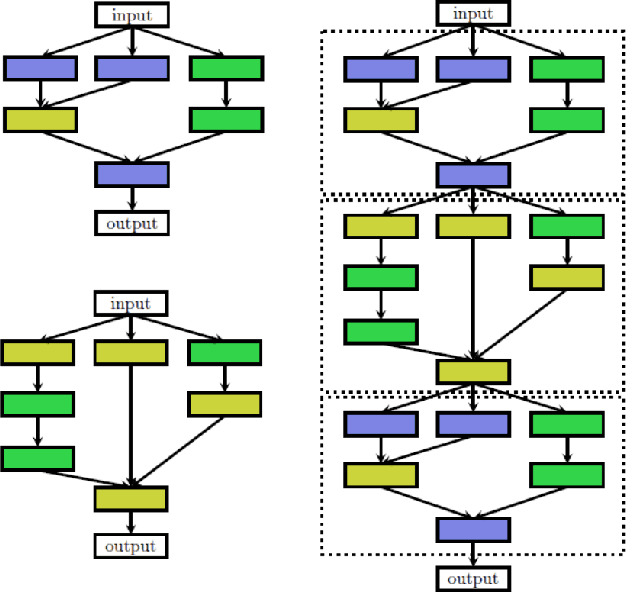
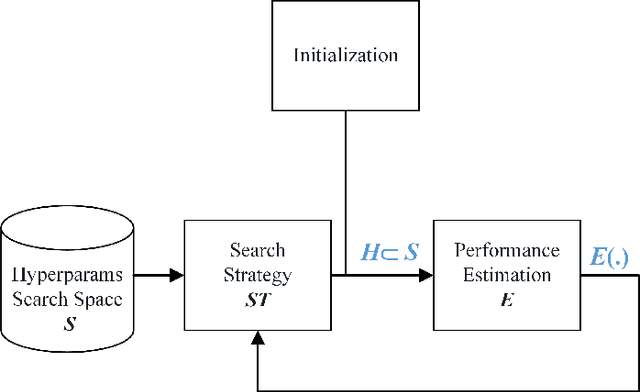
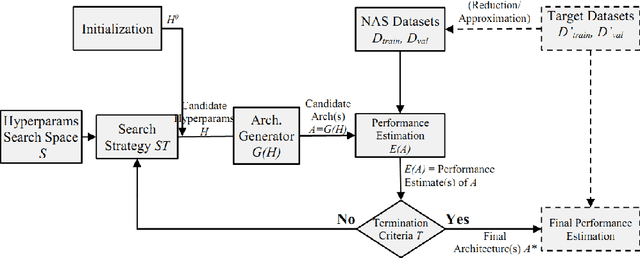
Abstract:Recently, the expert-crafted neural architectures is increasing overtaken by the utilization of neural architecture search (NAS) and automatic generation (and tuning) of network structures which has a close relation to the Hyperparameter Optimization and Auto Machine Learning (AutoML). After the earlier NAS attempts to optimize only the prediction accuracy, Multi-Objective Neural architecture Search (MONAS) has been attracting attentions which considers more goals such as computational complexity, power consumption, and size of the network for optimization, reaching a trade-off between the accuracy and other features like the computational cost. In this paper, we present an overview of principal and state-of-the-art works in the field of MONAS. Starting from a well-categorized taxonomy and formulation for the NAS, we address and correct some miscategorizations in previous surveys of the NAS field. We also provide a list of all known objectives used and add a number of new ones and elaborate their specifications. We have provides analyses about the most important objectives and shown that the stochastic properties of some the them should be differed from deterministic ones in the multi-objective optimization procedure of NAS. We finalize this paper with a number of future directions and topics in the field of MONAS.
Image/Video Deep Anomaly Detection: A Survey
Mar 02, 2021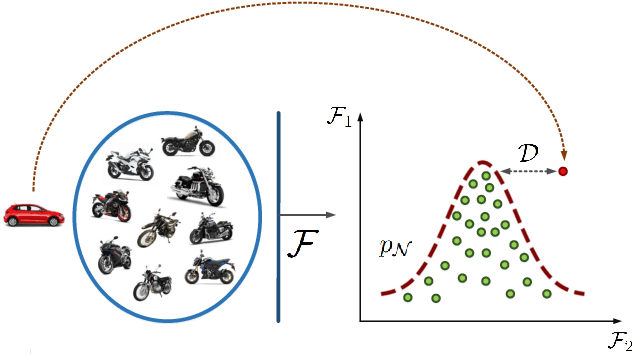
Abstract:The considerable significance of Anomaly Detection (AD) problem has recently drawn the attention of many researchers. Consequently, the number of proposed methods in this research field has been increased steadily. AD strongly correlates with the important computer vision and image processing tasks such as image/video anomaly, irregularity and sudden event detection. More recently, Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) offer a high performance set of solutions, but at the expense of a heavy computational cost. However, there is a noticeable gap between the previously proposed methods and an applicable real-word approach. Regarding the raised concerns about AD as an ongoing challenging problem, notably in images and videos, the time has come to argue over the pitfalls and prospects of methods have attempted to deal with visual AD tasks. Hereupon, in this survey we intend to conduct an in-depth investigation into the images/videos deep learning based AD methods. We also discuss current challenges and future research directions thoroughly.
Multi-level Context Gating of Embedded Collective Knowledge for Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 10, 2020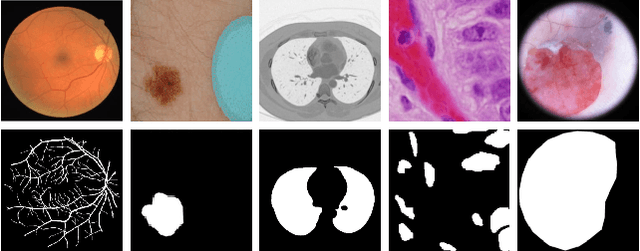
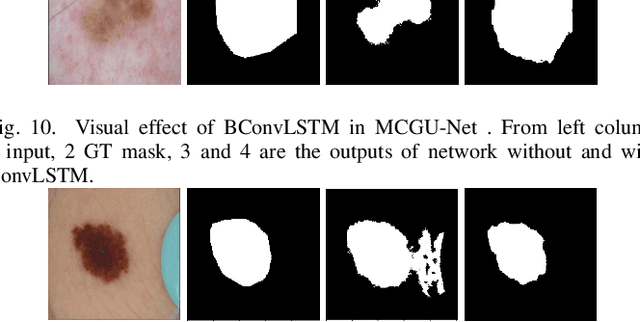
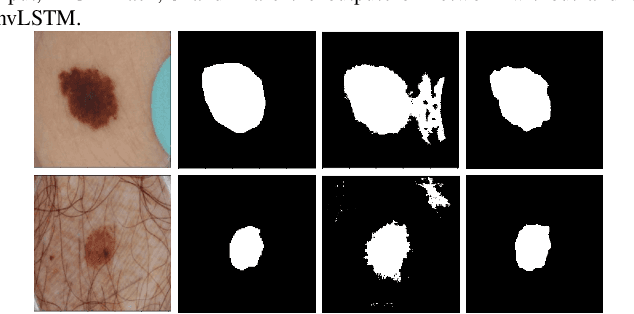
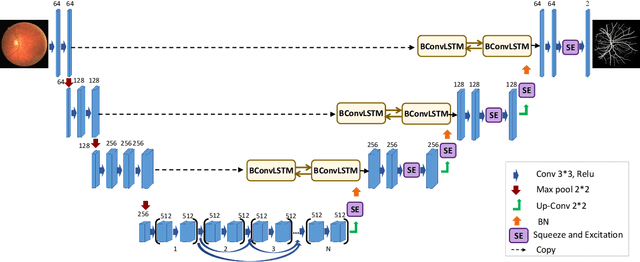
Abstract:Medical image segmentation has been very challenging due to the large variation of anatomy across different cases. Recent advances in deep learning frameworks have exhibited faster and more accurate performance in image segmentation. Among the existing networks, U-Net has been successfully applied on medical image segmentation. In this paper, we propose an extension of U-Net for medical image segmentation, in which we take full advantages of U-Net, Squeeze and Excitation (SE) block, bi-directional ConvLSTM (BConvLSTM), and the mechanism of dense convolutions. (I) We improve the segmentation performance by utilizing SE modules within the U-Net, with a minor effect on model complexity. These blocks adaptively recalibrate the channel-wise feature responses by utilizing a self-gating mechanism of the global information embedding of the feature maps. (II) To strengthen feature propagation and encourage feature reuse, we use densely connected convolutions in the last convolutional layer of the encoding path. (III) Instead of a simple concatenation in the skip connection of U-Net, we employ BConvLSTM in all levels of the network to combine the feature maps extracted from the corresponding encoding path and the previous decoding up-convolutional layer in a non-linear way. The proposed model is evaluated on six datasets DRIVE, ISIC 2017 and 2018, lung segmentation, $PH^2$, and cell nuclei segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Deep-HR: Fast Heart Rate Estimation from Face Video Under Realistic Conditions
Feb 12, 2020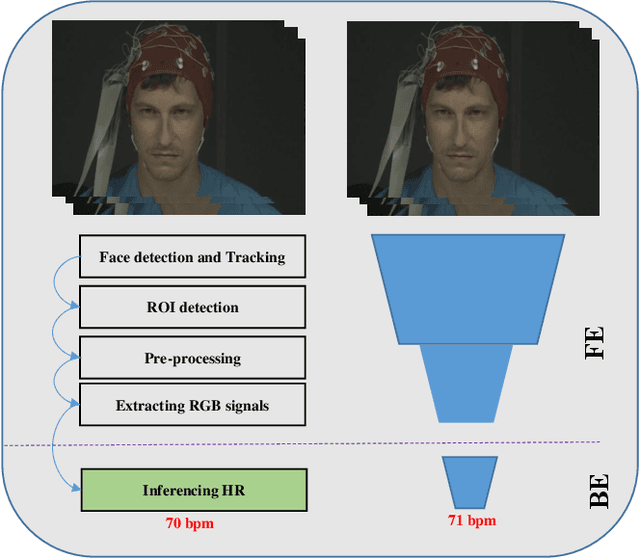
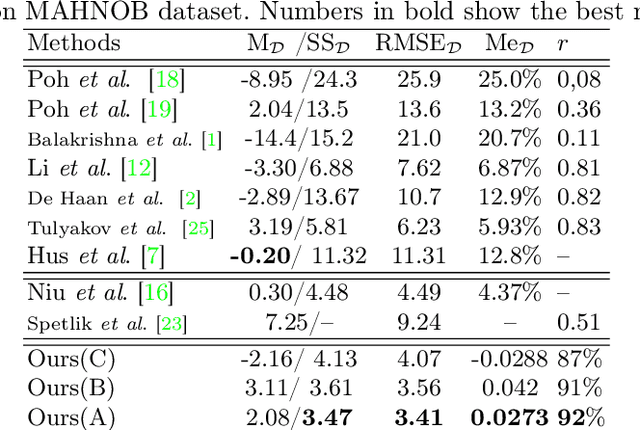
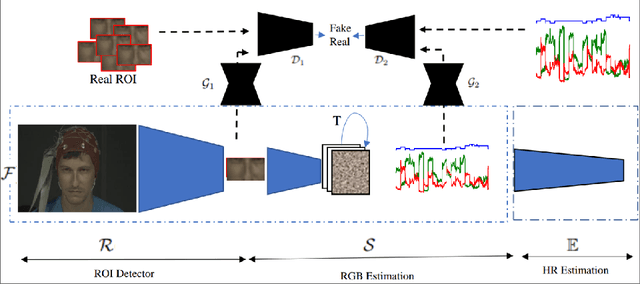
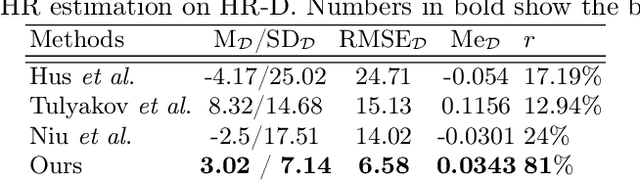
Abstract:This paper presents a novel method for remote heart rate (HR) estimation. Recent studies have proved that blood pumping by the heart is highly correlated to the intense color of face pixels, and surprisingly can be utilized for remote HR estimation. Researchers successfully proposed several methods for this task, but making it work in realistic situations is still a challenging problem in computer vision community. Furthermore, learning to solve such a complex task on a dataset with very limited annotated samples is not reasonable. Consequently, researchers do not prefer to use the deep learning approaches for this problem. In this paper, we propose a simple yet efficient approach to benefit the advantages of the Deep Neural Network (DNN) by simplifying HR estimation from a complex task to learning from very correlated representation to HR. Inspired by previous work, we learn a component called Front-End (FE) to provide a discriminative representation of face videos, afterward a light deep regression auto-encoder as Back-End (BE) is learned to map the FE representation to HR. Regression task on the informative representation is simple and could be learned efficiently on limited training samples. Beside of this, to be more accurate and work well on low-quality videos, two deep encoder-decoder networks are trained to refine the output of FE. We also introduce a challenging dataset (HR-D) to show that our method can efficiently work in realistic conditions. Experimental results on HR-D and MAHNOB datasets confirm that our method could run as a real-time method and estimate the average HR better than state-of-the-art ones.
Bi-Directional ConvLSTM U-Net with Densley Connected Convolutions
Aug 31, 2019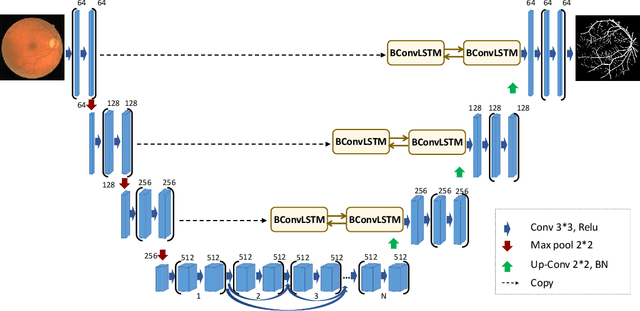
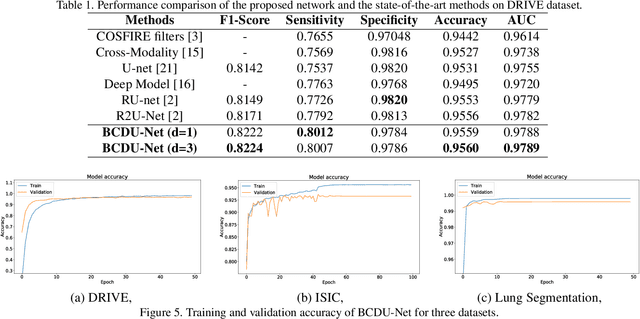
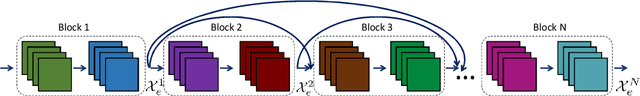
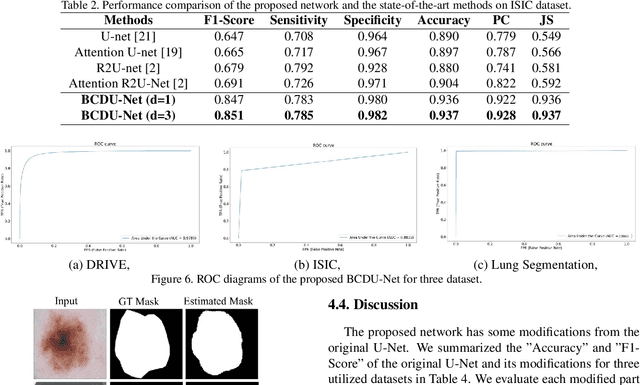
Abstract:In recent years, deep learning-based networks have achieved state-of-the-art performance in medical image segmentation. Among the existing networks, U-Net has been successfully applied on medical image segmentation. In this paper, we propose an extension of U-Net, Bi-directional ConvLSTM U-Net with Densely connected convolutions (BCDU-Net), for medical image segmentation, in which we take full advantages of U-Net, bi-directional ConvLSTM (BConvLSTM) and the mechanism of dense convolutions. Instead of a simple concatenation in the skip connection of U-Net, we employ BConvLSTM to combine the feature maps extracted from the corresponding encoding path and the previous decoding up-convolutional layer in a non-linear way. To strengthen feature propagation and encourage feature reuse, we use densely connected convolutions in the last convolutional layer of the encoding path. Finally, we can accelerate the convergence speed of the proposed network by employing batch normalization (BN). The proposed model is evaluated on three datasets of: retinal blood vessel segmentation, skin lesion segmentation, and lung nodule segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
AVID: Adversarial Visual Irregularity Detection
Jul 17, 2018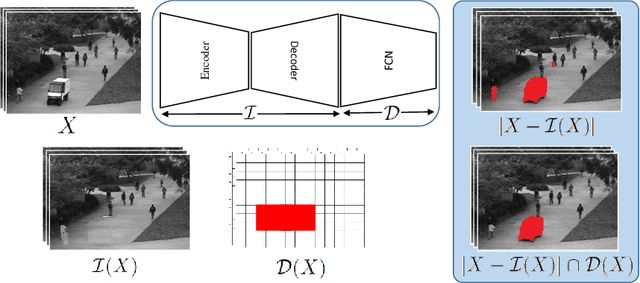
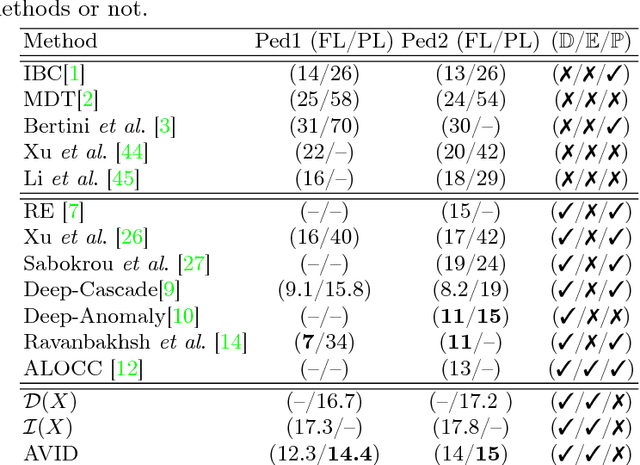
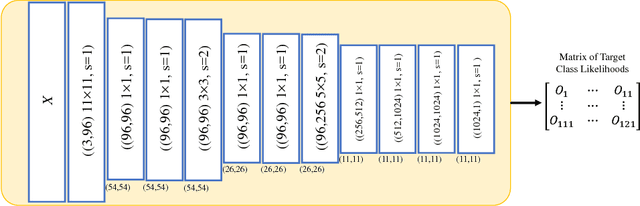
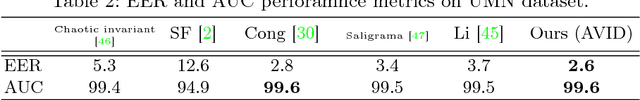
Abstract:Real-time detection of irregularities in visual data is very invaluable and useful in many prospective applications including surveillance, patient monitoring systems, etc. With the surge of deep learning methods in the recent years, researchers have tried a wide spectrum of methods for different applications. However, for the case of irregularity or anomaly detection in videos, training an end-to-end model is still an open challenge, since often irregularity is not well-defined and there are not enough irregular samples to use during training. In this paper, inspired by the success of generative adversarial networks (GANs) for training deep models in unsupervised or self-supervised settings, we propose an end-to-end deep network for detection and fine localization of irregularities in videos (and images). Our proposed architecture is composed of two networks, which are trained in competing with each other while collaborating to find the irregularity. One network works as a pixel-level irregularity Inpainter, and the other works as a patch-level Detector. After an adversarial self-supervised training, in which I tries to fool D into accepting its inpainted output as regular (normal), the two networks collaborate to detect and fine-segment the irregularity in any given testing video. Our results on three different datasets show that our method can outperform the state-of-the-art and fine-segment the irregularity.
Online Signature Verification using Deep Representation: A new Descriptor
Jun 24, 2018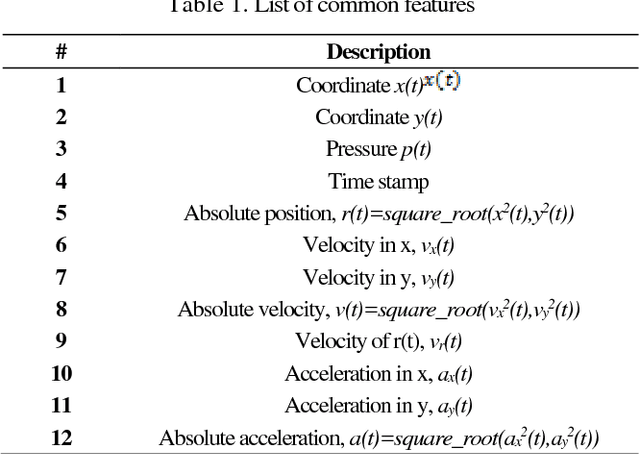
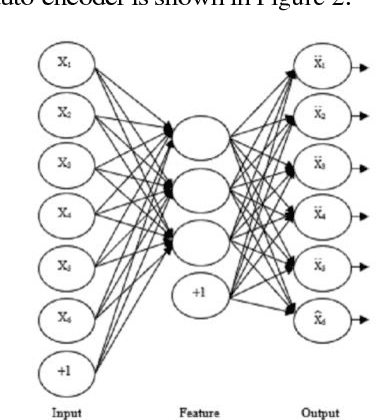
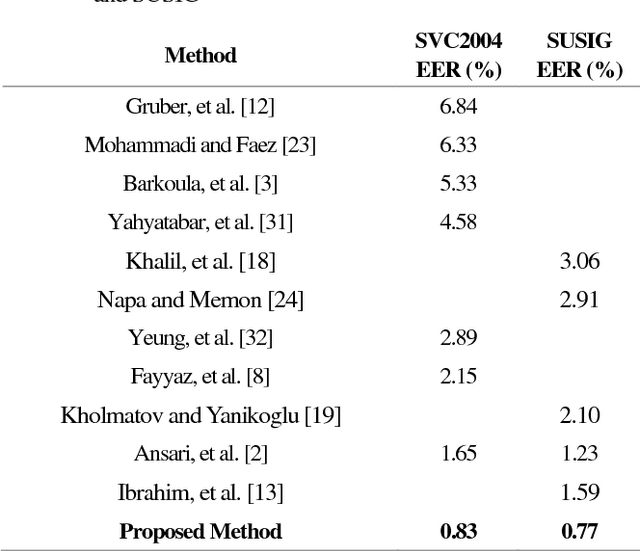
Abstract:This paper presents an accurate method for verifying online signatures. The main difficulty of signature verification come from: (1) Lacking enough training samples (2) The methods must be spatial change invariant. To deal with these difficulties and modeling the signatures efficiently, we propose a method that a one-class classifier per each user is built on discriminative features. First, we pre-train a sparse auto-encoder using a large number of unlabeled signatures, then we applied the discriminative features, which are learned by auto-encoder to represent the training and testing signatures as a self-thought learning method (i.e. we have introduced a signature descriptor). Finally, user's signatures are modeled and classified using a one-class classifier. The proposed method is independent on signature datasets thanks to self-taught learning. The experimental results indicate significant error reduction and accuracy enhancement in comparison with state-of-the-art methods on SVC2004 and SUSIG datasets.
Semantic Video Segmentation: A Review on Recent Approaches
Jun 16, 2018
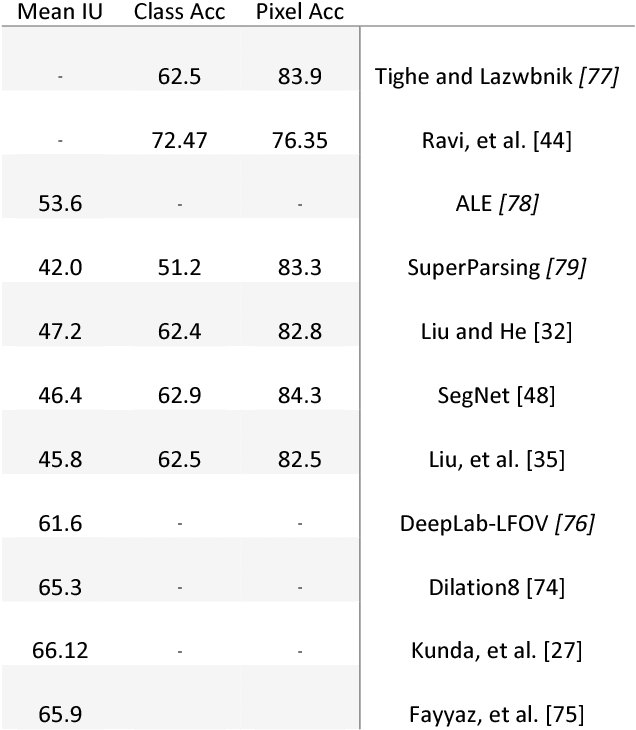

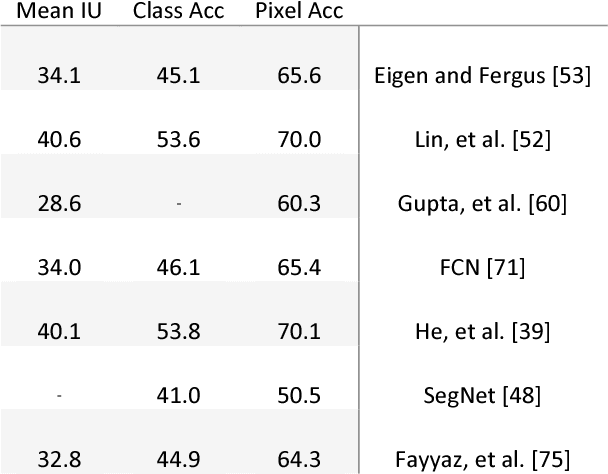
Abstract:This paper gives an overview on semantic segmentation consists of an explanation of this field, it's status and relation with other vision fundamental tasks, different datasets and common evaluation parameters that have been used by researchers. This survey also includes an overall review on a variety of recent approaches (RDF, MRF, CRF, etc.) and their advantages and challenges and shows the superiority of CNN-based semantic segmentation systems on CamVid and NYUDv2 datasets. In addition, some areas that is ideal for future work have mentioned.
Adversarially Learned One-Class Classifier for Novelty Detection
May 24, 2018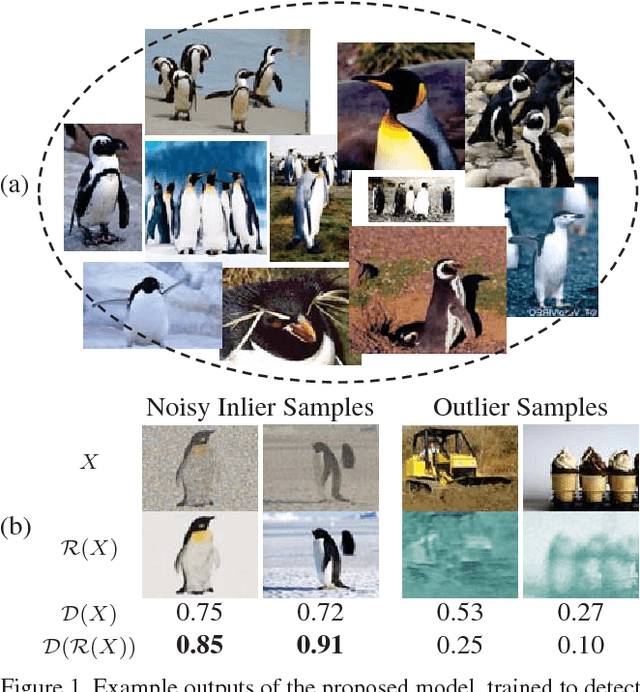
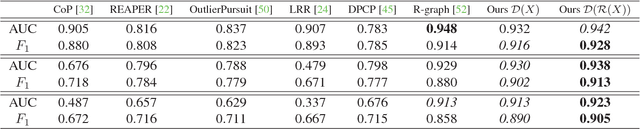
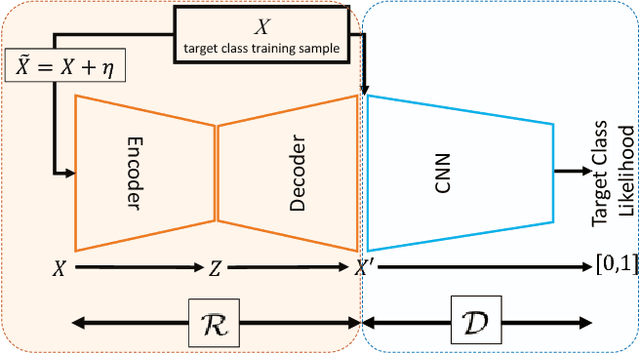
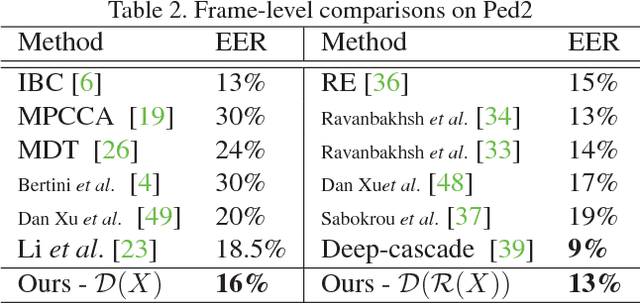
Abstract:Novelty detection is the process of identifying the observation(s) that differ in some respect from the training observations (the target class). In reality, the novelty class is often absent during training, poorly sampled or not well defined. Therefore, one-class classifiers can efficiently model such problems. However, due to the unavailability of data from the novelty class, training an end-to-end deep network is a cumbersome task. In this paper, inspired by the success of generative adversarial networks for training deep models in unsupervised and semi-supervised settings, we propose an end-to-end architecture for one-class classification. Our architecture is composed of two deep networks, each of which trained by competing with each other while collaborating to understand the underlying concept in the target class, and then classify the testing samples. One network works as the novelty detector, while the other supports it by enhancing the inlier samples and distorting the outliers. The intuition is that the separability of the enhanced inliers and distorted outliers is much better than deciding on the original samples. The proposed framework applies to different related applications of anomaly and outlier detection in images and videos. The results on MNIST and Caltech-256 image datasets, along with the challenging UCSD Ped2 dataset for video anomaly detection illustrate that our proposed method learns the target class effectively and is superior to the baseline and state-of-the-art methods.
Deep-Anomaly: Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Fast Anomaly Detection in Crowded Scenes
Apr 30, 2017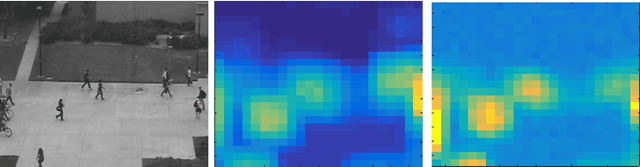

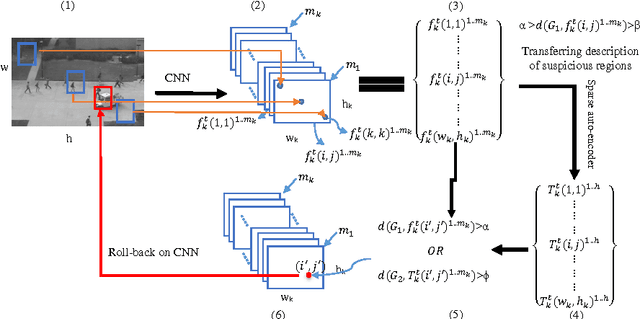
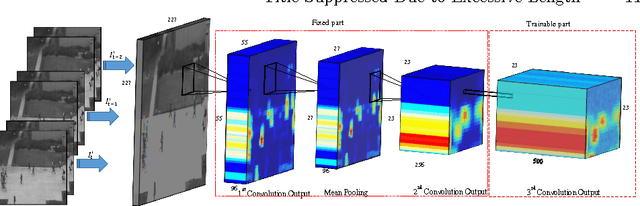
Abstract:The detection of abnormal behaviours in crowded scenes has to deal with many challenges. This paper presents an efficient method for detection and localization of anomalies in videos. Using fully convolutional neural networks (FCNs) and temporal data, a pre-trained supervised FCN is transferred into an unsupervised FCN ensuring the detection of (global) anomalies in scenes. High performance in terms of speed and accuracy is achieved by investigating the cascaded detection as a result of reducing computation complexities. This FCN-based architecture addresses two main tasks, feature representation and cascaded outlier detection. Experimental results on two benchmarks suggest that detection and localization of the proposed method outperforms existing methods in terms of accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge