Bahram Mohammadi
Learning to Reason and Navigate: Parameter Efficient Action Planning with Large Language Models
May 12, 2025Abstract:The remote embodied referring expression (REVERIE) task requires an agent to navigate through complex indoor environments and localize a remote object specified by high-level instructions, such as "bring me a spoon", without pre-exploration. Hence, an efficient navigation plan is essential for the final success. This paper proposes a novel parameter-efficient action planner using large language models (PEAP-LLM) to generate a single-step instruction at each location. The proposed model consists of two modules, LLM goal planner (LGP) and LoRA action planner (LAP). Initially, LGP extracts the goal-oriented plan from REVERIE instructions, including the target object and room. Then, LAP generates a single-step instruction with the goal-oriented plan, high-level instruction, and current visual observation as input. PEAP-LLM enables the embodied agent to interact with LAP as the path planner on the fly. A simple direct application of LLMs hardly achieves good performance. Also, existing hard-prompt-based methods are error-prone in complicated scenarios and need human intervention. To address these issues and prevent the LLM from generating hallucinations and biased information, we propose a novel two-stage method for fine-tuning the LLM, consisting of supervised fine-tuning (STF) and direct preference optimization (DPO). SFT improves the quality of generated instructions, while DPO utilizes environmental feedback. Experimental results show the superiority of our proposed model on REVERIE compared to the previous state-of-the-art.
Augmented Commonsense Knowledge for Remote Object Grounding
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:The vision-and-language navigation (VLN) task necessitates an agent to perceive the surroundings, follow natural language instructions, and act in photo-realistic unseen environments. Most of the existing methods employ the entire image or object features to represent navigable viewpoints. However, these representations are insufficient for proper action prediction, especially for the REVERIE task, which uses concise high-level instructions, such as ''Bring me the blue cushion in the master bedroom''. To address enhancing representation, we propose an augmented commonsense knowledge model (ACK) to leverage commonsense information as a spatio-temporal knowledge graph for improving agent navigation. Specifically, the proposed approach involves constructing a knowledge base by retrieving commonsense information from ConceptNet, followed by a refinement module to remove noisy and irrelevant knowledge. We further present ACK which consists of knowledge graph-aware cross-modal and concept aggregation modules to enhance visual representation and visual-textual data alignment by integrating visible objects, commonsense knowledge, and concept history, which includes object and knowledge temporal information. Moreover, we add a new pipeline for the commonsense-based decision-making process which leads to more accurate local action prediction. Experimental results demonstrate our proposed model noticeably outperforms the baseline and archives the state-of-the-art on the REVERIE benchmark.
ClaRe: Practical Class Incremental Learning By Remembering Previous Class Representations
Mar 29, 2021


Abstract:This paper presents a practical and simple yet efficient method to effectively deal with the catastrophic forgetting for Class Incremental Learning (CIL) tasks. CIL tends to learn new concepts perfectly, but not at the expense of performance and accuracy for old data. Learning new knowledge in the absence of data instances from previous classes or even imbalance samples of both old and new classes makes CIL an ongoing challenging problem. These issues can be tackled by storing exemplars belonging to the previous tasks or by utilizing the rehearsal strategy. Inspired by the rehearsal strategy with the approach of using generative models, we propose ClaRe, an efficient solution for CIL by remembering the representations of learned classes in each increment. Taking this approach leads to generating instances with the same distribution of the learned classes. Hence, our model is somehow retrained from the scratch using a new training set including both new and the generated samples. Subsequently, the imbalance data problem is also solved. ClaRe has a better generalization than prior methods thanks to producing diverse instances from the distribution of previously learned classes. We comprehensively evaluate ClaRe on the MNIST benchmark. Results show a very low degradation on accuracy against facing new knowledge over time. Furthermore, contrary to the most proposed solutions, the memory limitation is not problematic any longer which is considered as a consequential issue in this research area.
Image/Video Deep Anomaly Detection: A Survey
Mar 02, 2021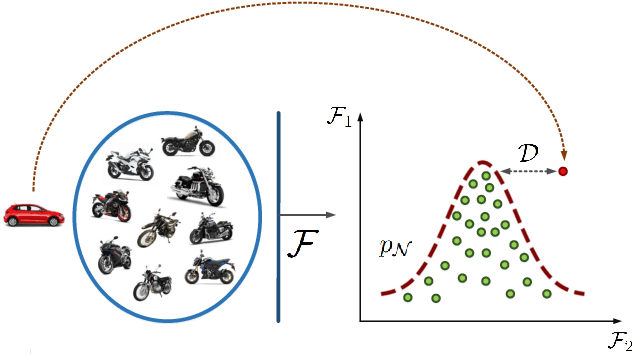
Abstract:The considerable significance of Anomaly Detection (AD) problem has recently drawn the attention of many researchers. Consequently, the number of proposed methods in this research field has been increased steadily. AD strongly correlates with the important computer vision and image processing tasks such as image/video anomaly, irregularity and sudden event detection. More recently, Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) offer a high performance set of solutions, but at the expense of a heavy computational cost. However, there is a noticeable gap between the previously proposed methods and an applicable real-word approach. Regarding the raised concerns about AD as an ongoing challenging problem, notably in images and videos, the time has come to argue over the pitfalls and prospects of methods have attempted to deal with visual AD tasks. Hereupon, in this survey we intend to conduct an in-depth investigation into the images/videos deep learning based AD methods. We also discuss current challenges and future research directions thoroughly.
G2D: Generate to Detect Anomaly
Jun 27, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel method for irregularity detection. Previous researches solve this problem as a One-Class Classification (OCC) task where they train a reference model on all of the available samples. Then, they consider a test sample as an anomaly if it has a diversion from the reference model. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have achieved the most promising results for OCC while implementing and training such networks, especially for the OCC task, is a cumbersome and computationally expensive procedure. To cope with the mentioned challenges, we present a simple but effective method to solve the irregularity detection as a binary classification task in order to make the implementation easier along with improving the detection performance. We learn two deep neural networks (generator and discriminator) in a GAN-style setting on merely the normal samples. During training, the generator gradually becomes an expert to generate samples which are similar to the normal ones. In the training phase, when the generator fails to produce normal data (in the early stages of learning and also prior to the complete convergence), it can be considered as an irregularity generator. In this way, we simultaneously generate the irregular samples. Afterward, we train a binary classifier on the generated anomalous samples along with the normal instances in order to be capable of detecting irregularities. The proposed framework applies to different related applications of outlier and anomaly detection in images and videos, respectively. The results confirm that our proposed method is superior to the baseline and state-of-the-art solutions.
AutoIDS: Auto-encoder Based Method for Intrusion Detection System
Nov 08, 2019
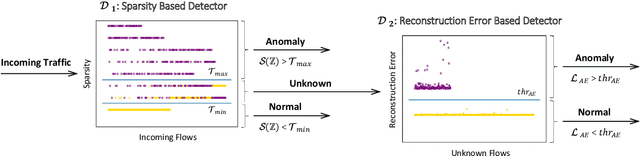
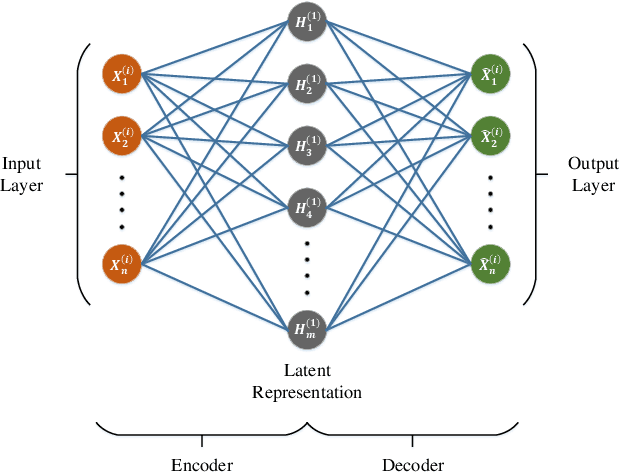
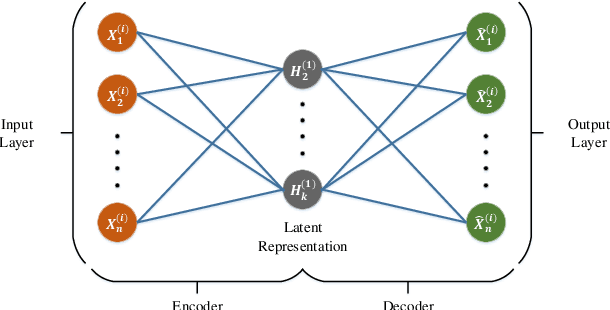
Abstract:Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is one of the most effective solutions for providing primary security services. IDSs are generally working based on attack signatures or by detecting anomalies. In this paper, we have presented AutoIDS, a novel yet efficient solution for IDS, based on a semi-supervised machine learning technique. AutoIDS can distinguish abnormal packet flows from normal ones by taking advantage of cascading two efficient detectors. These detectors are two encoder-decoder neural networks that are forced to provide a compressed and a sparse representation from the normal flows. In the test phase, failing these neural networks on providing compressed or sparse representation from an incoming packet flow, means such flow does not comply with the normal traffic and thus it is considered as an intrusion. For lowering the computational cost along with preserving the accuracy, a large number of flows are just processed by the first detector. In fact, the second detector is only used for difficult samples which the first detector is not confident about them. We have evaluated AutoIDS on the NSL-KDD benchmark as a widely-used and well-known dataset. The accuracy of AutoIDS is 90.17\% showing its superiority compared to the other state-of-the-art methods.
End-to-End Adversarial Learning for Intrusion Detection in Computer Networks
Apr 25, 2019



Abstract:This paper presents a simple yet efficient method for an anomaly-based Intrusion Detection System (IDS). In reality, IDSs can be defined as a one-class classification system, where the normal traffic is the target class. The high diversity of network attacks in addition to the need for generalization, motivate us to propose a semi-supervised method. Inspired by the successes of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for training deep models in semi-unsupervised setting, we have proposed an end-to-end deep architecture for IDS. The proposed architecture is composed of two deep networks, each of which trained by competing with each other to understand the underlying concept of the normal traffic class. The key idea of this paper is to compensate the lack of anomalous traffic by approximately obtain them from normal flows. In this case, our method is not biased towards the available intrusions in the training set leading to more accurate detection. The proposed method has been evaluated on NSL-KDD dataset. The results confirm that our method outperforms the other state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge