Made Nindyatama Nityasya
COPAL-ID: Indonesian Language Reasoning with Local Culture and Nuances
Nov 13, 2023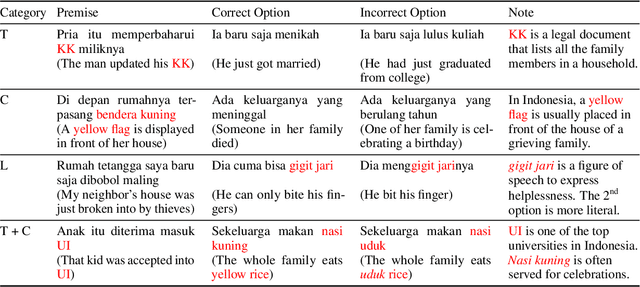
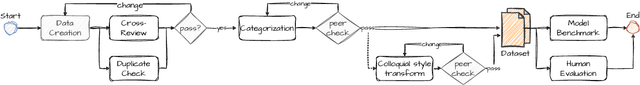
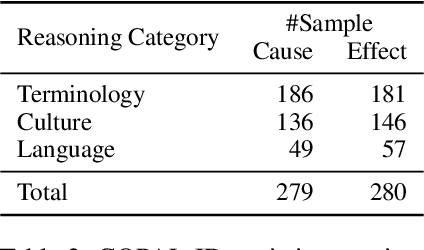
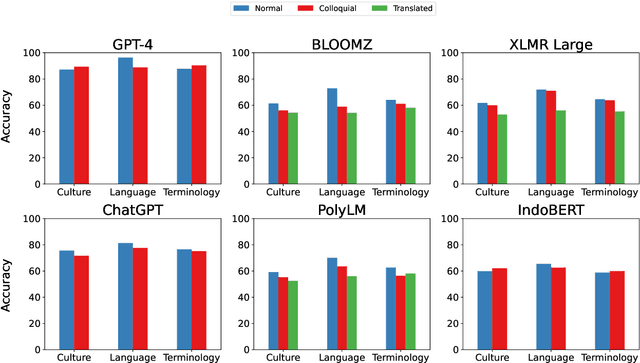
Abstract:We present publicly available COPAL-ID, a novel Indonesian language common sense reasoning dataset. Unlike the previous Indonesian COPA dataset (XCOPA-ID), COPAL-ID incorporates Indonesian local and cultural nuances, and therefore, provides a more natural portrayal of day-to-day causal reasoning within the Indonesian cultural sphere. Professionally written by natives from scratch, COPAL-ID is more fluent and free from awkward phrases, unlike the translated XCOPA-ID. In addition, we present COPAL-ID in both standard Indonesian and in Jakartan Indonesian--a dialect commonly used in daily conversation. COPAL-ID poses a greater challenge for existing open-sourced and closed state-of-the-art multilingual language models, yet is trivially easy for humans. Our findings suggest that even the current best open-source, multilingual model struggles to perform well, achieving 65.47% accuracy on COPAL-ID, significantly lower than on the culturally-devoid XCOPA-ID (79.40%). Despite GPT-4's impressive score, it suffers the same performance degradation compared to its XCOPA-ID score, and it still falls short of human performance. This shows that these language models are still way behind in comprehending the local nuances of Indonesian.
On "Scientific Debt" in NLP: A Case for More Rigour in Language Model Pre-Training Research
Jun 05, 2023Abstract:This evidence-based position paper critiques current research practices within the language model pre-training literature. Despite rapid recent progress afforded by increasingly better pre-trained language models (PLMs), current PLM research practices often conflate different possible sources of model improvement, without conducting proper ablation studies and principled comparisons between different models under comparable conditions. These practices (i) leave us ill-equipped to understand which pre-training approaches should be used under what circumstances; (ii) impede reproducibility and credit assignment; and (iii) render it difficult to understand: "How exactly does each factor contribute to the progress that we have today?" We provide a case in point by revisiting the success of BERT over its baselines, ELMo and GPT-1, and demonstrate how -- under comparable conditions where the baselines are tuned to a similar extent -- these baselines (and even-simpler variants thereof) can, in fact, achieve competitive or better performance than BERT. These findings demonstrate how disentangling different factors of model improvements can lead to valuable new insights. We conclude with recommendations for how to encourage and incentivize this line of work, and accelerate progress towards a better and more systematic understanding of what factors drive the progress of our foundation models today.
NusaCrowd: Open Source Initiative for Indonesian NLP Resources
Dec 20, 2022Abstract:We present NusaCrowd, a collaborative initiative to collect and unite existing resources for Indonesian languages, including opening access to previously non-public resources. Through this initiative, we have has brought together 137 datasets and 117 standardized data loaders. The quality of the datasets has been assessed manually and automatically, and their effectiveness has been demonstrated in multiple experiments. NusaCrowd's data collection enables the creation of the first zero-shot benchmarks for natural language understanding and generation in Indonesian and its local languages. Furthermore, NusaCrowd brings the creation of the first multilingual automatic speech recognition benchmark in Indonesian and its local languages. Our work is intended to help advance natural language processing research in under-represented languages.
Which Student is Best? A Comprehensive Knowledge Distillation Exam for Task-Specific BERT Models
Jan 03, 2022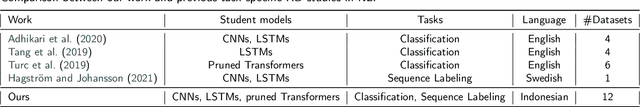
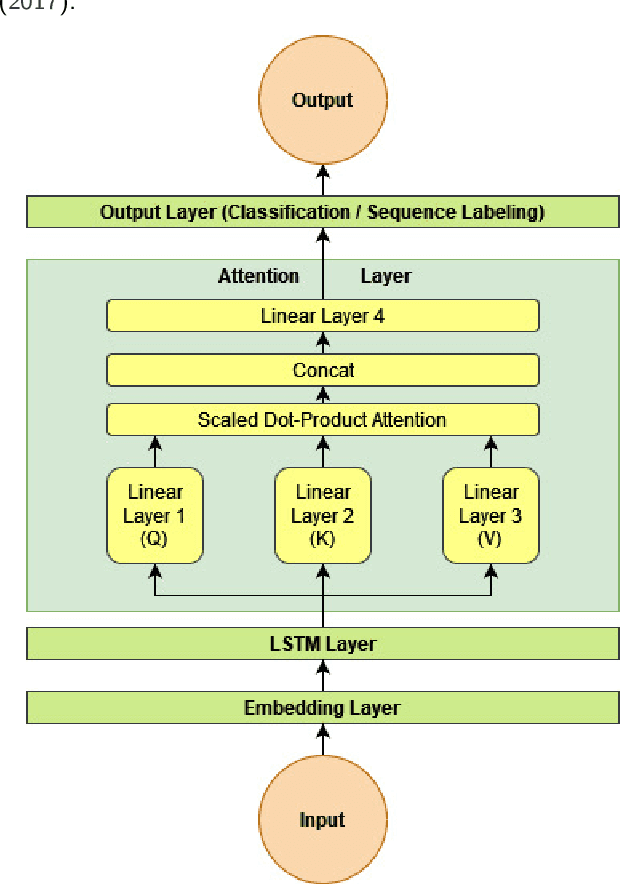
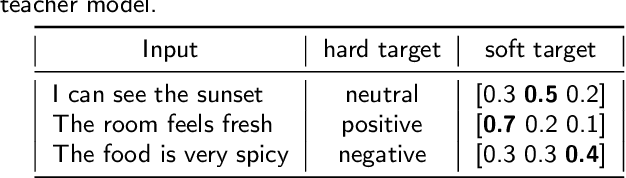
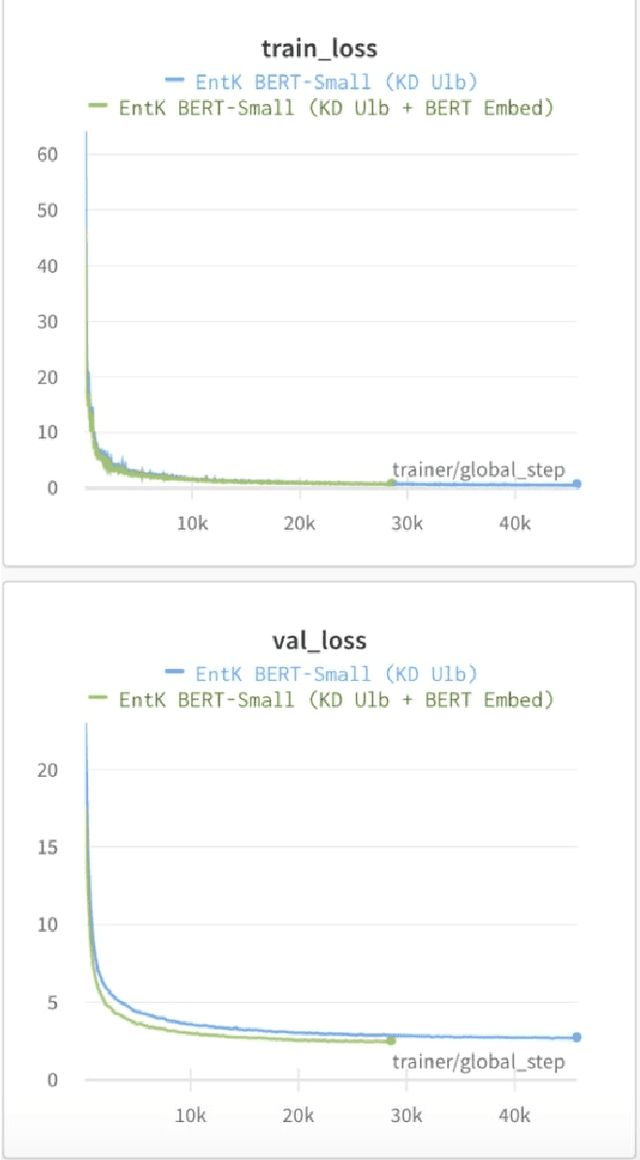
Abstract:We perform knowledge distillation (KD) benchmark from task-specific BERT-base teacher models to various student models: BiLSTM, CNN, BERT-Tiny, BERT-Mini, and BERT-Small. Our experiment involves 12 datasets grouped in two tasks: text classification and sequence labeling in the Indonesian language. We also compare various aspects of distillations including the usage of word embeddings and unlabeled data augmentation. Our experiments show that, despite the rising popularity of Transformer-based models, using BiLSTM and CNN student models provide the best trade-off between performance and computational resource (CPU, RAM, and storage) compared to pruned BERT models. We further propose some quick wins on performing KD to produce small NLP models via efficient KD training mechanisms involving simple choices of loss functions, word embeddings, and unlabeled data preparation.
No Budget? Don't Flex! Cost Consideration when Planning to Adopt NLP for Your Business
Dec 16, 2020
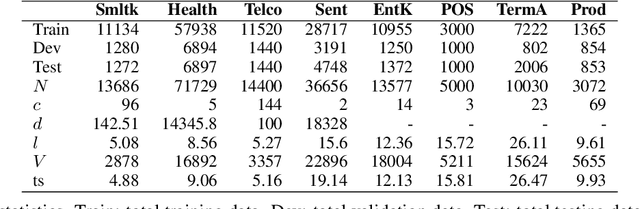
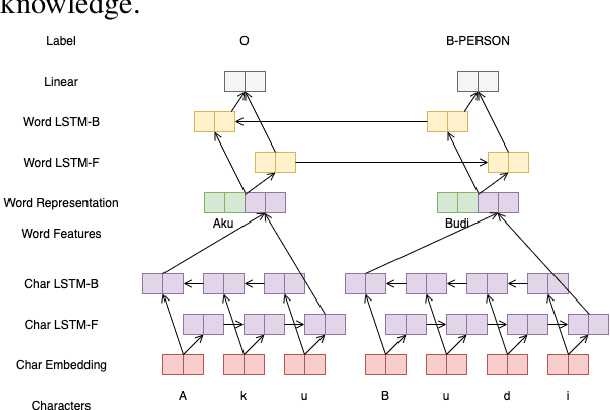
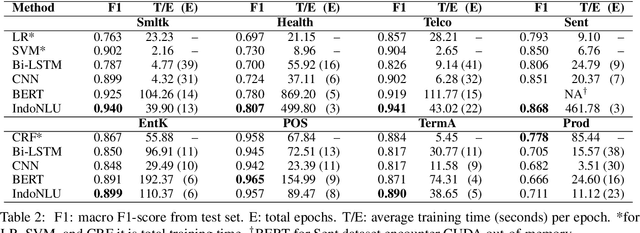
Abstract:Recent advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP) have largely pushed deep transformer-based models as the go-to state-of-the-art technique without much regard to the production and utilization cost. Companies planning to adopt these methods into their business face difficulties because of the lack of machine and human resources to build them. In this work, we compare both the performance and the cost of classical learning algorithms to the latest ones in common sequence and text labeling tasks. We find that classical models often perform on par with deep neural ones despite the lower cost. We argue that under many circumstances the smaller and lighter models fit better for AI-pivoting businesses and that we call for more research into low-cost models, especially for under-resourced languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge