Luiz A. Zanlorensi
An on-production high-resolution longitudinal neonatal fingerprint database in Brazil
Apr 27, 2025
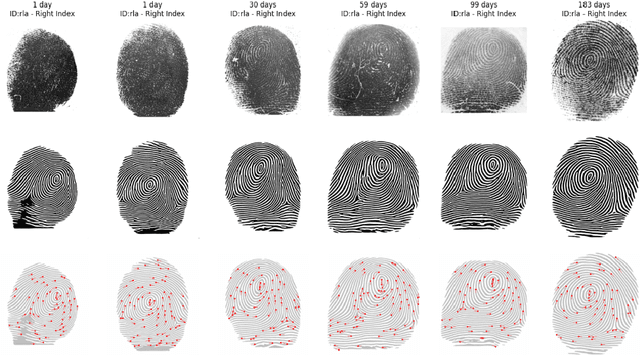
Abstract:The neonatal period is critical for survival, requiring accurate and early identification to enable timely interventions such as vaccinations, HIV treatment, and nutrition programs. Biometric solutions offer potential for child protection by helping to prevent baby swaps, locate missing children, and support national identity systems. However, developing effective biometric identification systems for newborns remains a major challenge due to the physiological variability caused by finger growth, weight changes, and skin texture alterations during early development. Current literature has attempted to address these issues by applying scaling factors to emulate growth-induced distortions in minutiae maps, but such approaches fail to capture the complex and non-linear growth patterns of infants. A key barrier to progress in this domain is the lack of comprehensive, longitudinal biometric datasets capturing the evolution of neonatal fingerprints over time. This study addresses this gap by focusing on designing and developing a high-quality biometric database of neonatal fingerprints, acquired at multiple early life stages. The dataset is intended to support the training and evaluation of machine learning models aimed at emulating the effects of growth on biometric features. We hypothesize that such a dataset will enable the development of more robust and accurate Deep Learning-based models, capable of predicting changes in the minutiae map with higher fidelity than conventional scaling-based methods. Ultimately, this effort lays the groundwork for more reliable biometric identification systems tailored to the unique developmental trajectory of newborns.
Leveraging Model Fusion for Improved License Plate Recognition
Sep 08, 2023Abstract:License Plate Recognition (LPR) plays a critical role in various applications, such as toll collection, parking management, and traffic law enforcement. Although LPR has witnessed significant advancements through the development of deep learning, there has been a noticeable lack of studies exploring the potential improvements in results by fusing the outputs from multiple recognition models. This research aims to fill this gap by investigating the combination of up to 12 different models using straightforward approaches, such as selecting the most confident prediction or employing majority vote-based strategies. Our experiments encompass a wide range of datasets, revealing substantial benefits of fusion approaches in both intra- and cross-dataset setups. Essentially, fusing multiple models reduces considerably the likelihood of obtaining subpar performance on a particular dataset/scenario. We also found that combining models based on their speed is an appealing approach. Specifically, for applications where the recognition task can tolerate some additional time, though not excessively, an effective strategy is to combine 4-6 models. These models may not be the most accurate individually, but their fusion strikes an optimal balance between accuracy and speed.
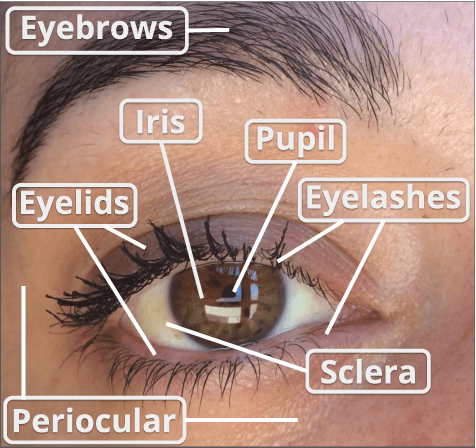
ORCNet: A context-based network to simultaneously segment the ocular region components
Apr 15, 2022

Abstract:Accurate extraction of the Region of Interest is critical for successful ocular region-based biometrics. In this direction, we propose a new context-based segmentation approach, entitled Ocular Region Context Network (ORCNet), introducing a specific loss function, i.e., he Punish Context Loss (PC-Loss). The PC-Loss punishes the segmentation losses of a network by using a percentage difference value between the ground truth and the segmented masks. We obtain the percentage difference by taking into account Biederman's semantic relationship concepts, in which we use three contexts (semantic, spatial, and scale) to evaluate the relationships of the objects in an image. Our proposal achieved promising results in the evaluated scenarios: iris, sclera, and ALL (iris + sclera) segmentations, utperforming the literature baseline techniques. The ORCNet with ResNet-152 outperforms the best baseline (EncNet with ResNet-152) on average by 2.27%, 28.26% and 6.43% in terms of F-Score, Error Rate and Intersection Over Union, respectively. We also provide (for research purposes) 3,191 manually labeled masks for the MICHE-I database, as another contribution of our work.
UFPR-Periocular: A Periocular Dataset Collected by Mobile Devices in Unconstrained Scenarios
Nov 24, 2020



Abstract:Recently, ocular biometrics in unconstrained environments using images obtained at visible wavelength have gained the researchers' attention, especially with images captured by mobile devices. Periocular recognition has been demonstrated to be an alternative when the iris trait is not available due to occlusions or low image resolution. However, the periocular trait does not have the high uniqueness presented in the iris trait. Thus, the use of datasets containing many subjects is essential to assess biometric systems' capacity to extract discriminating information from the periocular region. Also, to address the within-class variability caused by lighting and attributes in the periocular region, it is of paramount importance to use datasets with images of the same subject captured in distinct sessions. As the datasets available in the literature do not present all these factors, in this work, we present a new periocular dataset containing samples from 1,122 subjects, acquired in 3 sessions by 196 different mobile devices. The images were captured under unconstrained environments with just a single instruction to the participants: to place their eyes on a region of interest. We also performed an extensive benchmark with several Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures and models that have been employed in state-of-the-art approaches based on Multi-class Classification, Multitask Learning, Pairwise Filters Network, and Siamese Network. The results achieved in the closed- and open-world protocol, considering the identification and verification tasks, show that this area still needs research and development.
Towards image-based automatic meter reading in unconstrained scenarios: A robust and efficient approach
Sep 21, 2020



Abstract:Existing approaches for image-based Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) have been evaluated on images captured in well-controlled scenarios. However, real-world meter reading presents unconstrained scenarios that are way more challenging due to dirt, various lighting conditions, scale variations, in-plane and out-of-plane rotations, among other factors. In this work, we present an end-to-end approach for AMR focusing on unconstrained scenarios. Our main contribution is the insertion of a new stage in the AMR pipeline, called corner detection and counter classification, which enables the counter region to be rectified -- as well as the rejection of illegible/faulty meters -- prior to the recognition stage. We also introduce a publicly available dataset, called Copel-AMR, that contains 12,500 meter images acquired in the field by the service company's employees themselves, including 2,500 images of faulty meters or cases where the reading is illegible due to occlusions. Experimental evaluation demonstrates that the proposed system outperforms six baselines in terms of recognition rate while still being quite efficient. Moreover, as very few reading errors are tolerated in real-world applications, we show that our AMR system achieves impressive recognition rates (i.e., > 99%) when rejecting readings made with lower confidence values.
Unconstrained Periocular Recognition: Using Generative Deep Learning Frameworks for Attribute Normalization
Feb 10, 2020



Abstract:Ocular biometric systems working in unconstrained environments usually face the problem of small within-class compactness caused by the multiple factors that jointly degrade the quality of the obtained data. In this work, we propose an attribute normalization strategy based on deep learning generative frameworks, that reduces the variability of the samples used in pairwise comparisons, without reducing their discriminability. The proposed method can be seen as a preprocessing step that contributes for data regularization and improves the recognition accuracy, being fully agnostic to the recognition strategy used. As proof of concept, we consider the "eyeglasses" and "gaze" factors, comparing the levels of performance of five different recognition methods with/without using the proposed normalization strategy. Also, we introduce a new dataset for unconstrained periocular recognition, composed of images acquired by mobile devices, particularly suited to perceive the impact of "wearing eyeglasses" in recognition effectiveness. Our experiments were performed in two different datasets, and support the usefulness of our attribute normalization scheme to improve the recognition performance.
Ocular Recognition Databases and Competitions: A Survey
Nov 21, 2019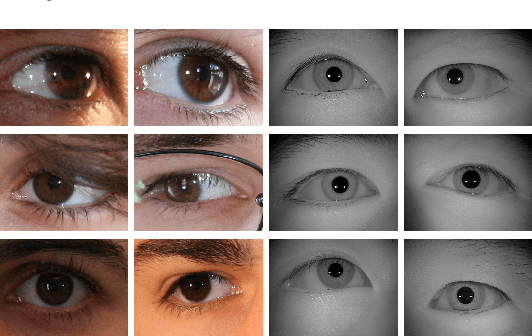
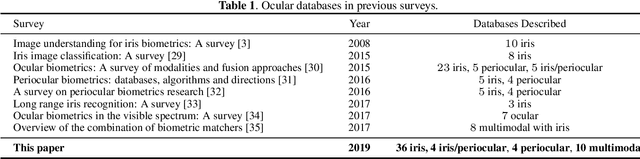
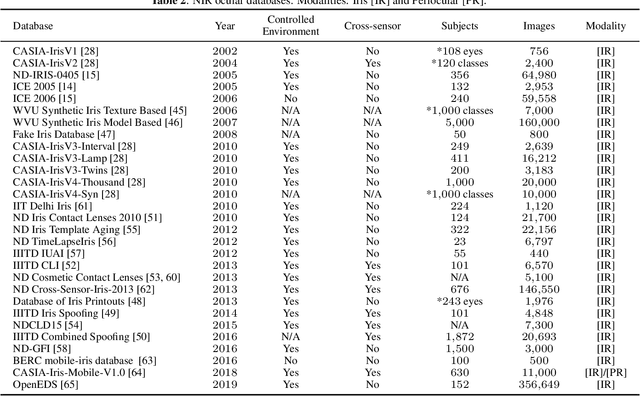
Abstract:The use of the iris and periocular region as biometric traits has been extensively investigated, mainly due to the singularity of the iris features and the use of the periocular region when the image resolution is not sufficient to extract iris information. In addition to providing information about an individual's identity, features extracted from these traits can also be explored to obtain other information such as the individual's gender, the influence of drug use, the use of contact lenses, spoofing, among others. This work presents a survey of the databases created for ocular recognition, detailing their protocols and how their images were acquired. We also describe and discuss the most popular ocular recognition competitions (contests), highlighting the submitted algorithms that achieved the best results using only iris trait and also fusing iris and periocular region information. Finally, we describe some relevant works applying deep learning techniques to ocular recognition and point out new challenges and future directions. Considering that there are a large number of ocular databases, and each one is usually designed for a specific problem, we believe this survey can provide a broad overview of the challenges in ocular biometrics.
Deep Representations for Cross-spectral Ocular Biometrics
Nov 21, 2019



Abstract:One of the major challenges in ocular biometrics is the cross-spectral scenario, i.e., how to match images acquired in different wavelengths (typically visible (VIS) against near-infrared (NIR)). This article designs and extensively evaluates cross-spectral ocular verification methods, for both the closed and open-world settings, using well known deep learning representations based on the iris and periocular regions. Using as inputs the bounding boxes of non-normalized iris/periocular regions, we fine-tune Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) models (based either on VGG16 or ResNet-50 architectures), originally trained for face recognition. Based on the experiments carried out in two publicly available cross-spectral ocular databases, we report results for intra-spectral and cross-spectral scenarios, with the best performance being observed when fusing ResNet-50 deep representations from both the periocular and iris regions. When compared to the state-of-the-art, we observed that the proposed solution consistently reduces the Equal Error Rate(EER) values by 90% / 93% / 96% and 61% / 77% / 83% on the cross-spectral scenario and in the PolyU Bi-spectral and Cross-eye-cross-spectral datasets. Lastly, we evaluate the effect that the "deepness" factor of feature representations has in recognition effectiveness, and - based on a subjective analysis of the most problematic pairwise comparisons - we point out further directions for this field of research.
An Efficient and Layout-Independent Automatic License Plate Recognition System Based on the YOLO detector
Sep 05, 2019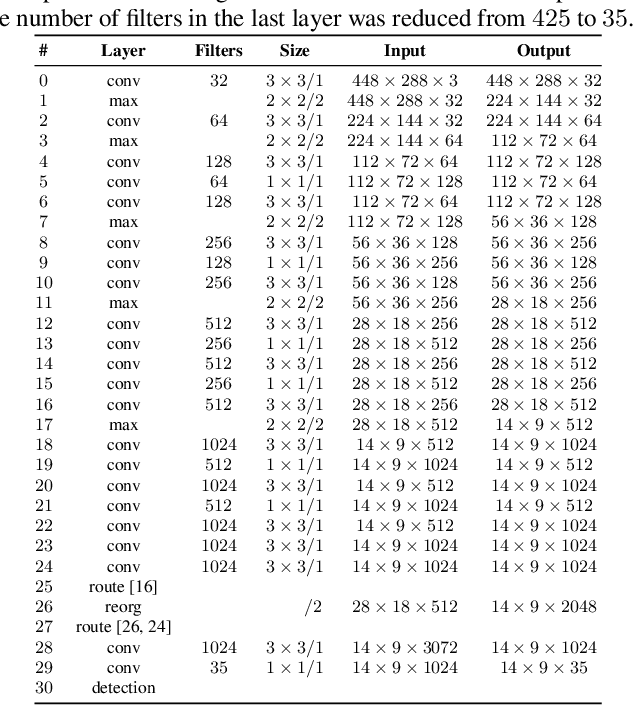
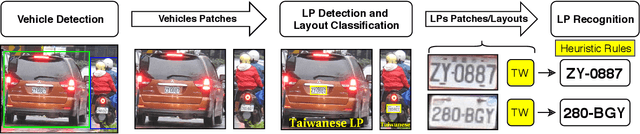
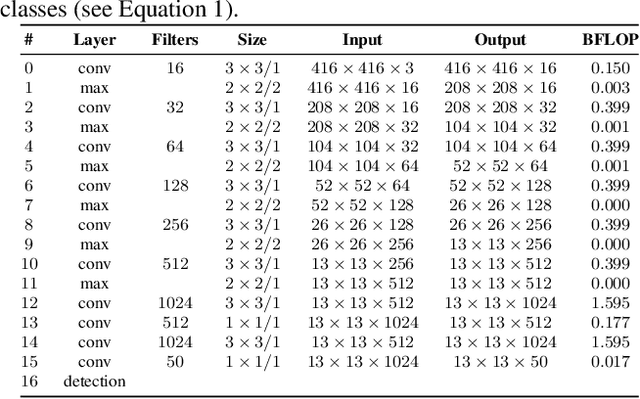

Abstract:In this paper, we present an efficient and layout-independent Automatic License Plate Recognition (ALPR) system based on the state-of-the-art YOLO object detector that contains a unified approach for license plate (LP) detection and layout classification to improve the recognition results using post-processing rules. The system is conceived by evaluating and optimizing different models with various modifications, aiming at achieving the best speed/accuracy trade-off at each stage. The networks are trained using images from several datasets, with the addition of various data augmentation techniques, so that they are robust under different conditions. The proposed system achieved an average end-to-end recognition rate of 96.8% across eight public datasets (from five different regions) used in the experiments, outperforming both previous works and commercial systems in the ChineseLP, OpenALPR-EU, SSIG-SegPlate and UFPR-ALPR datasets. In the other datasets, the proposed approach achieved competitive results to those attained by the baselines. Our system also achieved impressive frames per second (FPS) rates on a high-end GPU, being able to perform in real time even when there are four vehicles in the scene. An additional contribution is that we manually labeled 38,334 bounding boxes on 6,237 images from public datasets and made the annotations publicly available to the research community.
Simultaneous Iris and Periocular Region Detection Using Coarse Annotations
Jul 31, 2019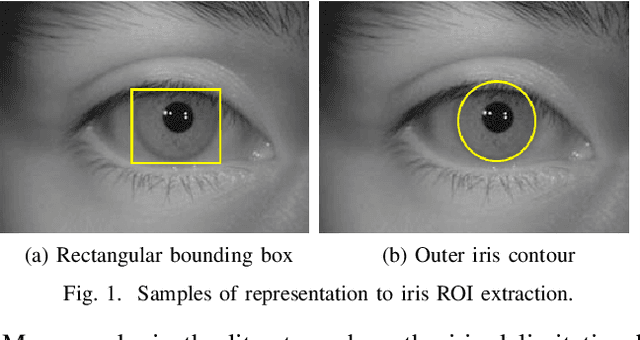
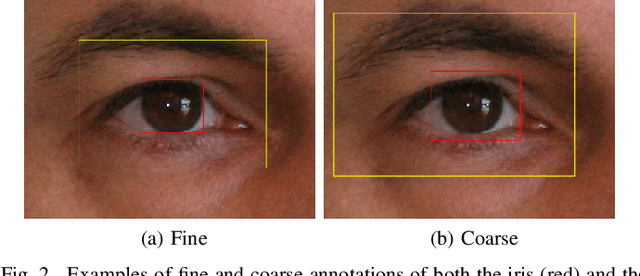
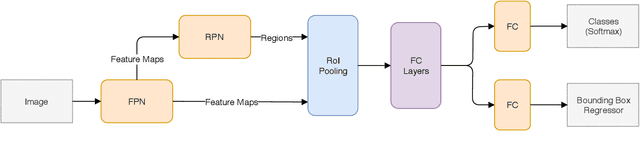
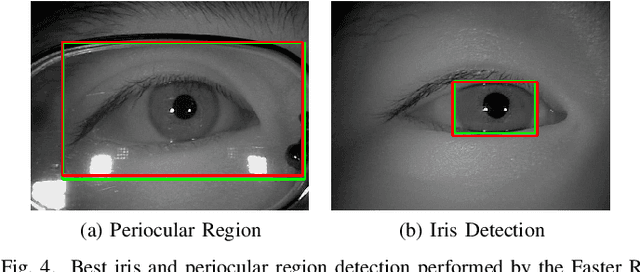
Abstract:In this work, we propose to detect the iris and periocular regions simultaneously using coarse annotations and two well-known object detectors: YOLOv2 and Faster R-CNN. We believe coarse annotations can be used in recognition systems based on the iris and periocular regions, given the much smaller engineering effort required to manually annotate the training images. We manually made coarse annotations of the iris and periocular regions (122K images from the visible (VIS) spectrum and 38K images from the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum). The iris annotations in the NIR databases were generated semi-automatically by first applying an iris segmentation CNN and then performing a manual inspection. These annotations were made for 11 well-known public databases (3 NIR and 8 VIS) designed for the iris-based recognition problem and are publicly available to the research community. Experimenting our proposal on these databases, we highlight two results. First, the Faster R-CNN + Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) model reported an Intersection over Union (IoU) higher than YOLOv2 (91.86% vs 85.30%). Second, the detection of the iris and periocular regions being performed simultaneously is as accurate as performed separately, but with a lower computational cost, i.e., two tasks were carried out at the cost of one.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge