Hugo Proença
Rectifying Geometry-Induced Similarity Distortions for Real-World Aerial-Ground Person Re-Identification
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Aerial-ground person re-identification (AG-ReID) is fundamentally challenged by extreme viewpoint and distance discrepancies between aerial and ground cameras, which induce severe geometric distortions and invalidate the assumption of a shared similarity space across views. Existing methods primarily rely on geometry-aware feature learning or appearance-conditioned prompting, while implicitly assuming that the geometry-invariant dot-product similarity used in attention mechanisms remains reliable under large viewpoint and scale variations. We argue that this assumption does not hold. Extreme camera geometry systematically distorts the query-key similarity space and degrades attention-based matching, even when feature representations are partially aligned. To address this issue, we introduce Geometry-Induced Query-Key Transformation (GIQT), a lightweight low-rank module that explicitly rectifies the similarity space by conditioning query-key interactions on camera geometry. Rather than modifying feature representations or the attention formulation itself, GIQT adapts the similarity computation to compensate for dominant geometry-induced anisotropic distortions. Building on this local similarity rectification, we further incorporate a geometry-conditioned prompt generation mechanism that provides global, view-adaptive representation priors derived directly from camera geometry. Experiments on four aerial-ground person re-identification benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed framework consistently improves robustness under extreme and previously unseen geometric conditions, while introducing minimal computational overhead compared to state-of-the-art methods.
FD-MAD: Frequency-Domain Residual Analysis for Face Morphing Attack Detection
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Face morphing attacks present a significant threat to face recognition systems used in electronic identity enrolment and border control, particularly in single-image morphing attack detection (S-MAD) scenarios where no trusted reference is available. In spite of the vast amount of research on this problem, morph detection systems struggle in cross-dataset scenarios. To address this problem, we introduce a region-aware frequency-based morph detection strategy that drastically improves over strong baseline methods in challenging cross-dataset and cross-morph settings using a lightweight approach. Having observed the separability of bona fide and morph samples in the frequency domain of different facial parts, our approach 1) introduces the concept of residual frequency domain, where the frequency of the signal is decoupled from the natural spectral decay to easily discriminate between morph and bona fide data; 2) additionally, we reason in a global and local manner by combining the evidence from different facial regions in a Markov Random Field, which infers a globally consistent decision. The proposed method, trained exclusively on the synthetic morphing attack detection development dataset (SMDD), is evaluated in challenging cross-dataset and cross-morph settings on FRLL-Morph and MAD22 sets. Our approach achieves an average equal error rate (EER) of 1.85\% on FRLL-Morph and ranks second on MAD22 with an average EER of 6.12\%, while also obtaining a good bona fide presentation classification error rate (BPCER) at a low attack presentation classification error rate (APCER) using only spectral features. These findings indicate that Fourier-domain residual modeling with structured regional fusion offers a competitive alternative to deep S-MAD architectures.
SortWaste: A Densely Annotated Dataset for Object Detection in Industrial Waste Sorting
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:The increasing production of waste, driven by population growth, has created challenges in managing and recycling materials effectively. Manual waste sorting is a common practice; however, it remains inefficient for handling large-scale waste streams and presents health risks for workers. On the other hand, existing automated sorting approaches still struggle with the high variability, clutter, and visual complexity of real-world waste streams. The lack of real-world datasets for waste sorting is a major reason automated systems for this problem are underdeveloped. Accordingly, we introduce SortWaste, a densely annotated object detection dataset collected from a Material Recovery Facility. Additionally, we contribute to standardizing waste detection in sorting lines by proposing ClutterScore, an objective metric that gauges the scene's hardness level using a set of proxies that affect visual complexity (e.g., object count, class and size entropy, and spatial overlap). In addition to these contributions, we provide an extensive benchmark of state-of-the-art object detection models, detailing their results with respect to the hardness level assessed by the proposed metric. Despite achieving promising results (mAP of 59.7% in the plastic-only detection task), performance significantly decreases in highly cluttered scenes. This highlights the need for novel and more challenging datasets on the topic.
VReID-XFD: Video-based Person Re-identification at Extreme Far Distance Challenge Results
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Person re-identification (ReID) across aerial and ground views at extreme far distances introduces a distinct operating regime where severe resolution degradation, extreme viewpoint changes, unstable motion cues, and clothing variation jointly undermine the appearance-based assumptions of existing ReID systems. To study this regime, we introduce VReID-XFD, a video-based benchmark and community challenge for extreme far-distance (XFD) aerial-to-ground person re-identification. VReID-XFD is derived from the DetReIDX dataset and comprises 371 identities, 11,288 tracklets, and 11.75 million frames, captured across altitudes from 5.8 m to 120 m, viewing angles from oblique (30 degrees) to nadir (90 degrees), and horizontal distances up to 120 m. The benchmark supports aerial-to-aerial, aerial-to-ground, and ground-to-aerial evaluation under strict identity-disjoint splits, with rich physical metadata. The VReID-XFD-25 Challenge attracted 10 teams with hundreds of submissions. Systematic analysis reveals monotonic performance degradation with altitude and distance, a universal disadvantage of nadir views, and a trade-off between peak performance and robustness. Even the best-performing SAS-PReID method achieves only 43.93 percent mAP in the aerial-to-ground setting. The dataset, annotations, and official evaluation protocols are publicly available at https://www.it.ubi.pt/DetReIDX/ .
ZQBA: Zero Query Black-box Adversarial Attack
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Current black-box adversarial attacks either require multiple queries or diffusion models to produce adversarial samples that can impair the target model performance. However, these methods require training a surrogate loss or diffusion models to produce adversarial samples, which limits their applicability in real-world settings. Thus, we propose a Zero Query Black-box Adversarial (ZQBA) attack that exploits the representations of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) to fool other networks. Instead of requiring thousands of queries to produce deceiving adversarial samples, we use the feature maps obtained from a DNN and add them to clean images to impair the classification of a target model. The results suggest that ZQBA can transfer the adversarial samples to different models and across various datasets, namely CIFAR and Tiny ImageNet. The experiments also show that ZQBA is more effective than state-of-the-art black-box attacks with a single query, while maintaining the imperceptibility of perturbations, evaluated both quantitatively (SSIM) and qualitatively, emphasizing the vulnerabilities of employing DNNs in real-world contexts. All the source code is available at https://github.com/Joana-Cabral/ZQBA.
Causality and "In-the-Wild" Video-Based Person Re-ID: A Survey
May 28, 2025
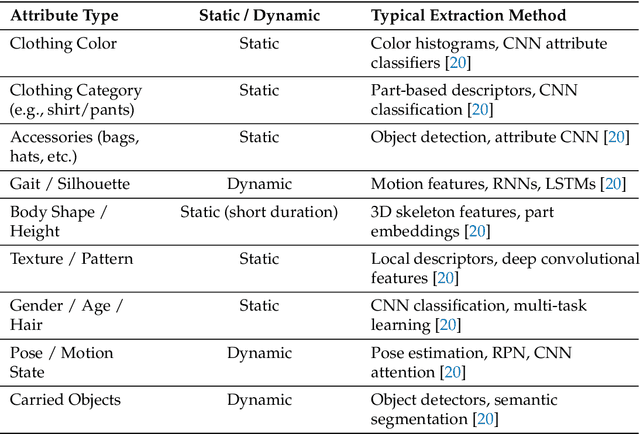
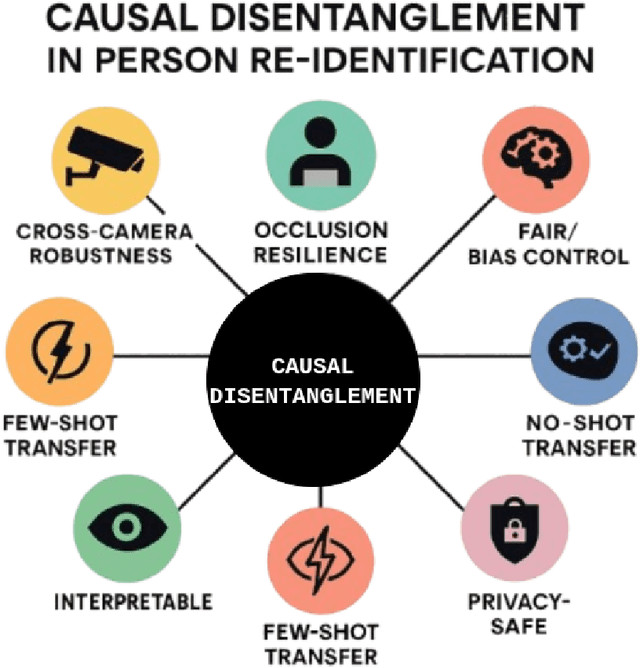
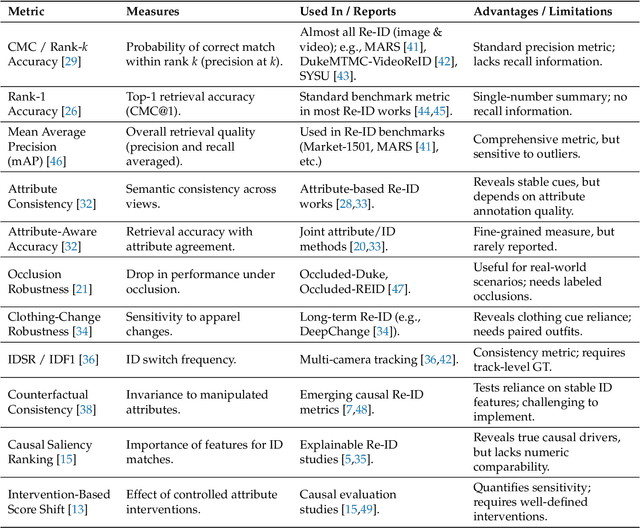
Abstract:Video-based person re-identification (Re-ID) remains brittle in real-world deployments despite impressive benchmark performance. Most existing models rely on superficial correlations such as clothing, background, or lighting that fail to generalize across domains, viewpoints, and temporal variations. This survey examines the emerging role of causal reasoning as a principled alternative to traditional correlation-based approaches in video-based Re-ID. We provide a structured and critical analysis of methods that leverage structural causal models, interventions, and counterfactual reasoning to isolate identity-specific features from confounding factors. The survey is organized around a novel taxonomy of causal Re-ID methods that spans generative disentanglement, domain-invariant modeling, and causal transformers. We review current evaluation metrics and introduce causal-specific robustness measures. In addition, we assess practical challenges of scalability, fairness, interpretability, and privacy that must be addressed for real-world adoption. Finally, we identify open problems and outline future research directions that integrate causal modeling with efficient architectures and self-supervised learning. This survey aims to establish a coherent foundation for causal video-based person Re-ID and to catalyze the next phase of research in this rapidly evolving domain.
DetReIDX: A Stress-Test Dataset for Real-World UAV-Based Person Recognition
May 07, 2025Abstract:Person reidentification (ReID) technology has been considered to perform relatively well under controlled, ground-level conditions, but it breaks down when deployed in challenging real-world settings. Evidently, this is due to extreme data variability factors such as resolution, viewpoint changes, scale variations, occlusions, and appearance shifts from clothing or session drifts. Moreover, the publicly available data sets do not realistically incorporate such kinds and magnitudes of variability, which limits the progress of this technology. This paper introduces DetReIDX, a large-scale aerial-ground person dataset, that was explicitly designed as a stress test to ReID under real-world conditions. DetReIDX is a multi-session set that includes over 13 million bounding boxes from 509 identities, collected in seven university campuses from three continents, with drone altitudes between 5.8 and 120 meters. More important, as a key novelty, DetReIDX subjects were recorded in (at least) two sessions on different days, with changes in clothing, daylight and location, making it suitable to actually evaluate long-term person ReID. Plus, data were annotated from 16 soft biometric attributes and multitask labels for detection, tracking, ReID, and action recognition. In order to provide empirical evidence of DetReIDX usefulness, we considered the specific tasks of human detection and ReID, where SOTA methods catastrophically degrade performance (up to 80% in detection accuracy and over 70% in Rank-1 ReID) when exposed to DetReIDXs conditions. The dataset, annotations, and official evaluation protocols are publicly available at https://www.it.ubi.pt/DetReIDX/
LISArD: Learning Image Similarity to Defend Against Gray-box Adversarial Attacks
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:State-of-the-art defense mechanisms are typically evaluated in the context of white-box attacks, which is not realistic, as it assumes the attacker can access the gradients of the target network. To protect against this scenario, Adversarial Training (AT) and Adversarial Distillation (AD) include adversarial examples during the training phase, and Adversarial Purification uses a generative model to reconstruct all the images given to the classifier. This paper considers an even more realistic evaluation scenario: gray-box attacks, which assume that the attacker knows the architecture and the dataset used to train the target network, but cannot access its gradients. We provide empirical evidence that models are vulnerable to gray-box attacks and propose LISArD, a defense mechanism that does not increase computational and temporal costs but provides robustness against gray-box and white-box attacks without including AT. Our method approximates a cross-correlation matrix, created with the embeddings of perturbed and clean images, to a diagonal matrix while simultaneously conducting classification learning. Our results show that LISArD can effectively protect against gray-box attacks, can be used in multiple architectures, and carries over its resilience to the white-box scenario. Also, state-of-the-art AD models underperform greatly when removing AT and/or moving to gray-box settings, highlighting the lack of robustness from existing approaches to perform in various conditions (aside from white-box settings). All the source code is available at https://github.com/Joana-Cabral/LISArD.
Human Re-ID Meets LVLMs: What can we expect?
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have been regarded as a breakthrough advance in an astoundingly variety of tasks, from content generation to virtual assistants and multimodal search or retrieval. However, for many of these applications, the performance of these methods has been widely criticized, particularly when compared with state-of-the-art methods and technologies in each specific domain. In this work, we compare the performance of the leading large vision-language models in the human re-identification task, using as baseline the performance attained by state-of-the-art AI models specifically designed for this problem. We compare the results due to ChatGPT-4o, Gemini-2.0-Flash, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Qwen-VL-Max to a baseline ReID PersonViT model, using the well-known Market1501 dataset. Our evaluation pipeline includes the dataset curation, prompt engineering, and metric selection to assess the models' performance. Results are analyzed from many different perspectives: similarity scores, classification accuracy, and classification metrics, including precision, recall, F1 score, and area under curve (AUC). Our results confirm the strengths of LVLMs, but also their severe limitations that often lead to catastrophic answers and should be the scope of further research. As a concluding remark, we speculate about some further research that should fuse traditional and LVLMs to combine the strengths from both families of techniques and achieve solid improvements in performance.
ASDnB: Merging Face with Body Cues For Robust Active Speaker Detection
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:State-of-the-art Active Speaker Detection (ASD) approaches mainly use audio and facial features as input. However, the main hypothesis in this paper is that body dynamics is also highly correlated to "speaking" (and "listening") actions and should be particularly useful in wild conditions (e.g., surveillance settings), where face cannot be reliably accessed. We propose ASDnB, a model that singularly integrates face with body information by merging the inputs at different steps of feature extraction. Our approach splits 3D convolution into 2D and 1D to reduce computation cost without loss of performance, and is trained with adaptive weight feature importance for improved complement of face with body data. Our experiments show that ASDnB achieves state-of-the-art results in the benchmark dataset (AVA-ActiveSpeaker), in the challenging data of WASD, and in cross-domain settings using Columbia. This way, ASDnB can perform in multiple settings, which is positively regarded as a strong baseline for robust ASD models (code available at https://github.com/Tiago-Roxo/ASDnB).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge