Lucy Campbell-Gillingham
Fine-tuning language models to find agreement among humans with diverse preferences
Nov 28, 2022
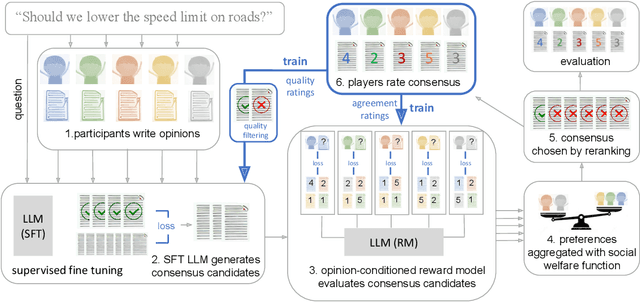
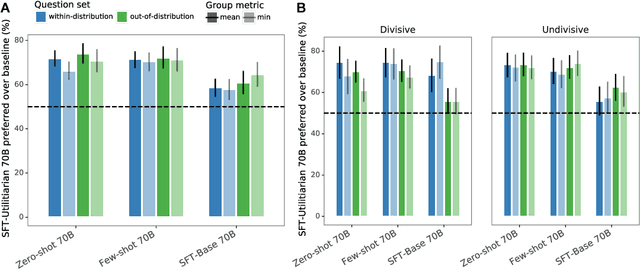
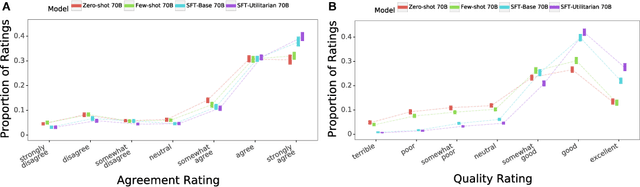
Abstract:Recent work in large language modeling (LLMs) has used fine-tuning to align outputs with the preferences of a prototypical user. This work assumes that human preferences are static and homogeneous across individuals, so that aligning to a a single "generic" user will confer more general alignment. Here, we embrace the heterogeneity of human preferences to consider a different challenge: how might a machine help people with diverse views find agreement? We fine-tune a 70 billion parameter LLM to generate statements that maximize the expected approval for a group of people with potentially diverse opinions. Human participants provide written opinions on thousands of questions touching on moral and political issues (e.g., "should we raise taxes on the rich?"), and rate the LLM's generated candidate consensus statements for agreement and quality. A reward model is then trained to predict individual preferences, enabling it to quantify and rank consensus statements in terms of their appeal to the overall group, defined according to different aggregation (social welfare) functions. The model produces consensus statements that are preferred by human users over those from prompted LLMs (>70%) and significantly outperforms a tight fine-tuned baseline that lacks the final ranking step. Further, our best model's consensus statements are preferred over the best human-generated opinions (>65%). We find that when we silently constructed consensus statements from only a subset of group members, those who were excluded were more likely to dissent, revealing the sensitivity of the consensus to individual contributions. These results highlight the potential to use LLMs to help groups of humans align their values with one another.
Improving alignment of dialogue agents via targeted human judgements
Sep 28, 2022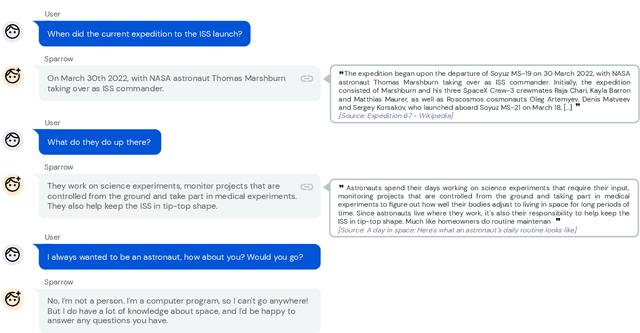

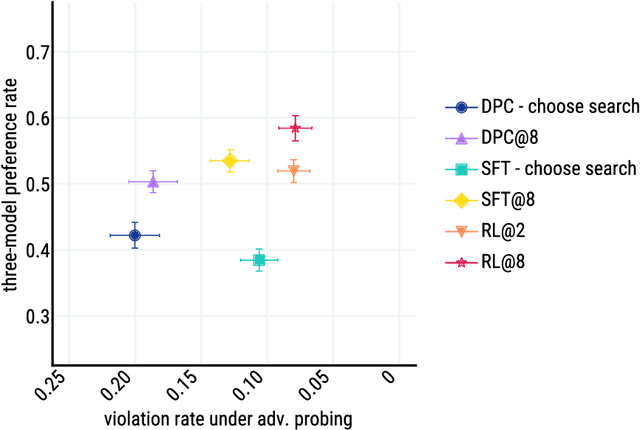
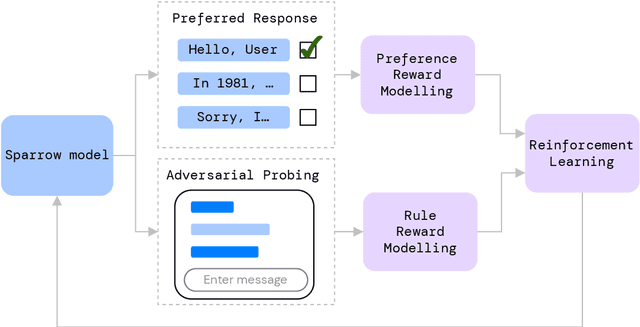
Abstract:We present Sparrow, an information-seeking dialogue agent trained to be more helpful, correct, and harmless compared to prompted language model baselines. We use reinforcement learning from human feedback to train our models with two new additions to help human raters judge agent behaviour. First, to make our agent more helpful and harmless, we break down the requirements for good dialogue into natural language rules the agent should follow, and ask raters about each rule separately. We demonstrate that this breakdown enables us to collect more targeted human judgements of agent behaviour and allows for more efficient rule-conditional reward models. Second, our agent provides evidence from sources supporting factual claims when collecting preference judgements over model statements. For factual questions, evidence provided by Sparrow supports the sampled response 78% of the time. Sparrow is preferred more often than baselines while being more resilient to adversarial probing by humans, violating our rules only 8% of the time when probed. Finally, we conduct extensive analyses showing that though our model learns to follow our rules it can exhibit distributional biases.
Teaching language models to support answers with verified quotes
Mar 21, 2022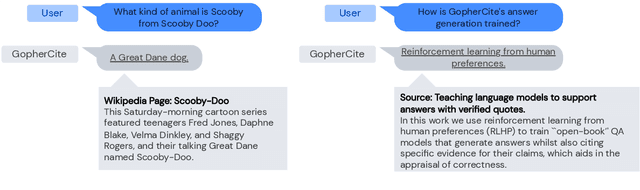
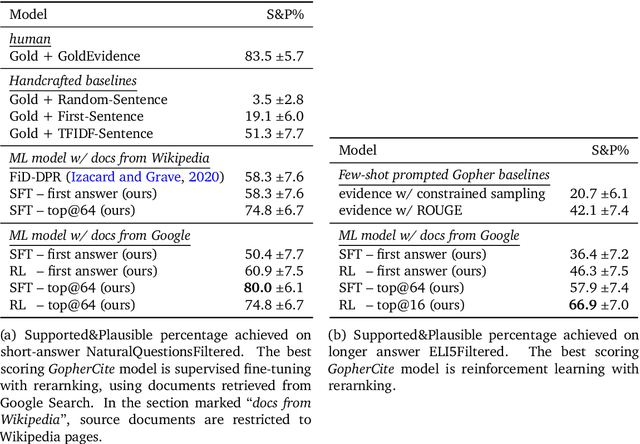
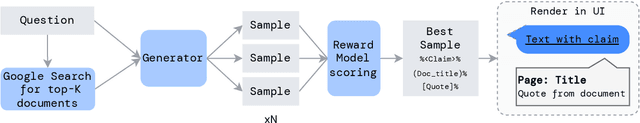
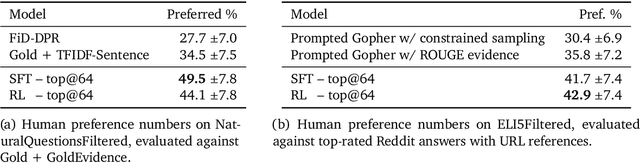
Abstract:Recent large language models often answer factual questions correctly. But users can't trust any given claim a model makes without fact-checking, because language models can hallucinate convincing nonsense. In this work we use reinforcement learning from human preferences (RLHP) to train "open-book" QA models that generate answers whilst also citing specific evidence for their claims, which aids in the appraisal of correctness. Supporting evidence is drawn from multiple documents found via a search engine, or from a single user-provided document. Our 280 billion parameter model, GopherCite, is able to produce answers with high quality supporting evidence and abstain from answering when unsure. We measure the performance of GopherCite by conducting human evaluation of answers to questions in a subset of the NaturalQuestions and ELI5 datasets. The model's response is found to be high-quality 80\% of the time on this Natural Questions subset, and 67\% of the time on the ELI5 subset. Abstaining from the third of questions for which it is most unsure improves performance to 90\% and 80\% respectively, approaching human baselines. However, analysis on the adversarial TruthfulQA dataset shows why citation is only one part of an overall strategy for safety and trustworthiness: not all claims supported by evidence are true.
HCMD-zero: Learning Value Aligned Mechanisms from Data
Feb 21, 2022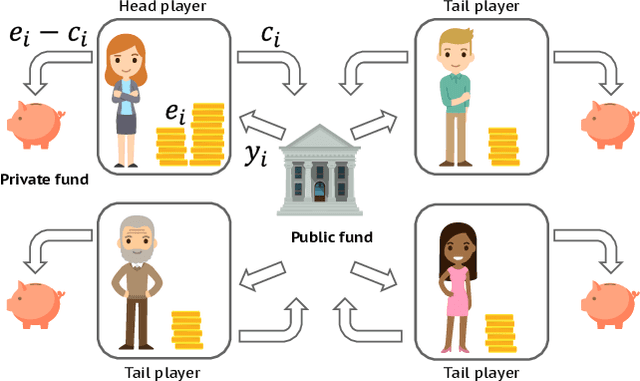
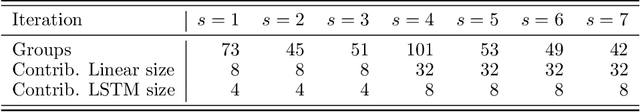
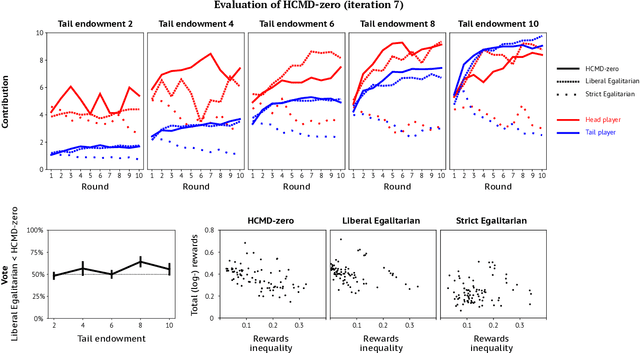
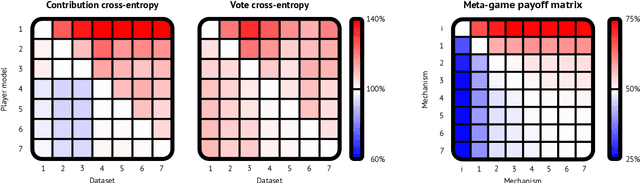
Abstract:Artificial learning agents are mediating a larger and larger number of interactions among humans, firms, and organizations, and the intersection between mechanism design and machine learning has been heavily investigated in recent years. However, mechanism design methods make strong assumptions on how participants behave (e.g. rationality), or on the kind of knowledge designers have access to a priori (e.g. access to strong baseline mechanisms). Here we introduce HCMD-zero, a general purpose method to construct mechanism agents. HCMD-zero learns by mediating interactions among participants, while remaining engaged in an electoral contest with copies of itself, thereby accessing direct feedback from participants. Our results on the Public Investment Game, a stylized resource allocation game that highlights the tension between productivity, equality and the temptation to free-ride, show that HCMD-zero produces competitive mechanism agents that are consistently preferred by human participants over baseline alternatives, and does so automatically, without requiring human knowledge, and by using human data sparingly and effectively Our detailed analysis shows HCMD-zero elicits consistent improvements over the course of training, and that it results in a mechanism with an interpretable and intuitive policy.
Human-centered mechanism design with Democratic AI
Jan 27, 2022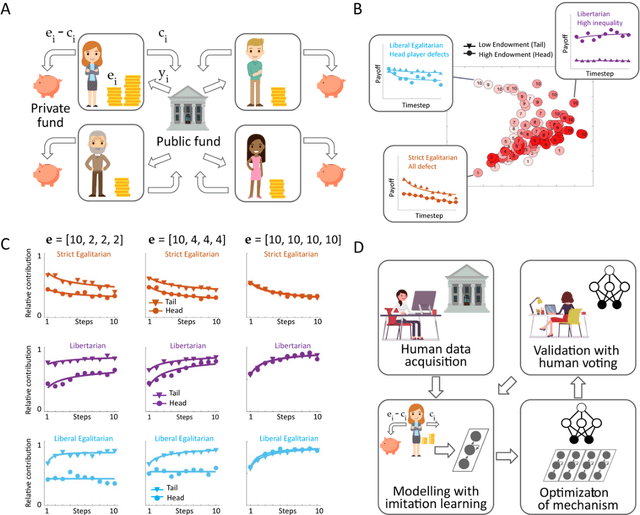
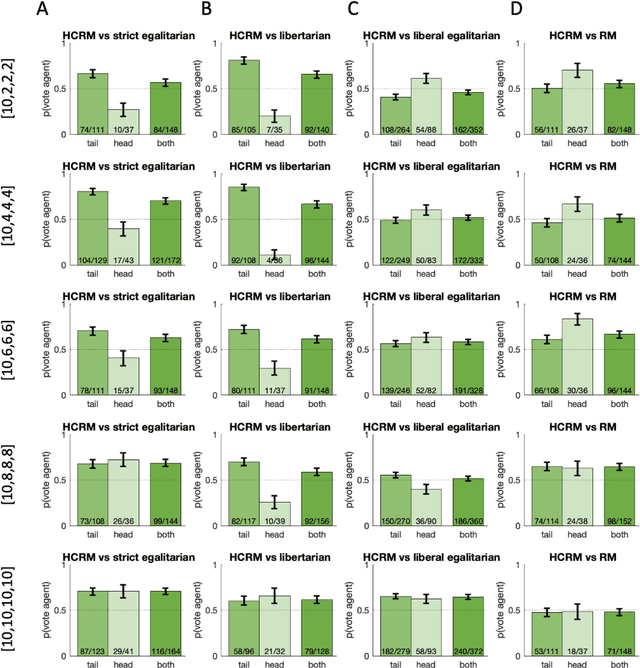
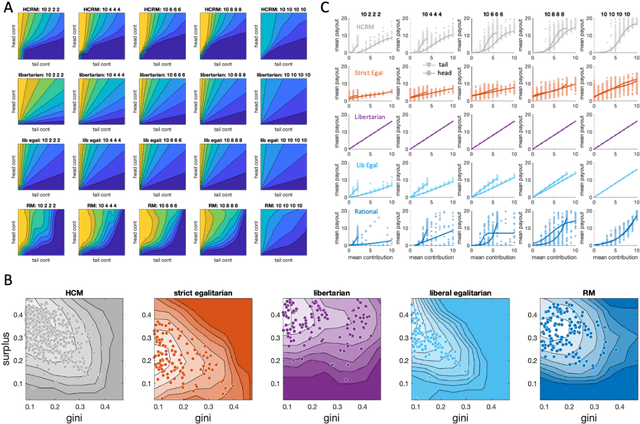
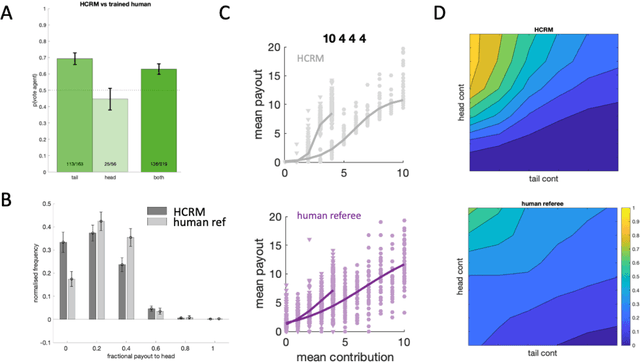
Abstract:Building artificial intelligence (AI) that aligns with human values is an unsolved problem. Here, we developed a human-in-the-loop research pipeline called Democratic AI, in which reinforcement learning is used to design a social mechanism that humans prefer by majority. A large group of humans played an online investment game that involved deciding whether to keep a monetary endowment or to share it with others for collective benefit. Shared revenue was returned to players under two different redistribution mechanisms, one designed by the AI and the other by humans. The AI discovered a mechanism that redressed initial wealth imbalance, sanctioned free riders, and successfully won the majority vote. By optimizing for human preferences, Democratic AI may be a promising method for value-aligned policy innovation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge