Luca Sestini
SAF-IS: a Spatial Annotation Free Framework for Instance Segmentation of Surgical Tools
Sep 04, 2023



Abstract:Instance segmentation of surgical instruments is a long-standing research problem, crucial for the development of many applications for computer-assisted surgery. This problem is commonly tackled via fully-supervised training of deep learning models, requiring expensive pixel-level annotations to train. In this work, we develop a framework for instance segmentation not relying on spatial annotations for training. Instead, our solution only requires binary tool masks, obtainable using recent unsupervised approaches, and binary tool presence labels, freely obtainable in robot-assisted surgery. Based on the binary mask information, our solution learns to extract individual tool instances from single frames, and to encode each instance into a compact vector representation, capturing its semantic features. Such representations guide the automatic selection of a tiny number of instances (8 only in our experiments), displayed to a human operator for tool-type labelling. The gathered information is finally used to match each training instance with a binary tool presence label, providing an effective supervision signal to train a tool instance classifier. We validate our framework on the EndoVis 2017 and 2018 segmentation datasets. We provide results using binary masks obtained either by manual annotation or as predictions of an unsupervised binary segmentation model. The latter solution yields an instance segmentation approach completely free from spatial annotations, outperforming several state-of-the-art fully-supervised segmentation approaches.
Surgical tool classification and localization: results and methods from the MICCAI 2022 SurgToolLoc challenge
May 11, 2023



Abstract:The ability to automatically detect and track surgical instruments in endoscopic videos can enable transformational interventions. Assessing surgical performance and efficiency, identifying skilled tool use and choreography, and planning operational and logistical aspects of OR resources are just a few of the applications that could benefit. Unfortunately, obtaining the annotations needed to train machine learning models to identify and localize surgical tools is a difficult task. Annotating bounding boxes frame-by-frame is tedious and time-consuming, yet large amounts of data with a wide variety of surgical tools and surgeries must be captured for robust training. Moreover, ongoing annotator training is needed to stay up to date with surgical instrument innovation. In robotic-assisted surgery, however, potentially informative data like timestamps of instrument installation and removal can be programmatically harvested. The ability to rely on tool installation data alone would significantly reduce the workload to train robust tool-tracking models. With this motivation in mind we invited the surgical data science community to participate in the challenge, SurgToolLoc 2022. The goal was to leverage tool presence data as weak labels for machine learning models trained to detect tools and localize them in video frames with bounding boxes. We present the results of this challenge along with many of the team's efforts. We conclude by discussing these results in the broader context of machine learning and surgical data science. The training data used for this challenge consisting of 24,695 video clips with tool presence labels is also being released publicly and can be accessed at https://console.cloud.google.com/storage/browser/isi-surgtoolloc-2022.
Dissecting Self-Supervised Learning Methods for Surgical Computer Vision
Jul 01, 2022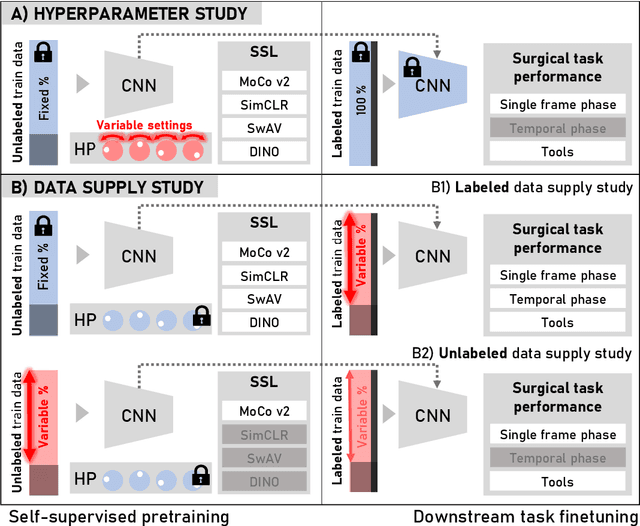
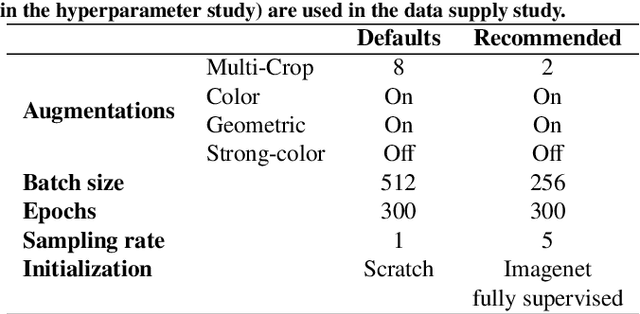
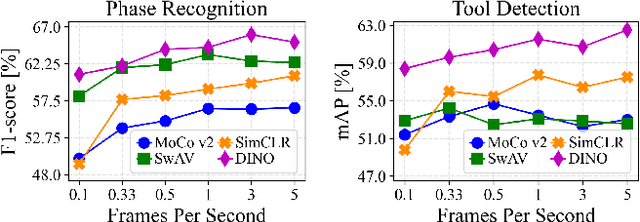
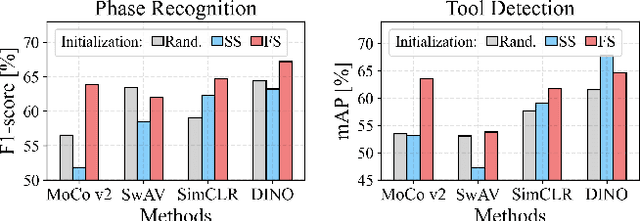
Abstract:The field of surgical computer vision has undergone considerable breakthroughs in recent years with the rising popularity of deep neural network-based methods. However, standard fully-supervised approaches for training such models require vast amounts of annotated data, imposing a prohibitively high cost; especially in the clinical domain. Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) methods, which have begun to gain traction in the general computer vision community, represent a potential solution to these annotation costs, allowing to learn useful representations from only unlabeled data. Still, the effectiveness of SSL methods in more complex and impactful domains, such as medicine and surgery, remains limited and unexplored. In this work, we address this critical need by investigating four state-of-the-art SSL methods (MoCo v2, SimCLR, DINO, SwAV) in the context of surgical computer vision. We present an extensive analysis of the performance of these methods on the Cholec80 dataset for two fundamental and popular tasks in surgical context understanding, phase recognition and tool presence detection. We examine their parameterization, then their behavior with respect to training data quantities in semi-supervised settings. Correct transfer of these methods to surgery, as described and conducted in this work, leads to substantial performance gains over generic uses of SSL - up to 7% on phase recognition and 20% on tool presence detection - as well as state-of-the-art semi-supervised phase recognition approaches by up to 14%. The code will be made available at https://github.com/CAMMA-public/SelfSupSurg.
FUN-SIS: a Fully UNsupervised approach for Surgical Instrument Segmentation
Feb 16, 2022



Abstract:Automatic surgical instrument segmentation of endoscopic images is a crucial building block of many computer-assistance applications for minimally invasive surgery. So far, state-of-the-art approaches completely rely on the availability of a ground-truth supervision signal, obtained via manual annotation, thus expensive to collect at large scale. In this paper, we present FUN-SIS, a Fully-UNsupervised approach for binary Surgical Instrument Segmentation. FUN-SIS trains a per-frame segmentation model on completely unlabelled endoscopic videos, by solely relying on implicit motion information and instrument shape-priors. We define shape-priors as realistic segmentation masks of the instruments, not necessarily coming from the same dataset/domain as the videos. The shape-priors can be collected in various and convenient ways, such as recycling existing annotations from other datasets. We leverage them as part of a novel generative-adversarial approach, allowing to perform unsupervised instrument segmentation of optical-flow images during training. We then use the obtained instrument masks as pseudo-labels in order to train a per-frame segmentation model; to this aim, we develop a learning-from-noisy-labels architecture, designed to extract a clean supervision signal from these pseudo-labels, leveraging their peculiar noise properties. We validate the proposed contributions on three surgical datasets, including the MICCAI 2017 EndoVis Robotic Instrument Segmentation Challenge dataset. The obtained fully-unsupervised results for surgical instrument segmentation are almost on par with the ones of fully-supervised state-of-the-art approaches. This suggests the tremendous potential of the proposed method to leverage the great amount of unlabelled data produced in the context of minimally invasive surgery.
A Kinematic Bottleneck Approach For Pose Regression of Flexible Surgical Instruments directly from Images
Feb 28, 2021



Abstract:3-D pose estimation of instruments is a crucial step towards automatic scene understanding in robotic minimally invasive surgery. Although robotic systems can potentially directly provide joint values, this information is not commonly exploited inside the operating room, due to its possible unreliability, limited access and the time-consuming calibration required, especially for continuum robots. For this reason, standard approaches for 3-D pose estimation involve the use of external tracking systems. Recently, image-based methods have emerged as promising, non-invasive alternatives. While many image-based approaches in the literature have shown accurate results, they generally require either a complex iterative optimization for each processed image, making them unsuitable for real-time applications, or a large number of manually-annotated images for efficient learning. In this paper we propose a self-supervised image-based method, exploiting, at training time only, the imprecise kinematic information provided by the robot. In order to avoid introducing time-consuming manual annotations, the problem is formulated as an auto-encoder, smartly bottlenecked by the presence of a physical model of the robotic instruments and surgical camera, forcing a separation between image background and kinematic content. Validation of the method was performed on semi-synthetic, phantom and in-vivo datasets, obtained using a flexible robotized endoscope, showing promising results for real-time image-based 3-D pose estimation of surgical instruments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge