Kushal Dave
Scaling the Vocabulary of Non-autoregressive Models for Efficient Generative Retrieval
Jun 10, 2024Abstract:Generative Retrieval introduces a new approach to Information Retrieval by reframing it as a constrained generation task, leveraging recent advancements in Autoregressive (AR) language models. However, AR-based Generative Retrieval methods suffer from high inference latency and cost compared to traditional dense retrieval techniques, limiting their practical applicability. This paper investigates fully Non-autoregressive (NAR) language models as a more efficient alternative for generative retrieval. While standard NAR models alleviate latency and cost concerns, they exhibit a significant drop in retrieval performance (compared to AR models) due to their inability to capture dependencies between target tokens. To address this, we question the conventional choice of limiting the target token space to solely words or sub-words. We propose PIXAR, a novel approach that expands the target vocabulary of NAR models to include multi-word entities and common phrases (up to 5 million tokens), thereby reducing token dependencies. PIXAR employs inference optimization strategies to maintain low inference latency despite the significantly larger vocabulary. Our results demonstrate that PIXAR achieves a relative improvement of 31.0% in MRR@10 on MS MARCO and 23.2% in Hits@5 on Natural Questions compared to standard NAR models with similar latency and cost. Furthermore, online A/B experiments on a large commercial search engine show that PIXAR increases ad clicks by 5.08% and revenue by 4.02%.
NGAME: Negative Mining-aware Mini-batching for Extreme Classification
Jul 10, 2022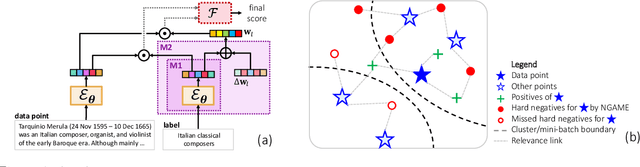
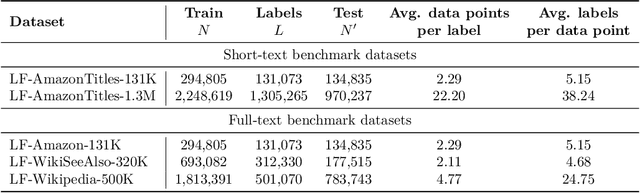
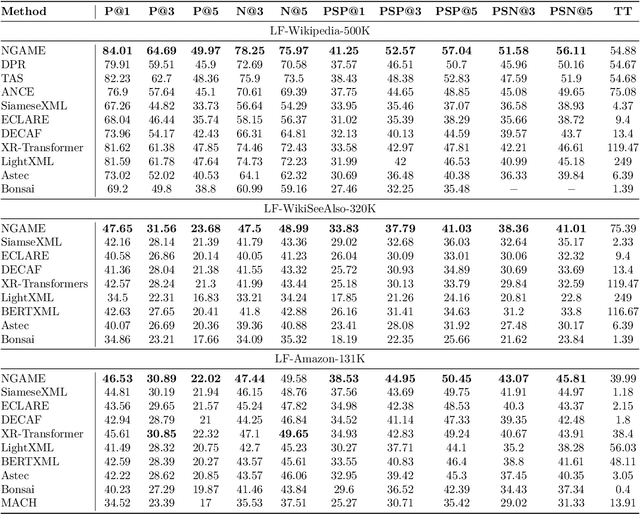
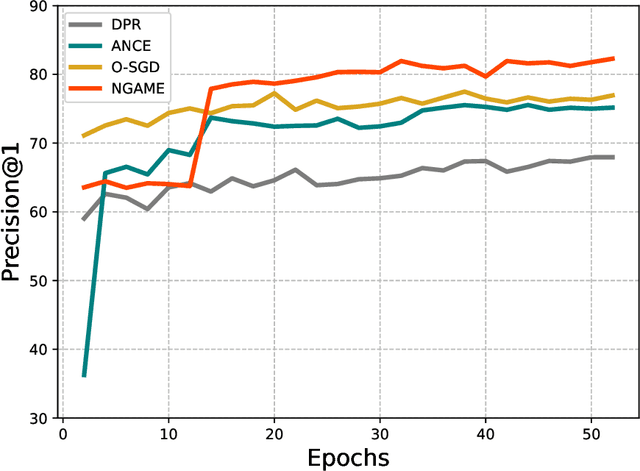
Abstract:Extreme Classification (XC) seeks to tag data points with the most relevant subset of labels from an extremely large label set. Performing deep XC with dense, learnt representations for data points and labels has attracted much attention due to its superiority over earlier XC methods that used sparse, hand-crafted features. Negative mining techniques have emerged as a critical component of all deep XC methods that allow them to scale to millions of labels. However, despite recent advances, training deep XC models with large encoder architectures such as transformers remains challenging. This paper identifies that memory overheads of popular negative mining techniques often force mini-batch sizes to remain small and slow training down. In response, this paper introduces NGAME, a light-weight mini-batch creation technique that offers provably accurate in-batch negative samples. This allows training with larger mini-batches offering significantly faster convergence and higher accuracies than existing negative sampling techniques. NGAME was found to be up to 16% more accurate than state-of-the-art methods on a wide array of benchmark datasets for extreme classification, as well as 3% more accurate at retrieving search engine queries in response to a user webpage visit to show personalized ads. In live A/B tests on a popular search engine, NGAME yielded up to 23% gains in click-through-rates.
DeepXML: A Deep Extreme Multi-Label Learning Framework Applied to Short Text Documents
Nov 12, 2021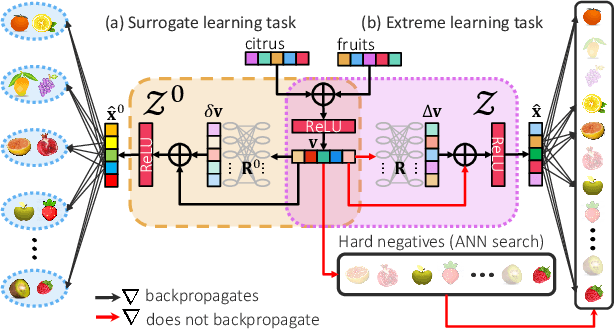
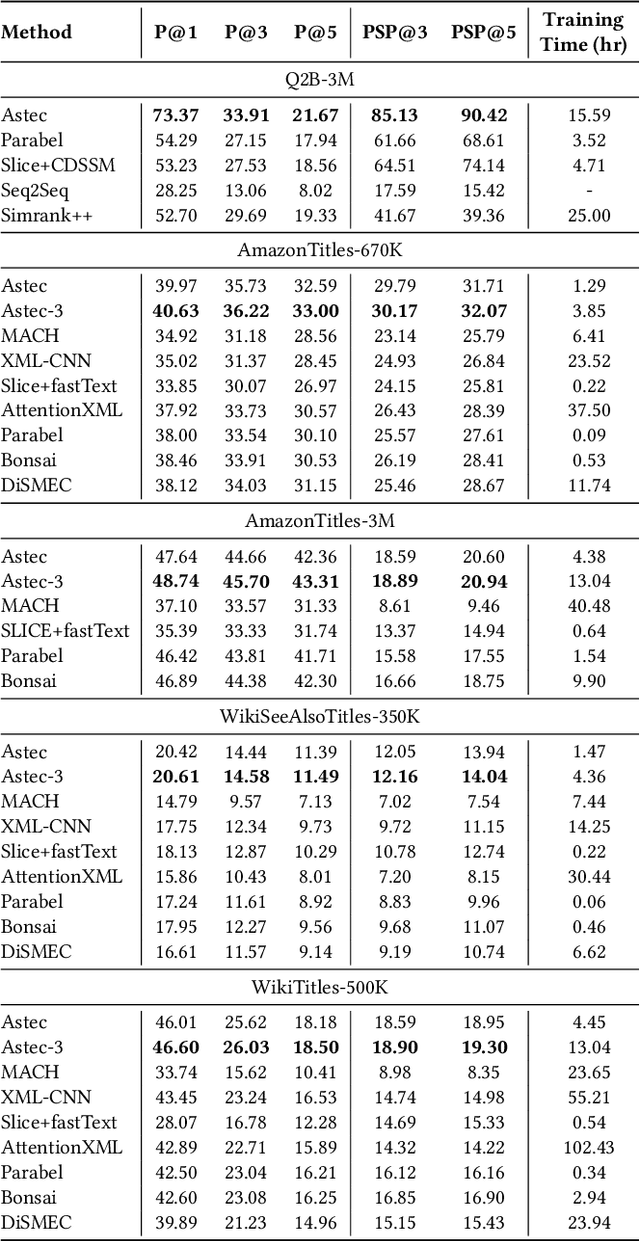
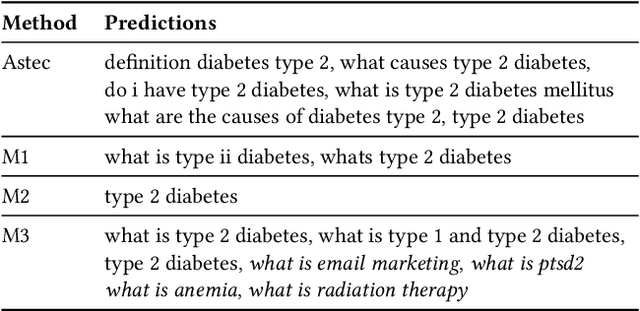
Abstract:Scalability and accuracy are well recognized challenges in deep extreme multi-label learning where the objective is to train architectures for automatically annotating a data point with the most relevant subset of labels from an extremely large label set. This paper develops the DeepXML framework that addresses these challenges by decomposing the deep extreme multi-label task into four simpler sub-tasks each of which can be trained accurately and efficiently. Choosing different components for the four sub-tasks allows DeepXML to generate a family of algorithms with varying trade-offs between accuracy and scalability. In particular, DeepXML yields the Astec algorithm that could be 2-12% more accurate and 5-30x faster to train than leading deep extreme classifiers on publically available short text datasets. Astec could also efficiently train on Bing short text datasets containing up to 62 million labels while making predictions for billions of users and data points per day on commodity hardware. This allowed Astec to be deployed on the Bing search engine for a number of short text applications ranging from matching user queries to advertiser bid phrases to showing personalized ads where it yielded significant gains in click-through-rates, coverage, revenue and other online metrics over state-of-the-art techniques currently in production. DeepXML's code is available at https://github.com/Extreme-classification/deepxml
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge