Akash Kumar Mohankumar
Improving Retrieval in Sponsored Search by Leveraging Query Context Signals
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:Accurately retrieving relevant bid keywords for user queries is critical in Sponsored Search but remains challenging, particularly for short, ambiguous queries. Existing dense and generative retrieval models often fail to capture nuanced user intent in these cases. To address this, we propose an approach to enhance query understanding by augmenting queries with rich contextual signals derived from web search results and large language models, stored in an online cache. Specifically, we use web search titles and snippets to ground queries in real-world information and utilize GPT-4 to generate query rewrites and explanations that clarify user intent. These signals are efficiently integrated through a Fusion-in-Decoder based Unity architecture, enabling both dense and generative retrieval with serving costs on par with traditional context-free models. To address scenarios where context is unavailable in the cache, we introduce context glancing, a curriculum learning strategy that improves model robustness and performance even without contextual signals during inference. Extensive offline experiments demonstrate that our context-aware approach substantially outperforms context-free models. Furthermore, online A/B testing on a prominent search engine across 160+ countries shows significant improvements in user engagement and revenue.
Scaling the Vocabulary of Non-autoregressive Models for Efficient Generative Retrieval
Jun 10, 2024Abstract:Generative Retrieval introduces a new approach to Information Retrieval by reframing it as a constrained generation task, leveraging recent advancements in Autoregressive (AR) language models. However, AR-based Generative Retrieval methods suffer from high inference latency and cost compared to traditional dense retrieval techniques, limiting their practical applicability. This paper investigates fully Non-autoregressive (NAR) language models as a more efficient alternative for generative retrieval. While standard NAR models alleviate latency and cost concerns, they exhibit a significant drop in retrieval performance (compared to AR models) due to their inability to capture dependencies between target tokens. To address this, we question the conventional choice of limiting the target token space to solely words or sub-words. We propose PIXAR, a novel approach that expands the target vocabulary of NAR models to include multi-word entities and common phrases (up to 5 million tokens), thereby reducing token dependencies. PIXAR employs inference optimization strategies to maintain low inference latency despite the significantly larger vocabulary. Our results demonstrate that PIXAR achieves a relative improvement of 31.0% in MRR@10 on MS MARCO and 23.2% in Hits@5 on Natural Questions compared to standard NAR models with similar latency and cost. Furthermore, online A/B experiments on a large commercial search engine show that PIXAR increases ad clicks by 5.08% and revenue by 4.02%.
HEARTS: Multi-task Fusion of Dense Retrieval and Non-autoregressive Generation for Sponsored Search
Sep 13, 2022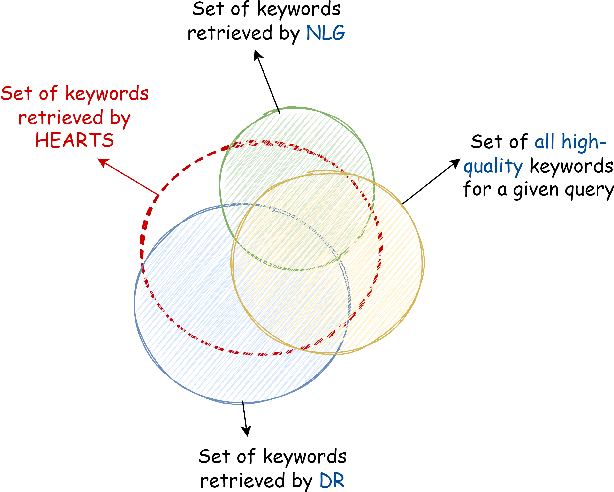
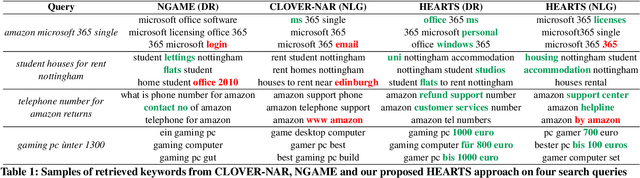
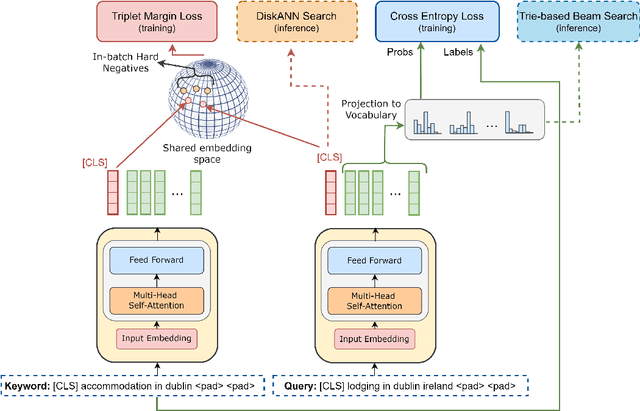
Abstract:Matching user search queries with relevant keywords bid by advertisers in real-time is a crucial problem in sponsored search. In the literature, two broad set of approaches have been explored to solve this problem: (i) Dense Retrieval (DR) - learning dense vector representations for queries and bid keywords in a shared space, and (ii) Natural Language Generation (NLG) - learning to directly generate bid keywords given queries. In this work, we first conduct an empirical study of these two approaches and show that they offer complementary benefits that are additive. In particular, a large fraction of the keywords retrieved from NLG haven't been retrieved by DR and vice-versa. We then show that it is possible to effectively combine the advantages of these two approaches in one model. Specifically, we propose HEARTS: a novel multi-task fusion framework where we jointly optimize a shared encoder to perform both DR and non-autoregressive NLG. Through extensive experiments on search queries from over 30+ countries spanning 20+ languages, we show that HEARTS retrieves 40.3% more high-quality bid keywords than the baseline approaches with the same GPU compute. We also demonstrate that inferring on a single HEARTS model is as good as inferring on two different DR and NLG baseline models, with 2x the compute. Further, we show that DR models trained with the HEARTS objective are significantly better than those trained with the standard contrastive loss functions. Finally, we show that our HEARTS objective can be adopted to short-text retrieval tasks other than sponsored search and achieve significant performance gains.
Active Evaluation: Efficient NLG Evaluation with Few Pairwise Comparisons
Mar 11, 2022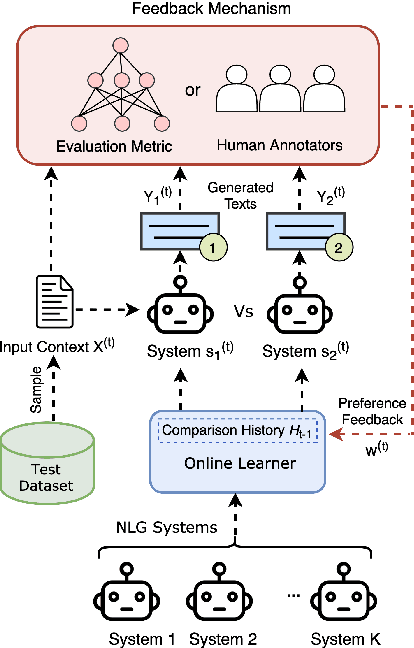
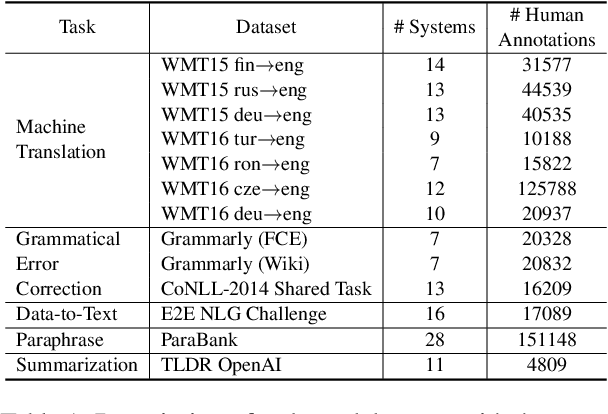
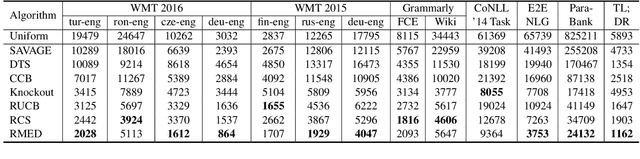
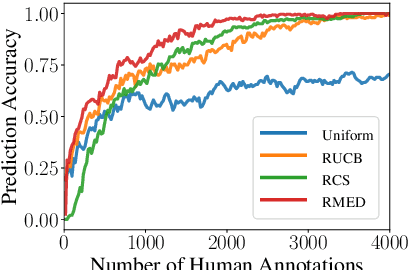
Abstract:Recent studies have shown the advantages of evaluating NLG systems using pairwise comparisons as opposed to direct assessment. Given $k$ systems, a naive approach for identifying the top-ranked system would be to uniformly obtain pairwise comparisons from all ${k \choose 2}$ pairs of systems. However, this can be very expensive as the number of human annotations required would grow quadratically with $k$. In this work, we introduce Active Evaluation, a framework to efficiently identify the top-ranked system by actively choosing system pairs for comparison using dueling bandit algorithms. We perform extensive experiments with 13 dueling bandits algorithms on 13 NLG evaluation datasets spanning 5 tasks and show that the number of human annotations can be reduced by 80%. To further reduce the number of human annotations, we propose model-based dueling bandit algorithms which combine automatic evaluation metrics with human evaluations. Specifically, we eliminate sub-optimal systems even before the human annotation process and perform human evaluations only on test examples where the automatic metric is highly uncertain. This reduces the number of human annotations required further by 89%. In effect, we show that identifying the top-ranked system requires only a few hundred human annotations, which grow linearly with $k$. Lastly, we provide practical recommendations and best practices to identify the top-ranked system efficiently. Our code has been made publicly available at https://github.com/akashkm99/duelnlg
Diversity driven Query Rewriting in Search Advertising
Jun 07, 2021

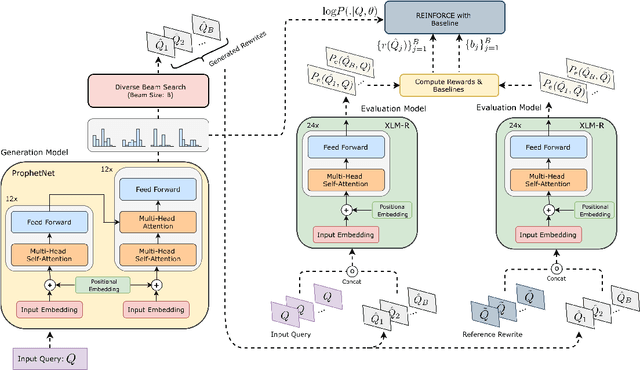
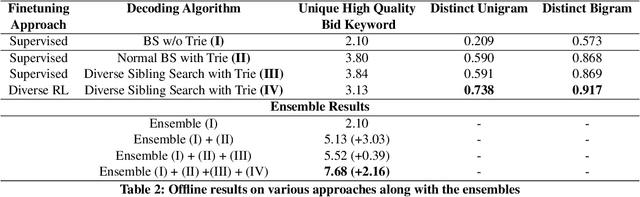
Abstract:Retrieving keywords (bidwords) with the same intent as query, referred to as close variant keywords, is of prime importance for effective targeted search advertising. For head and torso search queries, sponsored search engines use a huge repository of same intent queries and keywords, mined ahead of time. Online, this repository is used to rewrite the query and then lookup the rewrite in a repository of bid keywords contributing to significant revenue. Recently generative retrieval models have been shown to be effective at the task of generating such query rewrites. We observe two main limitations of such generative models. First, rewrites generated by these models exhibit low lexical diversity, and hence the rewrites fail to retrieve relevant keywords that have diverse linguistic variations. Second, there is a misalignment between the training objective - the likelihood of training data, v/s what we desire - improved quality and coverage of rewrites. In this work, we introduce CLOVER, a framework to generate both high-quality and diverse rewrites by optimizing for human assessment of rewrite quality using our diversity-driven reinforcement learning algorithm. We use an evaluation model, trained to predict human judgments, as the reward function to finetune the generation policy. We empirically show the effectiveness of our proposed approach through offline experiments on search queries across geographies spanning three major languages. We also perform online A/B experiments on Bing, a large commercial search engine, which shows (i) better user engagement with an average increase in clicks by 12.83% accompanied with an average defect reduction by 13.97%, and (ii) improved revenue by 21.29%.
A Survey of Evaluation Metrics Used for NLG Systems
Oct 05, 2020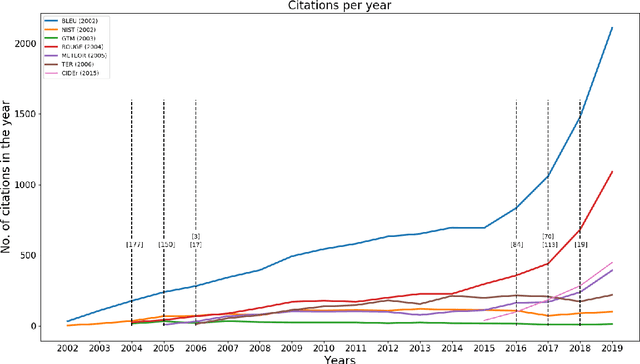
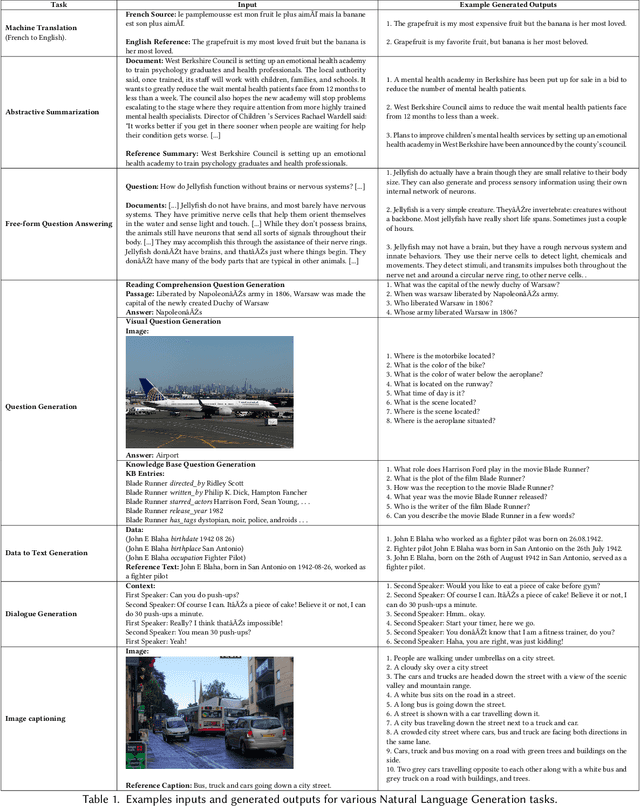

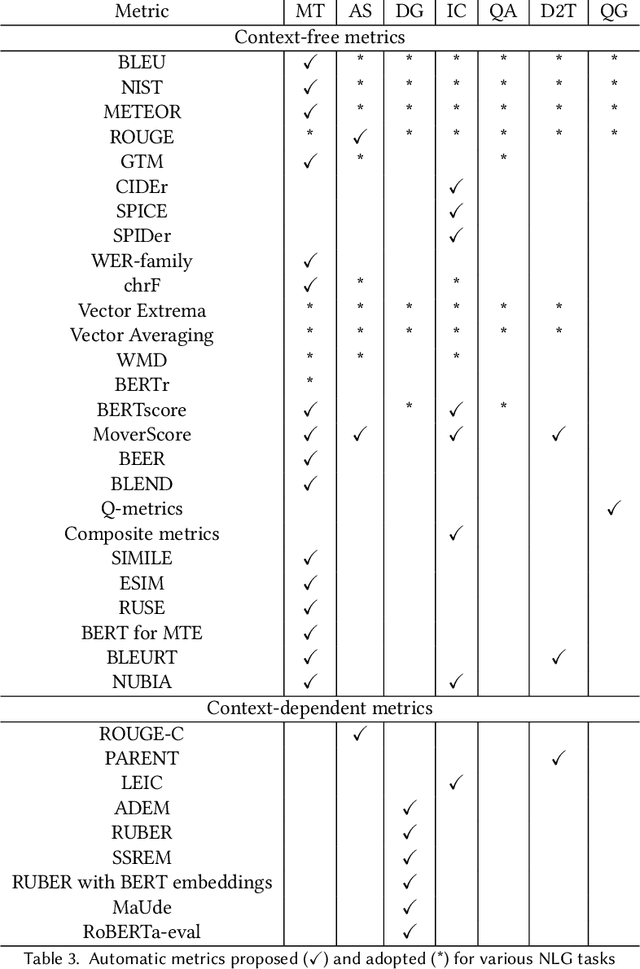
Abstract:The success of Deep Learning has created a surge in interest in a wide a range of Natural Language Generation (NLG) tasks. Deep Learning has not only pushed the state of the art in several existing NLG tasks but has also facilitated researchers to explore various newer NLG tasks such as image captioning. Such rapid progress in NLG has necessitated the development of accurate automatic evaluation metrics that would allow us to track the progress in the field of NLG. However, unlike classification tasks, automatically evaluating NLG systems in itself is a huge challenge. Several works have shown that early heuristic-based metrics such as BLEU, ROUGE are inadequate for capturing the nuances in the different NLG tasks. The expanding number of NLG models and the shortcomings of the current metrics has led to a rapid surge in the number of evaluation metrics proposed since 2014. Moreover, various evaluation metrics have shifted from using pre-determined heuristic-based formulae to trained transformer models. This rapid change in a relatively short time has led to the need for a survey of the existing NLG metrics to help existing and new researchers to quickly come up to speed with the developments that have happened in NLG evaluation in the last few years. Through this survey, we first wish to highlight the challenges and difficulties in automatically evaluating NLG systems. Then, we provide a coherent taxonomy of the evaluation metrics to organize the existing metrics and to better understand the developments in the field. We also describe the different metrics in detail and highlight their key contributions. Later, we discuss the main shortcomings identified in the existing metrics and describe the methodology used to evaluate evaluation metrics. Finally, we discuss our suggestions and recommendations on the next steps forward to improve the automatic evaluation metrics.
Improving Dialog Evaluation with a Multi-reference Adversarial Dataset and Large Scale Pretraining
Sep 23, 2020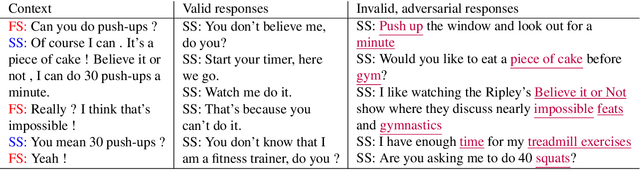
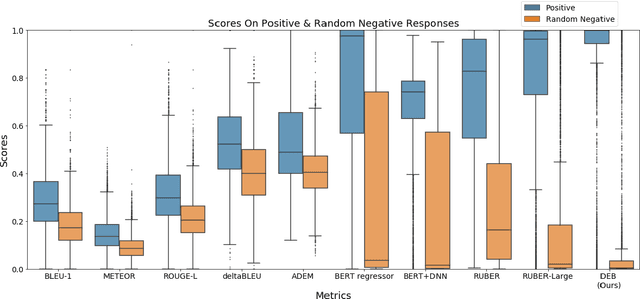

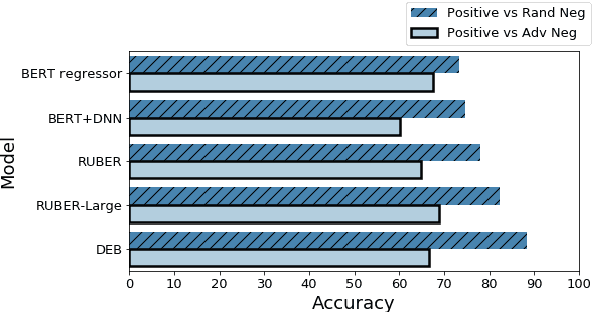
Abstract:There is an increasing focus on model-based dialog evaluation metrics such as ADEM, RUBER, and the more recent BERT-based metrics. These models aim to assign a high score to all relevant responses and a low score to all irrelevant responses. Ideally, such models should be trained using multiple relevant and irrelevant responses for any given context. However, no such data is publicly available, and hence existing models are usually trained using a single relevant response and multiple randomly selected responses from other contexts (random negatives). To allow for better training and robust evaluation of model-based metrics, we introduce the DailyDialog++ dataset, consisting of (i) five relevant responses for each context and (ii) five adversarially crafted irrelevant responses for each context. Using this dataset, we first show that even in the presence of multiple correct references, n-gram based metrics and embedding based metrics do not perform well at separating relevant responses from even random negatives. While model-based metrics perform better than n-gram and embedding based metrics on random negatives, their performance drops substantially when evaluated on adversarial examples. To check if large scale pretraining could help, we propose a new BERT-based evaluation metric called DEB, which is pretrained on 727M Reddit conversations and then finetuned on our dataset. DEB significantly outperforms existing models, showing better correlation with human judgements and better performance on random negatives (88.27% accuracy). However, its performance again drops substantially, when evaluated on adversarial responses, thereby highlighting that even large-scale pretrained evaluation models are not robust to the adversarial examples in our dataset. The dataset and code are publicly available.
Towards Transparent and Explainable Attention Models
Apr 29, 2020
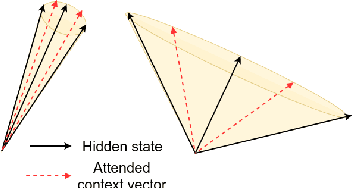
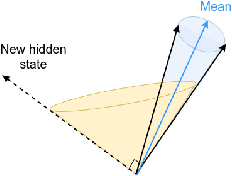
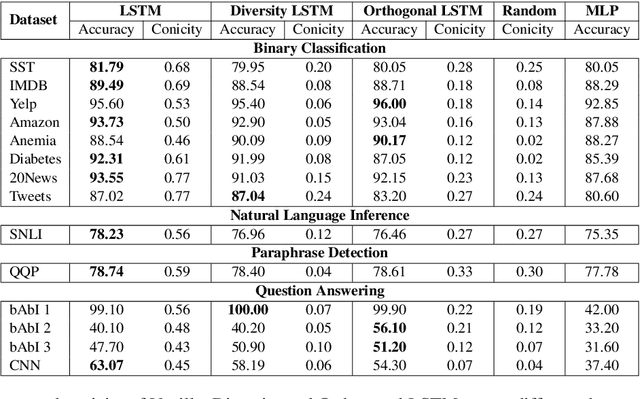
Abstract:Recent studies on interpretability of attention distributions have led to notions of faithful and plausible explanations for a model's predictions. Attention distributions can be considered a faithful explanation if a higher attention weight implies a greater impact on the model's prediction. They can be considered a plausible explanation if they provide a human-understandable justification for the model's predictions. In this work, we first explain why current attention mechanisms in LSTM based encoders can neither provide a faithful nor a plausible explanation of the model's predictions. We observe that in LSTM based encoders the hidden representations at different time-steps are very similar to each other (high conicity) and attention weights in these situations do not carry much meaning because even a random permutation of the attention weights does not affect the model's predictions. Based on experiments on a wide variety of tasks and datasets, we observe attention distributions often attribute the model's predictions to unimportant words such as punctuation and fail to offer a plausible explanation for the predictions. To make attention mechanisms more faithful and plausible, we propose a modified LSTM cell with a diversity-driven training objective that ensures that the hidden representations learned at different time steps are diverse. We show that the resulting attention distributions offer more transparency as they (i) provide a more precise importance ranking of the hidden states (ii) are better indicative of words important for the model's predictions (iii) correlate better with gradient-based attribution methods. Human evaluations indicate that the attention distributions learned by our model offer a plausible explanation of the model's predictions. Our code has been made publicly available at https://github.com/akashkm99/Interpretable-Attention
Let's Ask Again: Refine Network for Automatic Question Generation
Aug 31, 2019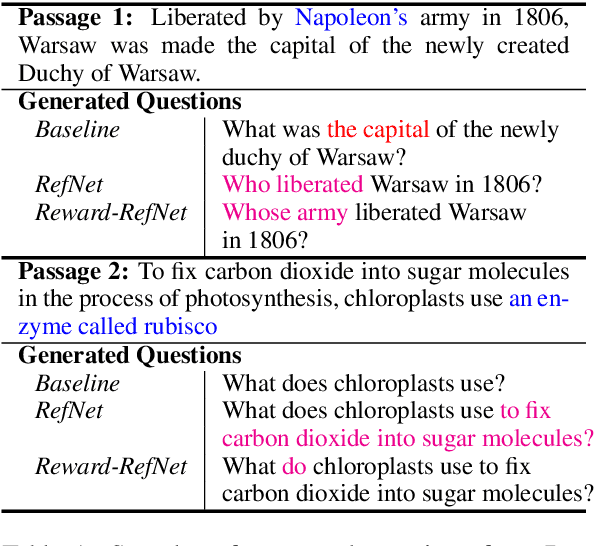
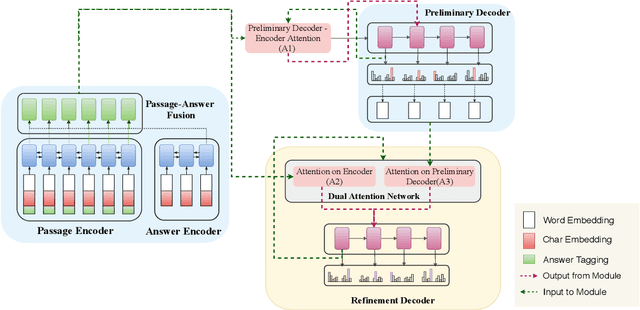

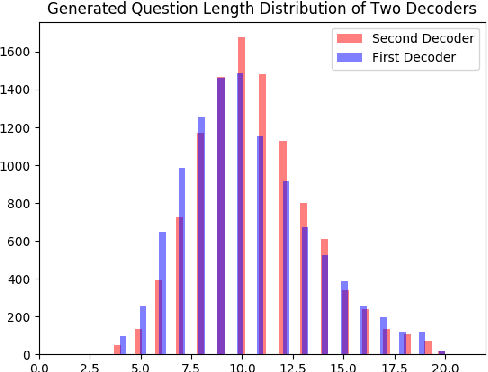
Abstract:In this work, we focus on the task of Automatic Question Generation (AQG) where given a passage and an answer the task is to generate the corresponding question. It is desired that the generated question should be (i) grammatically correct (ii) answerable from the passage and (iii) specific to the given answer. An analysis of existing AQG models shows that they produce questions which do not adhere to one or more of {the above-mentioned qualities}. In particular, the generated questions look like an incomplete draft of the desired question with a clear scope for refinement. {To alleviate this shortcoming}, we propose a method which tries to mimic the human process of generating questions by first creating an initial draft and then refining it. More specifically, we propose Refine Network (RefNet) which contains two decoders. The second decoder uses a dual attention network which pays attention to both (i) the original passage and (ii) the question (initial draft) generated by the first decoder. In effect, it refines the question generated by the first decoder, thereby making it more correct and complete. We evaluate RefNet on three datasets, \textit{viz.}, SQuAD, HOTPOT-QA, and DROP, and show that it outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods by 7-16\% on all of these datasets. Lastly, we show that we can improve the quality of the second decoder on specific metrics, such as, fluency and answerability by explicitly rewarding revisions that improve on the corresponding metric during training. The code has been made publicly available \footnote{https://github.com/PrekshaNema25/RefNet-QG}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge