Diversity driven Query Rewriting in Search Advertising
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2021

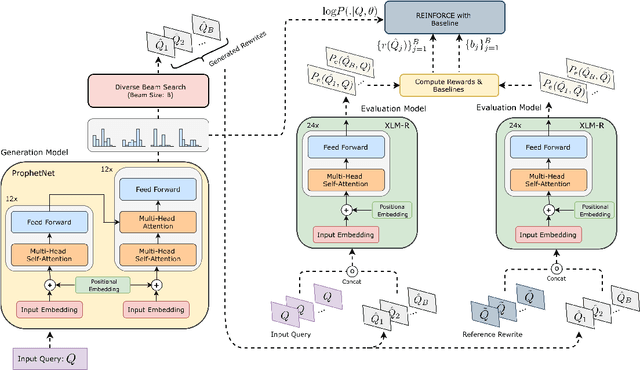
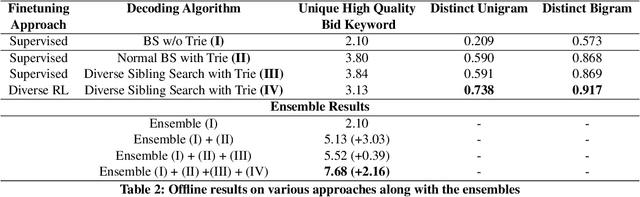
Retrieving keywords (bidwords) with the same intent as query, referred to as close variant keywords, is of prime importance for effective targeted search advertising. For head and torso search queries, sponsored search engines use a huge repository of same intent queries and keywords, mined ahead of time. Online, this repository is used to rewrite the query and then lookup the rewrite in a repository of bid keywords contributing to significant revenue. Recently generative retrieval models have been shown to be effective at the task of generating such query rewrites. We observe two main limitations of such generative models. First, rewrites generated by these models exhibit low lexical diversity, and hence the rewrites fail to retrieve relevant keywords that have diverse linguistic variations. Second, there is a misalignment between the training objective - the likelihood of training data, v/s what we desire - improved quality and coverage of rewrites. In this work, we introduce CLOVER, a framework to generate both high-quality and diverse rewrites by optimizing for human assessment of rewrite quality using our diversity-driven reinforcement learning algorithm. We use an evaluation model, trained to predict human judgments, as the reward function to finetune the generation policy. We empirically show the effectiveness of our proposed approach through offline experiments on search queries across geographies spanning three major languages. We also perform online A/B experiments on Bing, a large commercial search engine, which shows (i) better user engagement with an average increase in clicks by 12.83% accompanied with an average defect reduction by 13.97%, and (ii) improved revenue by 21.29%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge