Kunming Li
Endangered Alert: A Field-Validated Self-Training Scheme for Detecting and Protecting Threatened Wildlife on Roads and Roadsides
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Traffic accidents are a global safety concern, resulting in numerous fatalities each year. A considerable number of these deaths are caused by animal-vehicle collisions (AVCs), which not only endanger human lives but also present serious risks to animal populations. This paper presents an innovative self-training methodology aimed at detecting rare animals, such as the cassowary in Australia, whose survival is threatened by road accidents. The proposed method addresses critical real-world challenges, including acquiring and labelling sensor data for rare animal species in resource-limited environments. It achieves this by leveraging cloud and edge computing, and automatic data labelling to improve the detection performance of the field-deployed model iteratively. Our approach introduces Label-Augmentation Non-Maximum Suppression (LA-NMS), which incorporates a vision-language model (VLM) to enable automated data labelling. During a five-month deployment, we confirmed the method's robustness and effectiveness, resulting in improved object detection accuracy and increased prediction confidence. The source code is available: https://github.com/acfr/CassDetect
Knowledge-aware Graph Transformer for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
Jan 10, 2024



Abstract:Predicting pedestrian motion trajectories is crucial for path planning and motion control of autonomous vehicles. Accurately forecasting crowd trajectories is challenging due to the uncertain nature of human motions in different environments. For training, recent deep learning-based prediction approaches mainly utilize information like trajectory history and interactions between pedestrians, among others. This can limit the prediction performance across various scenarios since the discrepancies between training datasets have not been properly incorporated. To overcome this limitation, this paper proposes a graph transformer structure to improve prediction performance, capturing the differences between the various sites and scenarios contained in the datasets. In particular, a self-attention mechanism and a domain adaption module have been designed to improve the generalization ability of the model. Moreover, an additional metric considering cross-dataset sequences is introduced for training and performance evaluation purposes. The proposed framework is validated and compared against existing methods using popular public datasets, i.e., ETH and UCY. Experimental results demonstrate the improved performance of our proposed scheme.
Socially Aware Crowd Navigation with Multimodal Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction for Autonomous Vehicles
Nov 23, 2020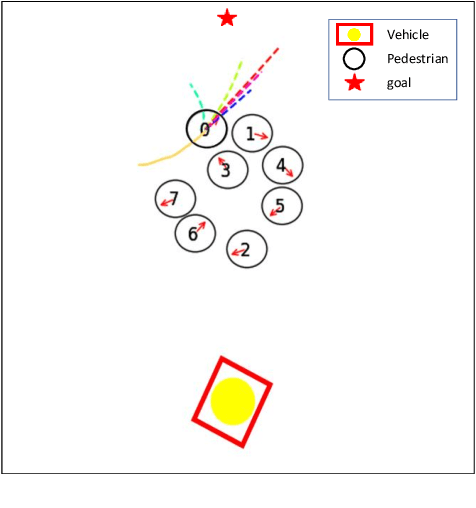
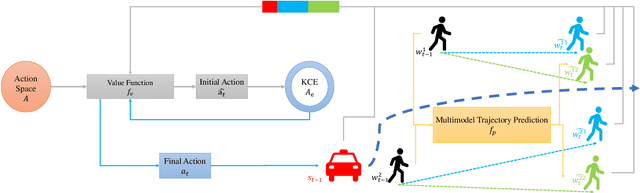
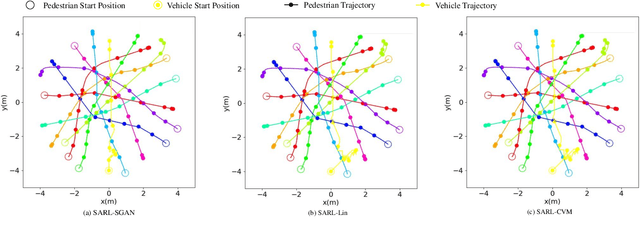
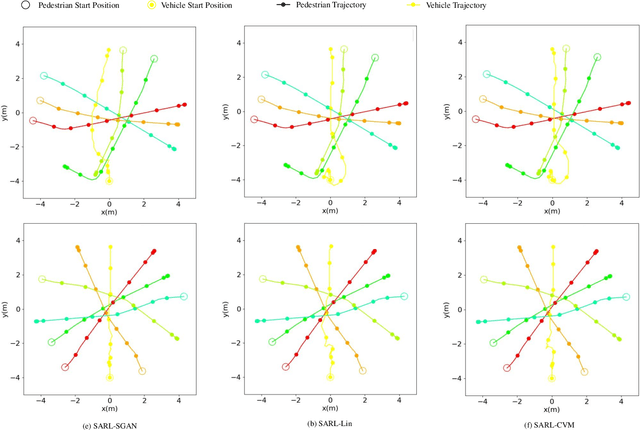
Abstract:Seamlessly operating an autonomous vehicle in a crowded pedestrian environment is a very challenging task. This is because human movement and interactions are very hard to predict in such environments. Recent work has demonstrated that reinforcement learning-based methods have the ability to learn to drive in crowds. However, these methods can have very poor performance due to inaccurate predictions of the pedestrians' future state as human motion prediction has a large variance. To overcome this problem, we propose a new method, SARL-SGAN-KCE, that combines a deep socially aware attentive value network with a human multimodal trajectory prediction model to help identify the optimal driving policy. We also introduce a novel technique to extend the discrete action space with minimal additional computational requirements. The kinematic constraints of the vehicle are also considered to ensure smooth and safe trajectories. We evaluate our method against the state of art methods for crowd navigation and provide an ablation study to show that our method is safer and closer to human behaviour.
Attentional-GCNN: Adaptive Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction towards Generic Autonomous Vehicle Use Cases
Nov 23, 2020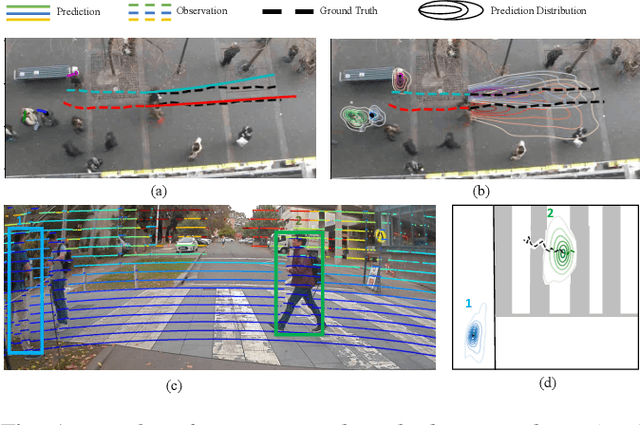
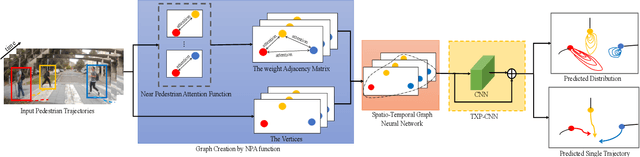
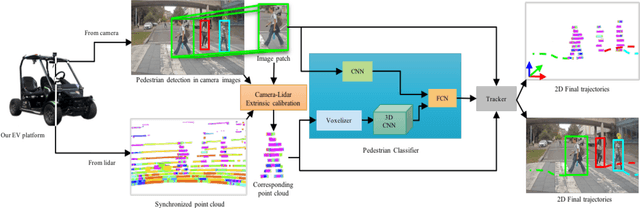

Abstract:Autonomous vehicle navigation in shared pedestrian environments requires the ability to predict future crowd motion both accurately and with minimal delay. Understanding the uncertainty of the prediction is also crucial. Most existing approaches however can only estimate uncertainty through repeated sampling of generative models. Additionally, most current predictive models are trained on datasets that assume complete observability of the crowd using an aerial view. These are generally not representative of real-world usage from a vehicle perspective, and can lead to the underestimation of uncertainty bounds when the on-board sensors are occluded. Inspired by prior work in motion prediction using spatio-temporal graphs, we propose a novel Graph Convolutional Neural Network (GCNN)-based approach, Attentional-GCNN, which aggregates information of implicit interaction between pedestrians in a crowd by assigning attention weight in edges of the graph. Our model can be trained to either output a probabilistic distribution or faster deterministic prediction, demonstrating applicability to autonomous vehicle use cases where either speed or accuracy with uncertainty bounds are required. To further improve the training of predictive models, we propose an automatically labelled pedestrian dataset collected from an intelligent vehicle platform representative of real-world use. Through experiments on a number of datasets, we show our proposed method achieves an improvement over the state of art by 10% Average Displacement Error (ADE) and 12% Final Displacement Error (FDE) with fast inference speeds.
Probabilistic Crowd GAN: Multimodal Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction using a Graph Vehicle-Pedestrian Attention Network
Jul 12, 2020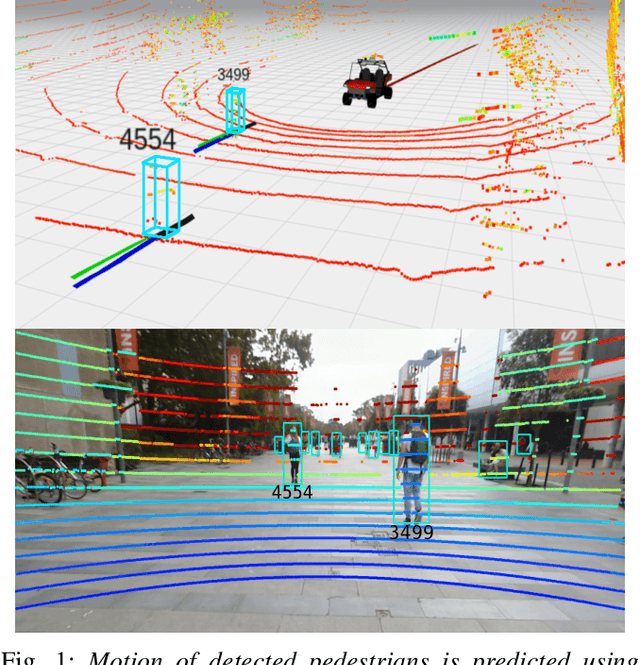
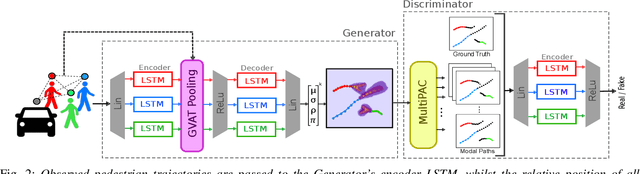

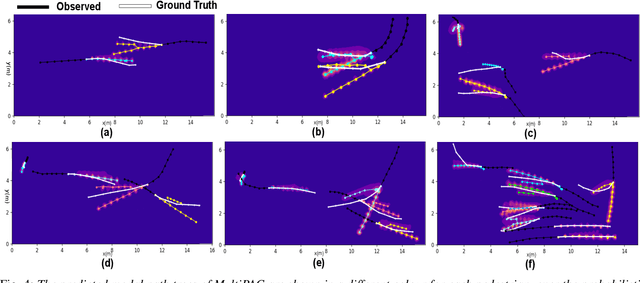
Abstract:Understanding and predicting the intention of pedestrians is essential to enable autonomous vehicles and mobile robots to navigate crowds. This problem becomes increasingly complex when we consider the uncertainty and multimodality of pedestrian motion, as well as the implicit interactions between members of a crowd, including any response to a vehicle. Our approach, Probabilistic Crowd GAN, extends recent work in trajectory prediction, combining Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) with Mixture Density Networks (MDNs) to output probabilistic multimodal predictions, from which likely modal paths are found and used for adversarial training. We also propose the use of Graph Vehicle-Pedestrian Attention Network (GVAT), which models social interactions and allows input of a shared vehicle feature, showing that inclusion of this module leads to improved trajectory prediction both with and without the presence of a vehicle. Through evaluation on various datasets, we demonstrate improvements on the existing state of the art methods for trajectory prediction and illustrate how the true multimodal and uncertain nature of crowd interactions can be directly modelled.
Adversarial Noise Layer: Regularize Neural Network By Adding Noise
Oct 30, 2018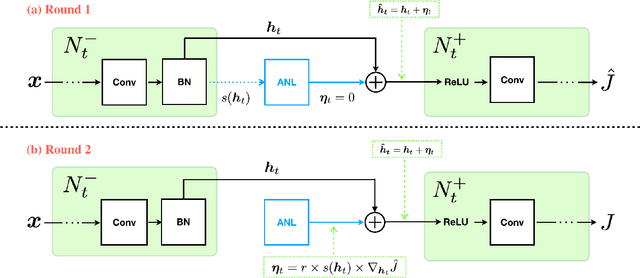
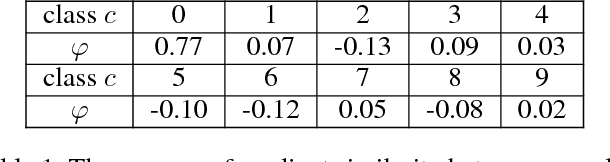
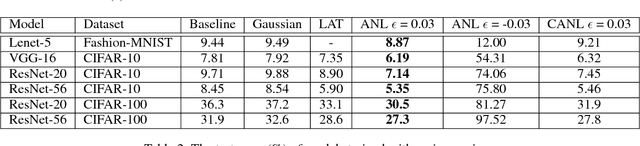
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel regularization method called Adversarial Noise Layer (ANL) and its efficient version called Class Adversarial Noise Layer (CANL), which are able to significantly improve CNN's generalization ability by adding carefully crafted noise into the intermediate layer activations. ANL and CANL can be easily implemented and integrated with most of the mainstream CNN-based models. We compared the effects of the different types of noise and visually demonstrate that our proposed adversarial noise instruct CNN models to learn to extract cleaner feature maps, which further reduce the risk of over-fitting. We also conclude that models trained with ANL or CANL are more robust to the adversarial examples generated by FGSM than the traditional adversarial training approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge