Kodai Nakashima
Primitive Geometry Segment Pre-training for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 08, 2024



Abstract:The construction of 3D medical image datasets presents several issues, including requiring significant financial costs in data collection and specialized expertise for annotation, as well as strict privacy concerns for patient confidentiality compared to natural image datasets. Therefore, it has become a pressing issue in 3D medical image segmentation to enable data-efficient learning with limited 3D medical data and supervision. A promising approach is pre-training, but improving its performance in 3D medical image segmentation is difficult due to the small size of existing 3D medical image datasets. We thus present the Primitive Geometry Segment Pre-training (PrimGeoSeg) method to enable the learning of 3D semantic features by pre-training segmentation tasks using only primitive geometric objects for 3D medical image segmentation. PrimGeoSeg performs more accurate and efficient 3D medical image segmentation without manual data collection and annotation. Further, experimental results show that PrimGeoSeg on SwinUNETR improves performance over learning from scratch on BTCV, MSD (Task06), and BraTS datasets by 3.7%, 4.4%, and 0.3%, respectively. Remarkably, the performance was equal to or better than state-of-the-art self-supervised learning despite the equal number of pre-training data. From experimental results, we conclude that effective pre-training can be achieved by looking at primitive geometric objects only. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/SUPER-TADORY/PrimGeoSeg.
SegRCDB: Semantic Segmentation via Formula-Driven Supervised Learning
Sep 29, 2023



Abstract:Pre-training is a strong strategy for enhancing visual models to efficiently train them with a limited number of labeled images. In semantic segmentation, creating annotation masks requires an intensive amount of labor and time, and therefore, a large-scale pre-training dataset with semantic labels is quite difficult to construct. Moreover, what matters in semantic segmentation pre-training has not been fully investigated. In this paper, we propose the Segmentation Radial Contour DataBase (SegRCDB), which for the first time applies formula-driven supervised learning for semantic segmentation. SegRCDB enables pre-training for semantic segmentation without real images or any manual semantic labels. SegRCDB is based on insights about what is important in pre-training for semantic segmentation and allows efficient pre-training. Pre-training with SegRCDB achieved higher mIoU than the pre-training with COCO-Stuff for fine-tuning on ADE-20k and Cityscapes with the same number of training images. SegRCDB has a high potential to contribute to semantic segmentation pre-training and investigation by enabling the creation of large datasets without manual annotation. The SegRCDB dataset will be released under a license that allows research and commercial use. Code is available at: https://github.com/dahlian00/SegRCDB
Replacing Labeled Real-image Datasets with Auto-generated Contours
Jun 18, 2022



Abstract:In the present work, we show that the performance of formula-driven supervised learning (FDSL) can match or even exceed that of ImageNet-21k without the use of real images, human-, and self-supervision during the pre-training of Vision Transformers (ViTs). For example, ViT-Base pre-trained on ImageNet-21k shows 81.8% top-1 accuracy when fine-tuned on ImageNet-1k and FDSL shows 82.7% top-1 accuracy when pre-trained under the same conditions (number of images, hyperparameters, and number of epochs). Images generated by formulas avoid the privacy/copyright issues, labeling cost and errors, and biases that real images suffer from, and thus have tremendous potential for pre-training general models. To understand the performance of the synthetic images, we tested two hypotheses, namely (i) object contours are what matter in FDSL datasets and (ii) increased number of parameters to create labels affects performance improvement in FDSL pre-training. To test the former hypothesis, we constructed a dataset that consisted of simple object contour combinations. We found that this dataset can match the performance of fractals. For the latter hypothesis, we found that increasing the difficulty of the pre-training task generally leads to better fine-tuning accuracy.
Describing and Localizing Multiple Changes with Transformers
Mar 25, 2021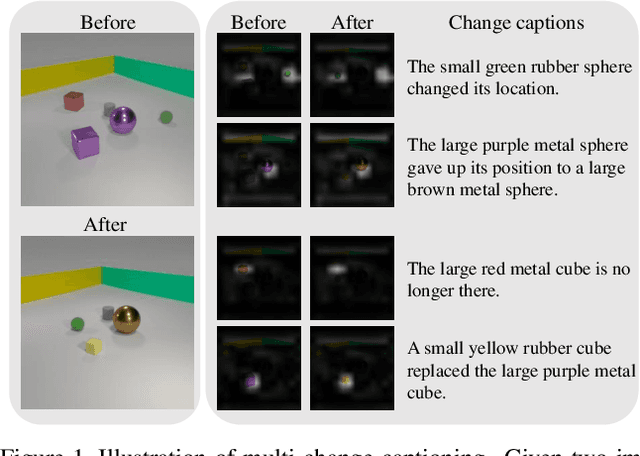
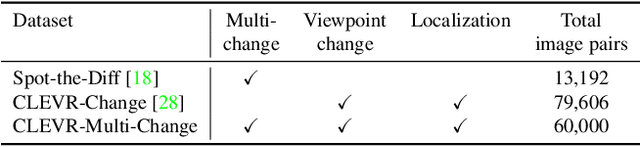
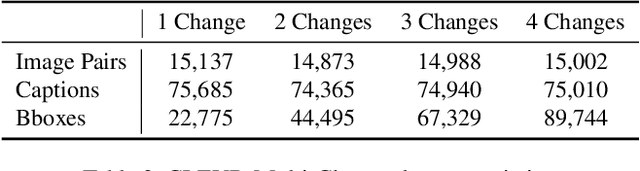

Abstract:Change captioning tasks aim to detect changes in image pairs observed before and after a scene change and generate a natural language description of the changes. Existing change captioning studies have mainly focused on scenes with a single change. However, detecting and describing multiple changed parts in image pairs is essential for enhancing adaptability to complex scenarios. We solve the above issues from three aspects: (i) We propose a CG-based multi-change captioning dataset; (ii) We benchmark existing state-of-the-art methods of single change captioning on multi-change captioning; (iii) We further propose Multi-Change Captioning transformers (MCCFormers) that identify change regions by densely correlating different regions in image pairs and dynamically determines the related change regions with words in sentences. The proposed method obtained the highest scores on four conventional change captioning evaluation metrics for multi-change captioning. In addition, existing methods generate a single attention map for multiple changes and lack the ability to distinguish change regions. In contrast, our proposed method can separate attention maps for each change and performs well with respect to change localization. Moreover, the proposed framework outperformed the previous state-of-the-art methods on an existing change captioning benchmark, CLEVR-Change, by a large margin (+6.1 on BLEU-4 and +9.7 on CIDEr scores), indicating its general ability in change captioning tasks.
Can Vision Transformers Learn without Natural Images?
Mar 24, 2021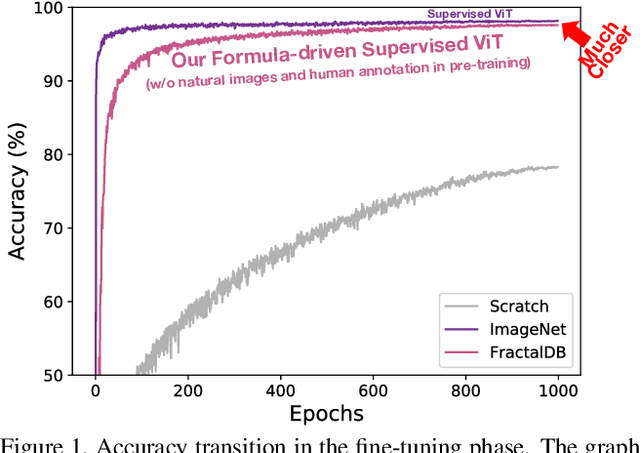
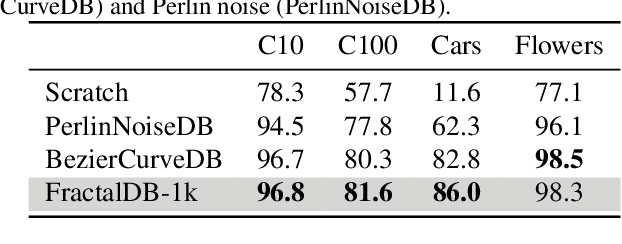
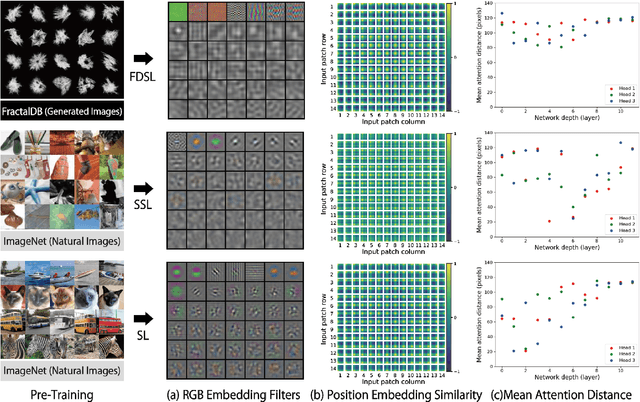
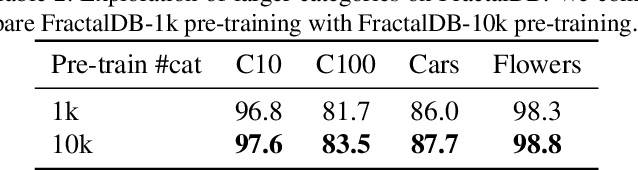
Abstract:Can we complete pre-training of Vision Transformers (ViT) without natural images and human-annotated labels? Although a pre-trained ViT seems to heavily rely on a large-scale dataset and human-annotated labels, recent large-scale datasets contain several problems in terms of privacy violations, inadequate fairness protection, and labor-intensive annotation. In the present paper, we pre-train ViT without any image collections and annotation labor. We experimentally verify that our proposed framework partially outperforms sophisticated Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) methods like SimCLRv2 and MoCov2 without using any natural images in the pre-training phase. Moreover, although the ViT pre-trained without natural images produces some different visualizations from ImageNet pre-trained ViT, it can interpret natural image datasets to a large extent. For example, the performance rates on the CIFAR-10 dataset are as follows: our proposal 97.6 vs. SimCLRv2 97.4 vs. ImageNet 98.0.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge