Justin Theiss
BLENDER: Blended Text Embeddings and Diffusion Residuals for Intra-Class Image Synthesis in Deep Metric Learning
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The rise of Deep Generative Models (DGM) has enabled the generation of high-quality synthetic data. When used to augment authentic data in Deep Metric Learning (DML), these synthetic samples enhance intra-class diversity and improve the performance of downstream DML tasks. We introduce BLenDeR, a diffusion sampling method designed to increase intra-class diversity for DML in a controllable way by leveraging set-theory inspired union and intersection operations on denoising residuals. The union operation encourages any attribute present across multiple prompts, while the intersection extracts the common direction through a principal component surrogate. These operations enable controlled synthesis of diverse attribute combinations within each class, addressing key limitations of existing generative approaches. Experiments on standard DML benchmarks demonstrate that BLenDeR consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines across multiple datasets and backbones. Specifically, BLenDeR achieves 3.7% increase in Recall@1 on CUB-200 and a 1.8% increase on Cars-196, compared to state-of-the-art baselines under standard experimental settings.
VLM-3R: Vision-Language Models Augmented with Instruction-Aligned 3D Reconstruction
May 26, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) for 2D images and videos has motivated extending these models to understand 3D scenes, aiming for human-like visual-spatial intelligence. Nevertheless, achieving deep spatial understanding comparable to human capabilities poses significant challenges in model encoding and data acquisition. Existing methods frequently depend on external depth sensors for geometry capture or utilize off-the-shelf algorithms for pre-constructing 3D maps, thereby limiting their scalability, especially with prevalent monocular video inputs and for time-sensitive applications. In this work, we introduce VLM-3R, a unified framework for Vision-Language Models (VLMs) that incorporates 3D Reconstructive instruction tuning. VLM-3R processes monocular video frames by employing a geometry encoder to derive implicit 3D tokens that represent spatial understanding. Leveraging our Spatial-Visual-View Fusion and over 200K curated 3D reconstructive instruction tuning question-answer (QA) pairs, VLM-3R effectively aligns real-world spatial context with language instructions. This enables monocular 3D spatial assistance and embodied reasoning. To facilitate the evaluation of temporal reasoning, we introduce the Vision-Spatial-Temporal Intelligence benchmark, featuring over 138.6K QA pairs across five distinct tasks focused on evolving spatial relationships. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model, VLM-3R, not only facilitates robust visual-spatial reasoning but also enables the understanding of temporal 3D context changes, excelling in both accuracy and scalability.
InteractAvatar: Modeling Hand-Face Interaction in Photorealistic Avatars with Deformable Gaussians
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:With the rising interest from the community in digital avatars coupled with the importance of expressions and gestures in communication, modeling natural avatar behavior remains an important challenge across many industries such as teleconferencing, gaming, and AR/VR. Human hands are the primary tool for interacting with the environment and essential for realistic human behavior modeling, yet existing 3D hand and head avatar models often overlook the crucial aspect of hand-body interactions, such as between hand and face. We present InteracttAvatar, the first model to faithfully capture the photorealistic appearance of dynamic hand and non-rigid hand-face interactions. Our novel Dynamic Gaussian Hand model, combining template model and 3D Gaussian Splatting as well as a dynamic refinement module, captures pose-dependent change, e.g. the fine wrinkles and complex shadows that occur during articulation. Importantly, our hand-face interaction module models the subtle geometry and appearance dynamics that underlie common gestures. Through experiments of novel view synthesis, self reenactment and cross-identity reenactment, we demonstrate that InteracttAvatar can reconstruct hand and hand-face interactions from monocular or multiview videos with high-fidelity details and be animated with novel poses.
Multi-view Image Diffusion via Coordinate Noise and Fourier Attention
Dec 04, 2024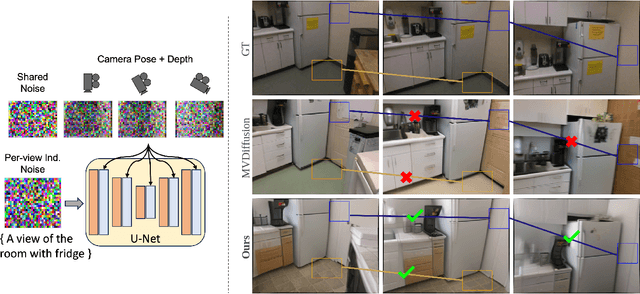
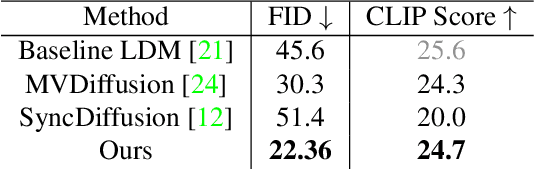
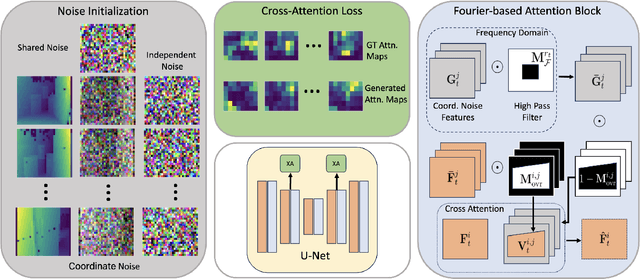
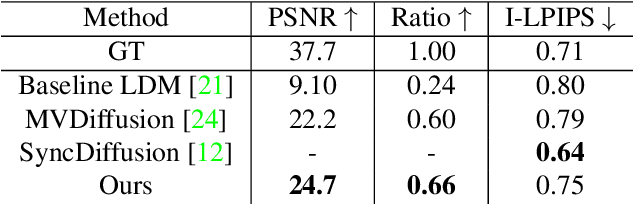
Abstract:Recently, text-to-image generation with diffusion models has made significant advancements in both higher fidelity and generalization capabilities compared to previous baselines. However, generating holistic multi-view consistent images from prompts still remains an important and challenging task. To address this challenge, we propose a diffusion process that attends to time-dependent spatial frequencies of features with a novel attention mechanism as well as novel noise initialization technique and cross-attention loss. This Fourier-based attention block focuses on features from non-overlapping regions of the generated scene in order to better align the global appearance. Our noise initialization technique incorporates shared noise and low spatial frequency information derived from pixel coordinates and depth maps to induce noise correlations across views. The cross-attention loss further aligns features sharing the same prompt across the scene. Our technique improves SOTA on several quantitative metrics with qualitatively better results when compared to other state-of-the-art approaches for multi-view consistency.
Unpaired Image Translation via Vector Symbolic Architectures
Sep 06, 2022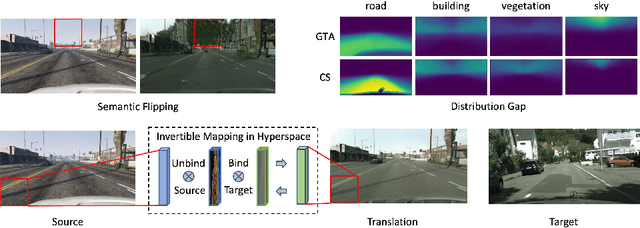
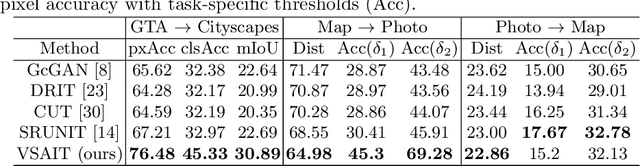


Abstract:Image-to-image translation has played an important role in enabling synthetic data for computer vision. However, if the source and target domains have a large semantic mismatch, existing techniques often suffer from source content corruption aka semantic flipping. To address this problem, we propose a new paradigm for image-to-image translation using Vector Symbolic Architectures (VSA), a theoretical framework which defines algebraic operations in a high-dimensional vector (hypervector) space. We introduce VSA-based constraints on adversarial learning for source-to-target translations by learning a hypervector mapping that inverts the translation to ensure consistency with source content. We show both qualitatively and quantitatively that our method improves over other state-of-the-art techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge