Junming Chen
Expressive Whole-Body Control for Humanoid Robots
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Can we enable humanoid robots to generate rich, diverse, and expressive motions in the real world? We propose to learn a whole-body control policy on a human-sized robot to mimic human motions as realistic as possible. To train such a policy, we leverage the large-scale human motion capture data from the graphics community in a Reinforcement Learning framework. However, directly performing imitation learning with the motion capture dataset would not work on the real humanoid robot, given the large gap in degrees of freedom and physical capabilities. Our method Expressive Whole-Body Control (Exbody) tackles this problem by encouraging the upper humanoid body to imitate a reference motion, while relaxing the imitation constraint on its two legs and only requiring them to follow a given velocity robustly. With training in simulation and Sim2Real transfer, our policy can control a humanoid robot to walk in different styles, shake hands with humans, and even dance with a human in the real world. We conduct extensive studies and comparisons on diverse motions in both simulation and the real world to show the effectiveness of our approach.
DiffSHEG: A Diffusion-Based Approach for Real-Time Speech-driven Holistic 3D Expression and Gesture Generation
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:We propose DiffSHEG, a Diffusion-based approach for Speech-driven Holistic 3D Expression and Gesture generation with arbitrary length. While previous works focused on co-speech gesture or expression generation individually, the joint generation of synchronized expressions and gestures remains barely explored. To address this, our diffusion-based co-speech motion generation transformer enables uni-directional information flow from expression to gesture, facilitating improved matching of joint expression-gesture distributions. Furthermore, we introduce an outpainting-based sampling strategy for arbitrary long sequence generation in diffusion models, offering flexibility and computational efficiency. Our method provides a practical solution that produces high-quality synchronized expression and gesture generation driven by speech. Evaluated on two public datasets, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively. Additionally, a user study confirms the superiority of DiffSHEG over prior approaches. By enabling the real-time generation of expressive and synchronized motions, DiffSHEG showcases its potential for various applications in the development of digital humans and embodied agents.
Federated Domain Generalization for Image Recognition via Cross-Client Style Transfer
Oct 03, 2022



Abstract:Domain generalization (DG) has been a hot topic in image recognition, with a goal to train a general model that can perform well on unseen domains. Recently, federated learning (FL), an emerging machine learning paradigm to train a global model from multiple decentralized clients without compromising data privacy, brings new challenges, also new possibilities, to DG. In the FL scenario, many existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) DG methods become ineffective, because they require the centralization of data from different domains during training. In this paper, we propose a novel domain generalization method for image recognition under federated learning through cross-client style transfer (CCST) without exchanging data samples. Our CCST method can lead to more uniform distributions of source clients, and thus make each local model learn to fit the image styles of all the clients to avoid the different model biases. Two types of style (single image style and overall domain style) with corresponding mechanisms are proposed to be chosen according to different scenarios. Our style representation is exceptionally lightweight and can hardly be used for the reconstruction of the dataset. The level of diversity is also flexible to be controlled with a hyper-parameter. Our method outperforms recent SOTA DG methods on two DG benchmarks (PACS, OfficeHome) and a large-scale medical image dataset (Camelyon17) in the FL setting. Last but not least, our method is orthogonal to many classic DG methods, achieving additive performance by combined utilization.
Real-time Streaming Video Denoising with Bidirectional Buffers
Jul 14, 2022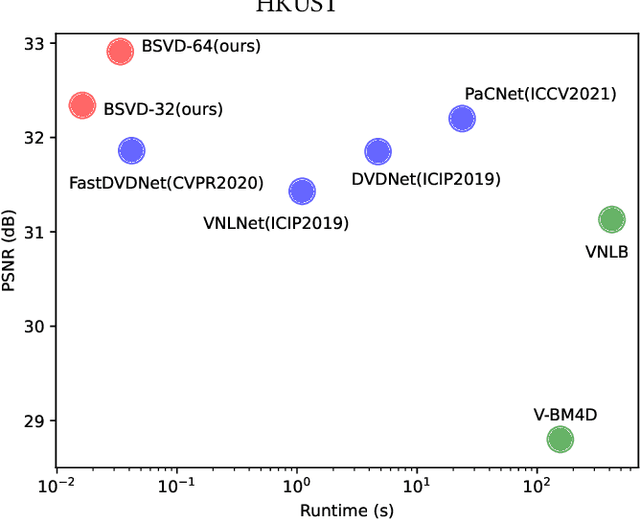
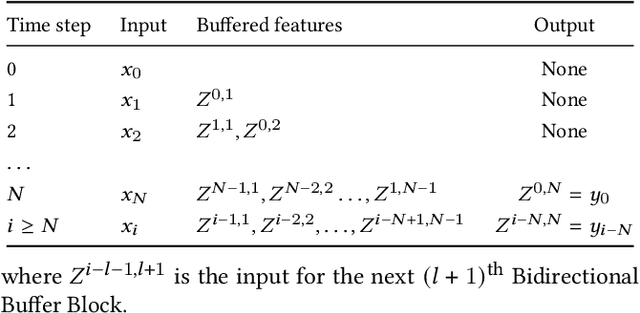
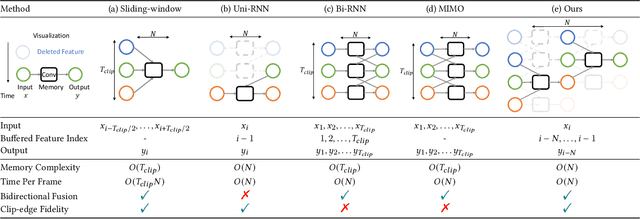
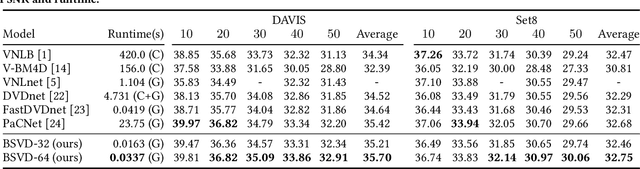
Abstract:Video streams are delivered continuously to save the cost of storage and device memory. Real-time denoising algorithms are typically adopted on the user device to remove the noise involved during the shooting and transmission of video streams. However, sliding-window-based methods feed multiple input frames for a single output and lack computation efficiency. Recent multi-output inference works propagate the bidirectional temporal feature with a parallel or recurrent framework, which either suffers from performance drops on the temporal edges of clips or can not achieve online inference. In this paper, we propose a Bidirectional Streaming Video Denoising (BSVD) framework, to achieve high-fidelity real-time denoising for streaming videos with both past and future temporal receptive fields. The bidirectional temporal fusion for online inference is considered not applicable in the MoViNet. However, we introduce a novel Bidirectional Buffer Block as the core module of our BSVD, which makes it possible during our pipeline-style inference. In addition, our method is concise and flexible to be utilized in both non-blind and blind video denoising. We compare our model with various state-of-the-art video denoising models qualitatively and quantitatively on synthetic and real noise. Our method outperforms previous methods in terms of restoration fidelity and runtime. Our source code is publicly available at https://github.com/ChenyangQiQi/BSVD
Deep Image Spatial Transformation for Person Image Generation
Mar 18, 2020



Abstract:Pose-guided person image generation is to transform a source person image to a target pose. This task requires spatial manipulations of source data. However, Convolutional Neural Networks are limited by the lack of ability to spatially transform the inputs. In this paper, we propose a differentiable global-flow local-attention framework to reassemble the inputs at the feature level. Specifically, our model first calculates the global correlations between sources and targets to predict flow fields. Then, the flowed local patch pairs are extracted from the feature maps to calculate the local attention coefficients. Finally, we warp the source features using a content-aware sampling method with the obtained local attention coefficients. The results of both subjective and objective experiments demonstrate the superiority of our model. Besides, additional results in video animation and view synthesis show that our model is applicable to other tasks requiring spatial transformation. Our source code is available at https://github.com/RenYurui/Global-Flow-Local-Attention.
C3DVQA: Full-Reference Video Quality Assessment with 3D Convolutional Neural Network
Oct 30, 2019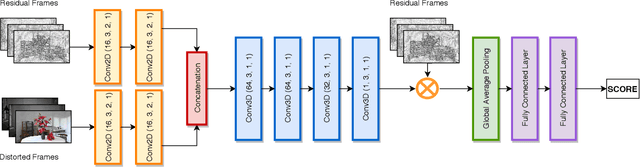
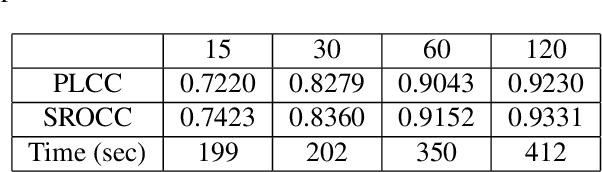
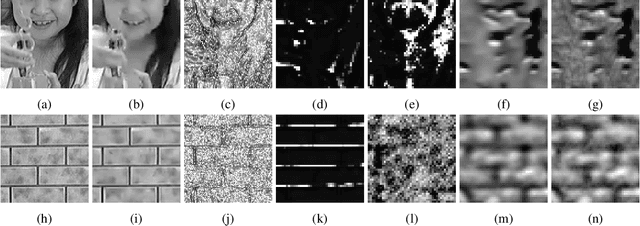
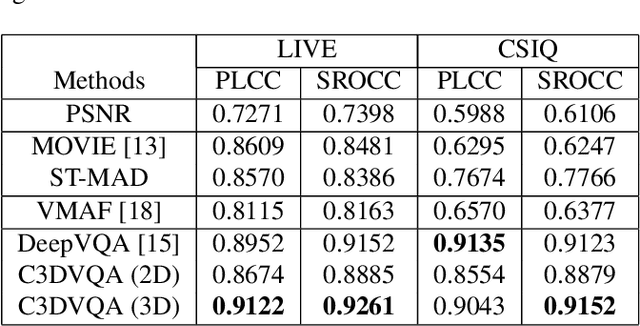
Abstract:Traditional video quality assessment (VQA) methods evaluate localized picture quality and video score is predicted by temporally aggregating frame scores. However, video quality exhibits different characteristics from static image quality due to the existence of temporal masking effects. In this paper, we present a novel architecture, namely C3DVQA, that uses Convolutional Neural Network with 3D kernels (C3D) for full-reference VQA task. C3DVQA combines feature learning and score pooling into one spatiotemporal feature learning process. We use 2D convolutional layers to extract spatial features and 3D convolutional layers to learn spatiotemporal features. We empirically found that 3D convolutional layers are capable to capture temporal masking effects of videos.We evaluated the proposed method on the LIVE and CSIQ datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge