John Suckling
Unified Generative Latent Representation for Functional Brain Graphs
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Functional brain graphs are often characterized with separate graph-theoretic or spectral descriptors, overlooking how these properties covary and partially overlap across brains and conditions. We anticipate that dense, weighted functional connectivity graphs occupy a low-dimensional latent geometry along which both topological and spectral structures display graded variations. Here, we estimated this unified graph representation and enabled generation of dense functional brain graphs through a graph transformer autoencoder with latent diffusion, with spectral geometry providing an inductive bias to guide learning. This geometry-aware latent representation, although unsupervised, meaningfully separated working-memory states and decoded visual stimuli, with performance further enhanced by incorporating neural dynamics. From the diffusion modeled distribution, we were able to sample biologically plausible and structurally grounded synthetic dense graphs.
The Explanation Necessity for Healthcare AI
May 31, 2024


Abstract:Explainability is often critical to the acceptable implementation of artificial intelligence (AI). Nowhere is this more important than healthcare where decision-making directly impacts patients and trust in AI systems is essential. This trust is often built on the explanations and interpretations the AI provides. Despite significant advancements in AI interpretability, there remains the need for clear guidelines on when and to what extent explanations are necessary in the medical context. We propose a novel categorization system with four distinct classes of explanation necessity, guiding the level of explanation required: patient or sample (local) level, cohort or dataset (global) level, or both levels. We introduce a mathematical formulation that distinguishes these categories and offers a practical framework for researchers to determine the necessity and depth of explanations required in medical AI applications. Three key factors are considered: the robustness of the evaluation protocol, the variability of expert observations, and the representation dimensionality of the application. In this perspective, we address the question: When does an AI medical application need to be explained, and at what level of detail?
Contrastive-Adversarial and Diffusion: Exploring pre-training and fine-tuning strategies for sulcal identification
May 29, 2024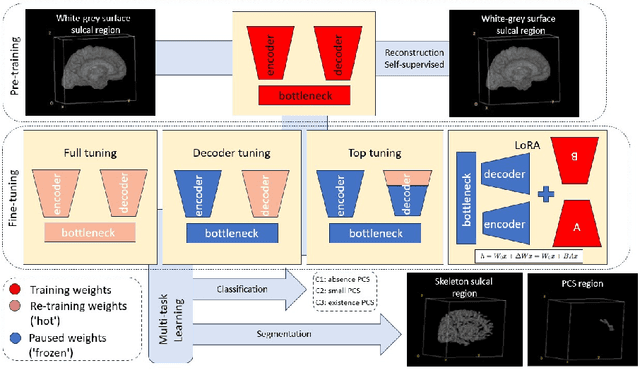
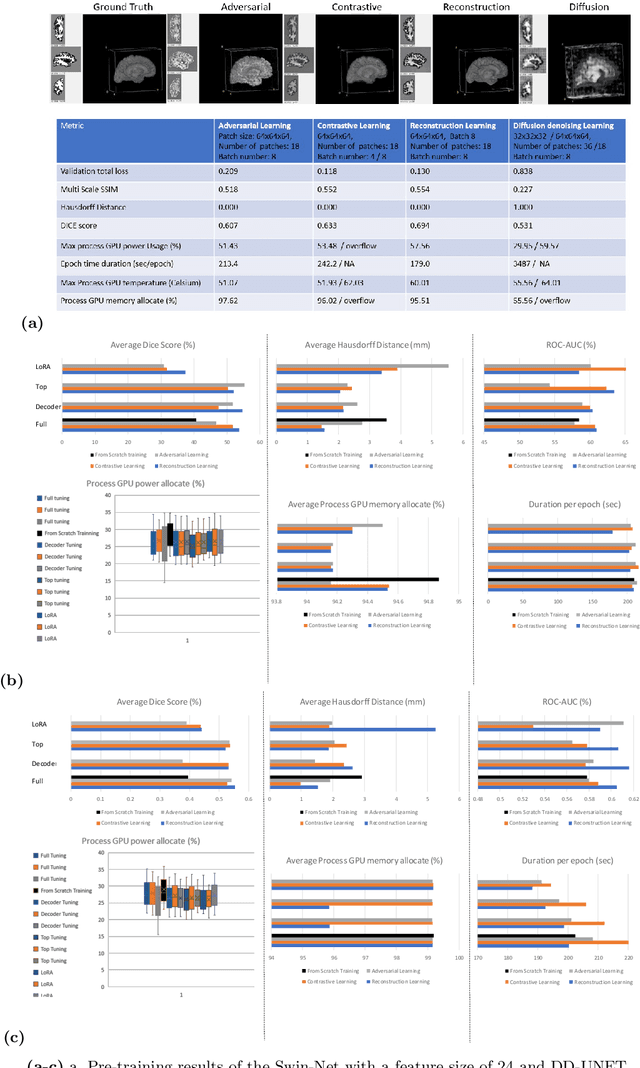
Abstract:In the last decade, computer vision has witnessed the establishment of various training and learning approaches. Techniques like adversarial learning, contrastive learning, diffusion denoising learning, and ordinary reconstruction learning have become standard, representing state-of-the-art methods extensively employed for fully training or pre-training networks across various vision tasks. The exploration of fine-tuning approaches has emerged as a current focal point, addressing the need for efficient model tuning with reduced GPU memory usage and time costs while enhancing overall performance, as exemplified by methodologies like low-rank adaptation (LoRA). Key questions arise: which pre-training technique yields optimal results - adversarial, contrastive, reconstruction, or diffusion denoising? How does the performance of these approaches vary as the complexity of fine-tuning is adjusted? This study aims to elucidate the advantages of pre-training techniques and fine-tuning strategies to enhance the learning process of neural networks in independent identical distribution (IID) cohorts. We underscore the significance of fine-tuning by examining various cases, including full tuning, decoder tuning, top-level tuning, and fine-tuning of linear parameters using LoRA. Systematic summaries of model performance and efficiency are presented, leveraging metrics such as accuracy, time cost, and memory efficiency. To empirically demonstrate our findings, we focus on a multi-task segmentation-classification challenge involving the paracingulate sulcus (PCS) using different 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures by using the TOP-OSLO cohort comprising 596 subjects.
Solving the enigma: Deriving optimal explanations of deep networks
May 16, 2024Abstract:The accelerated progress of artificial intelligence (AI) has popularized deep learning models across domains, yet their inherent opacity poses challenges, notably in critical fields like healthcare, medicine and the geosciences. Explainable AI (XAI) has emerged to shed light on these "black box" models, helping decipher their decision making process. Nevertheless, different XAI methods yield highly different explanations. This inter-method variability increases uncertainty and lowers trust in deep networks' predictions. In this study, for the first time, we propose a novel framework designed to enhance the explainability of deep networks, by maximizing both the accuracy and the comprehensibility of the explanations. Our framework integrates various explanations from established XAI methods and employs a non-linear "explanation optimizer" to construct a unique and optimal explanation. Through experiments on multi-class and binary classification tasks in 2D object and 3D neuroscience imaging, we validate the efficacy of our approach. Our explanation optimizer achieved superior faithfulness scores, averaging 155% and 63% higher than the best performing XAI method in the 3D and 2D applications, respectively. Additionally, our approach yielded lower complexity, increasing comprehensibility. Our results suggest that optimal explanations based on specific criteria are derivable and address the issue of inter-method variability in the current XAI literature.
A 3D explainability framework to uncover learning patterns and crucial sub-regions in variable sulci recognition
Sep 02, 2023Abstract:Precisely identifying sulcal features in brain MRI is made challenging by the variability of brain folding. This research introduces an innovative 3D explainability frame-work that validates outputs from deep learning networks in their ability to detect the paracingulate sulcus, an anatomical feature that may or may not be present on the frontal medial surface of the human brain. This study trained and tested two networks, amalgamating local explainability techniques GradCam and SHAP with a dimensionality reduction method. The explainability framework provided both localized and global explanations, along with accuracy of classification results, revealing pertinent sub-regions contributing to the decision process through a post-fusion transformation of explanatory and statistical features. Leveraging the TOP-OSLO dataset of MRI acquired from patients with schizophrenia, greater accuracies of paracingulate sulcus detection (presence or absence) were found in the left compared to right hemispheres with distinct, but extensive sub-regions contributing to each classification outcome. The study also inadvertently highlighted the critical role of an unbiased annotation protocol in maintaining network performance fairness. Our proposed method not only offers automated, impartial annotations of a variable sulcus but also provides insights into the broader anatomical variations associated with its presence throughout the brain. The adoption of this methodology holds promise for instigating further explorations and inquiries in the field of neuroscience.
Deep Learning in current Neuroimaging: a multivariate approach with power and type I error control but arguable generalization ability
Mar 30, 2021
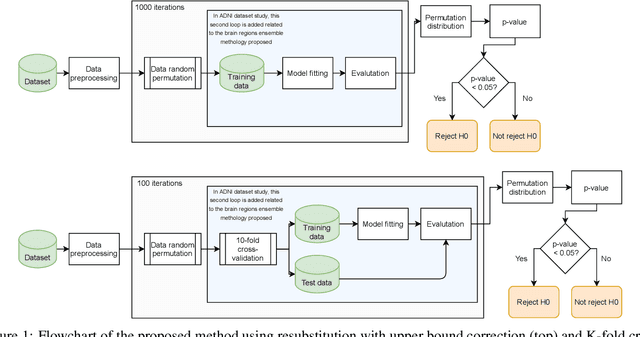
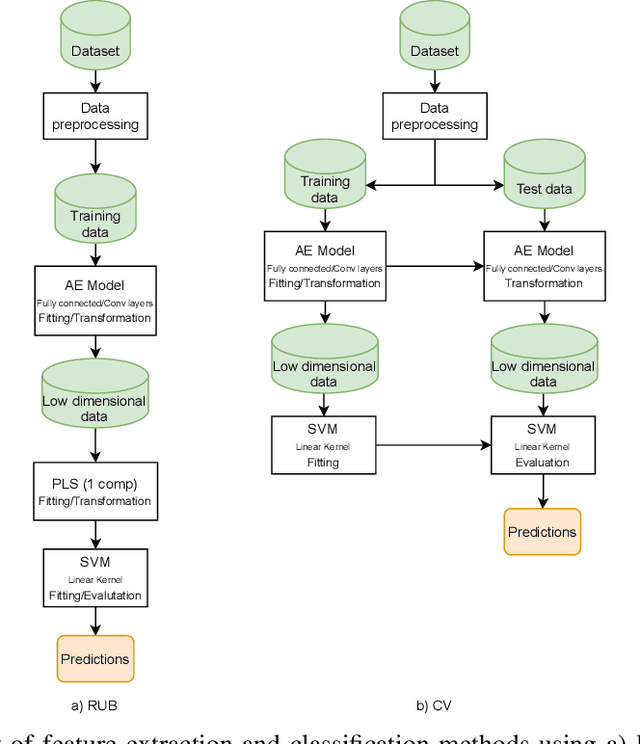
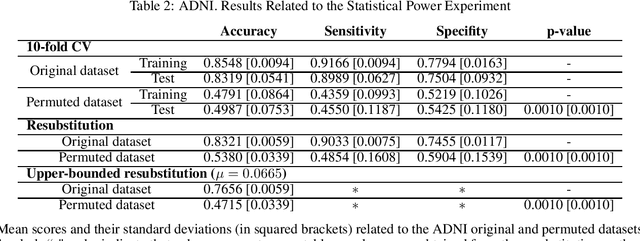
Abstract:Discriminative analysis in neuroimaging by means of deep/machine learning techniques is usually tested with validation techniques, whereas the associated statistical significance remains largely under-developed due to their computational complexity. In this work, a non-parametric framework is proposed that estimates the statistical significance of classifications using deep learning architectures. In particular, a combination of autoencoders (AE) and support vector machines (SVM) is applied to: (i) a one-condition, within-group designs often of normal controls (NC) and; (ii) a two-condition, between-group designs which contrast, for example, Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients with NC (the extension to multi-class analyses is also included). A random-effects inference based on a label permutation test is proposed in both studies using cross-validation (CV) and resubstitution with upper bound correction (RUB) as validation methods. This allows both false positives and classifier overfitting to be detected as well as estimating the statistical power of the test. Several experiments were carried out using the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset, the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network (DIAN) dataset, and a MCI prediction dataset. We found in the permutation test that CV and RUB methods offer a false positive rate close to the significance level and an acceptable statistical power (although lower using cross-validation). A large separation between training and test accuracies using CV was observed, especially in one-condition designs. This implies a low generalization ability as the model fitted in training is not informative with respect to the test set. We propose as solution by applying RUB, whereby similar results are obtained to those of the CV test set, but considering the whole set and with a lower computational cost per iteration.
A connection between the pattern classification problem and the General Linear Model for statistical inference
Dec 16, 2020



Abstract:A connection between the General Linear Model (GLM) in combination with classical statistical inference and the machine learning (MLE)-based inference is described in this paper. Firstly, the estimation of the GLM parameters is expressed as a Linear Regression Model (LRM) of an indicator matrix, that is, in terms of the inverse problem of regressing the observations. In other words, both approaches, i.e. GLM and LRM, apply to different domains, the observation and the label domains, and are linked by a normalization value at the least-squares solution. Subsequently, from this relationship we derive a statistical test based on a more refined predictive algorithm, i.e. the (non)linear Support Vector Machine (SVM) that maximizes the class margin of separation, within a permutation analysis. The MLE-based inference employs a residual score and includes the upper bound to compute a better estimation of the actual (real) error. Experimental results demonstrate how the parameter estimations derived from each model resulted in different classification performances in the equivalent inverse problem. Moreover, using real data the aforementioned predictive algorithms within permutation tests, including such model-free estimators, are able to provide a good trade-off between type I error and statistical power.
Single-participant structural connectivity matrices lead to greater accuracy in classification of participants than function in autism in MRI
May 27, 2020



Abstract:In this work, we introduce a technique of deriving symmetric connectivity matrices from regional histograms of grey-matter volume estimated from T1-weighted MRIs. We then validated the technique by inputting the connectivity matrices into a convolutional neural network (CNN) to classify between participants with autism and age-, motion-, and intracranial-volume-matched controls from six different databases (29,288 total connectomes, mean age = 30.72, range 0.42-78.00, including 1555 subjects with autism). We compared this method to similar classifications of the same participants using fMRI connectivity matrices as well as univariate estimates of grey-matter volumes. We further applied graph-theoretical metrics on output class activation maps to identify areas of the matrices that the CNN preferentially used to make the classification, focusing particularly on hubs. Our results gave AUROCs of 0.7298 (69.71% accuracy) when classifying by only structural connectivity, 0.6964 (67.72% accuracy) when classifying by only functional connectivity, and 0.7037 (66.43% accuracy) when classifying by univariate grey matter volumes. Combining structural and functional connectivities gave an AUROC of 0.7354 (69.40% accuracy). Graph analysis of class activation maps revealed no distinguishable network patterns for functional inputs, but did reveal localized differences between groups in bilateral Heschl's gyrus and upper vermis for structural connectivity. This work provides a simple means of feature extraction for inputting large numbers of structural MRIs into machine learning models.
Stochastic encoding of graphs in deep learning allows for complex analysis of gender classification in resting-state and task functional brain networks from the UK Biobank
Feb 25, 2020



Abstract:Classification of whole-brain functional connectivity MRI data with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) has shown promise, but the complexity of these models impedes understanding of which aspects of brain activity contribute to classification. While visualization techniques have been developed to interpret CNNs, bias inherent in the method of encoding abstract input data, as well as the natural variance of deep learning models, detract from the accuracy of these techniques. We introduce a stochastic encoding method in an ensemble of CNNs to classify functional connectomes by gender. We applied our method to resting-state and task data from the UK BioBank, using two visualization techniques to measure the salience of three brain networks involved in task- and resting-states, and their interaction. To regress confounding factors such as head motion, age, and intracranial volume, we introduced a multivariate balancing algorithm to ensure equal distributions of such covariates between classes in our data. We achieved a final AUROC of 0.8459. We found that resting-state data classifies more accurately than task data, with the inner salience network playing the most important role of the three networks overall in classification of resting-state data and connections to the central executive network in task data.
Ensemble Deep Learning on Large, Mixed-Site fMRI Datasets in Autism and Other Tasks
Feb 14, 2020



Abstract:Deep learning models for MRI classification face two recurring problems: they are typically limited by low sample size, and are abstracted by their own complexity (the "black box problem"). In this paper, we train a convolutional neural network (CNN) with the largest multi-source, functional MRI (fMRI) connectomic dataset ever compiled, consisting of 43,858 datapoints. We apply this model to a cross-sectional comparison of autism (ASD) vs typically developing (TD) controls that has proved difficult to characterise with inferential statistics. To contextualise these findings, we additionally perform classifications of gender and task vs rest. Employing class-balancing to build a training set, we trained 3$\times$300 modified CNNs in an ensemble model to classify fMRI connectivity matrices with overall AUROCs of 0.6774, 0.7680, and 0.9222 for ASD vs TD, gender, and task vs rest, respectively. Additionally, we aim to address the black box problem in this context using two visualization methods. First, class activation maps show which functional connections of the brain our models focus on when performing classification. Second, by analyzing maximal activations of the hidden layers, we were also able to explore how the model organizes a large and mixed-centre dataset, finding that it dedicates specific areas of its hidden layers to processing different covariates of data (depending on the independent variable analyzed), and other areas to mix data from different sources. Our study finds that deep learning models that distinguish ASD from TD controls focus broadly on temporal and cerebellar connections, with a particularly high focus on the right caudate nucleus and paracentral sulcus.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge