John Onofrey
Multi-View and Multi-Scale Alignment for Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training in Mammography
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) shows promise in medical image analysis but requires substantial data and computational resources. Due to these restrictions, existing CLIP applications in medical imaging focus mainly on modalities like chest X-rays that have abundant image-report data available, leaving many other important modalities under-explored. Here, we propose the first adaptation of the full CLIP model to mammography, which presents significant challenges due to labeled data scarcity, high-resolution images with small regions of interest, and data imbalance. We first develop a specialized supervision framework for mammography that leverages its multi-view nature. Furthermore, we design a symmetric local alignment module to better focus on detailed features in high-resolution images. Lastly, we incorporate a parameter-efficient fine-tuning approach for large language models pre-trained with medical knowledge to address data limitations. Our multi-view and multi-scale alignment (MaMA) method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines for three different tasks on two large real-world mammography datasets, EMBED and RSNA-Mammo, with only 52% model size compared with the largest baseline.
Multi-scale Super-resolution Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging with Adjustable Sharpness
Jun 17, 2022



Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging (MRSI) is a valuable tool for studying metabolic activities in the human body, but the current applications are limited to low spatial resolutions. The existing deep learning-based MRSI super-resolution methods require training a separate network for each upscaling factor, which is time-consuming and memory inefficient. We tackle this multi-scale super-resolution problem using a Filter Scaling strategy that modulates the convolution filters based on the upscaling factor, such that a single network can be used for various upscaling factors. Observing that each metabolite has distinct spatial characteristics, we also modulate the network based on the specific metabolite. Furthermore, our network is conditioned on the weight of adversarial loss so that the perceptual sharpness of the super-resolved metabolic maps can be adjusted within a single network. We incorporate these network conditionings using a novel Multi-Conditional Module. The experiments were carried out on a 1H-MRSI dataset from 15 high-grade glioma patients. Results indicate that the proposed network achieves the best performance among several multi-scale super-resolution methods and can provide super-resolved metabolic maps with adjustable sharpness.
Incremental Learning Meets Transfer Learning: Application to Multi-site Prostate MRI Segmentation
Jun 03, 2022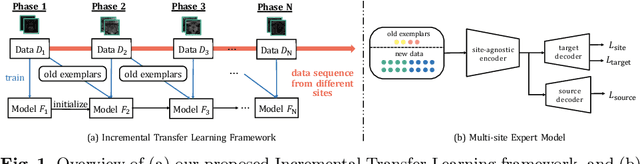
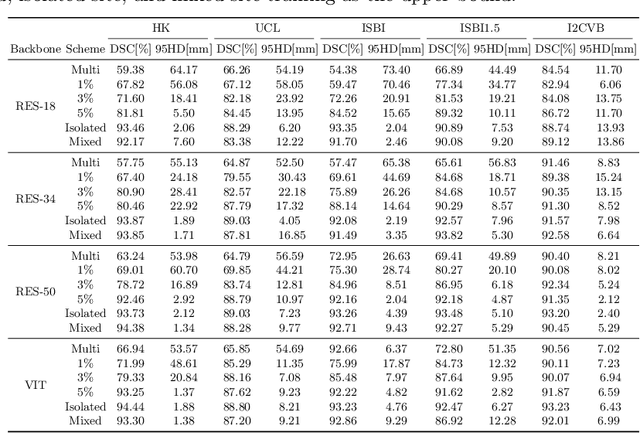
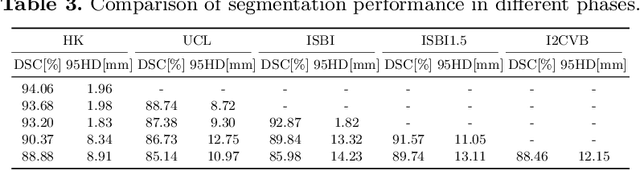
Abstract:Many medical datasets have recently been created for medical image segmentation tasks, and it is natural to question whether we can use them to sequentially train a single model that (1) performs better on all these datasets, and (2) generalizes well and transfers better to the unknown target site domain. Prior works have achieved this goal by jointly training one model on multi-site datasets, which achieve competitive performance on average but such methods rely on the assumption about the availability of all training data, thus limiting its effectiveness in practical deployment. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-site segmentation framework called incremental-transfer learning (ITL), which learns a model from multi-site datasets in an end-to-end sequential fashion. Specifically, "incremental" refers to training sequentially constructed datasets, and "transfer" is achieved by leveraging useful information from the linear combination of embedding features on each dataset. In addition, we introduce our ITL framework, where we train the network including a site-agnostic encoder with pre-trained weights and at most two segmentation decoder heads. We also design a novel site-level incremental loss in order to generalize well on the target domain. Second, we show for the first time that leveraging our ITL training scheme is able to alleviate challenging catastrophic forgetting problems in incremental learning. We conduct experiments using five challenging benchmark datasets to validate the effectiveness of our incremental-transfer learning approach. Our approach makes minimal assumptions on computation resources and domain-specific expertise, and hence constitutes a strong starting point in multi-site medical image segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge