Johannes Kofler
Residual Neural Networks for the Prediction of Planetary Collision Outcomes
Oct 09, 2022Abstract:Fast and accurate treatment of collisions in the context of modern N-body planet formation simulations remains a challenging task due to inherently complex collision processes. We aim to tackle this problem with machine learning (ML), in particular via residual neural networks. Our model is motivated by the underlying physical processes of the data-generating process and allows for flexible prediction of post-collision states. We demonstrate that our model outperforms commonly used collision handling methods such as perfect inelastic merging and feed-forward neural networks in both prediction accuracy and out-of-distribution generalization. Our model outperforms the current state of the art in 20/24 experiments. We provide a dataset that consists of 10164 Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) simulations of pairwise planetary collisions. The dataset is specifically suited for ML research to improve computational aspects for collision treatment and for studying planetary collisions in general. We formulate the ML task as a multi-task regression problem, allowing simple, yet efficient training of ML models for collision treatment in an end-to-end manner. Our models can be easily integrated into existing N-body frameworks and can be used within our chosen parameter space of initial conditions, i.e. where similar-sized collisions during late-stage terrestrial planet formation typically occur.
Few-Shot Learning by Dimensionality Reduction in Gradient Space
Jun 07, 2022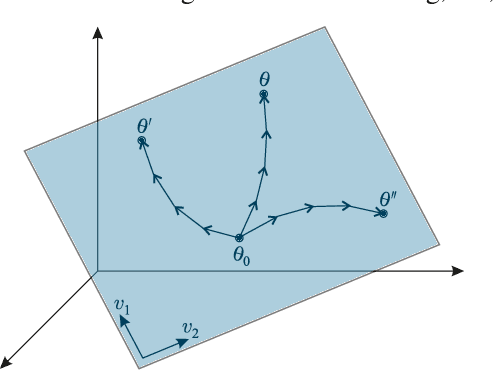
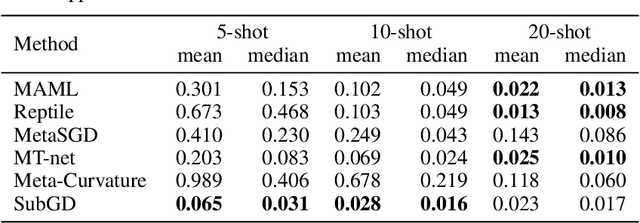
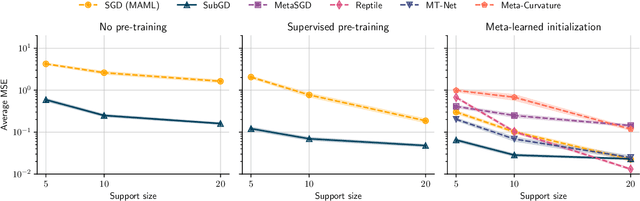
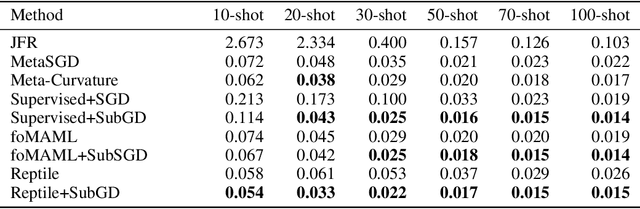
Abstract:We introduce SubGD, a novel few-shot learning method which is based on the recent finding that stochastic gradient descent updates tend to live in a low-dimensional parameter subspace. In experimental and theoretical analyses, we show that models confined to a suitable predefined subspace generalize well for few-shot learning. A suitable subspace fulfills three criteria across the given tasks: it (a) allows to reduce the training error by gradient flow, (b) leads to models that generalize well, and (c) can be identified by stochastic gradient descent. SubGD identifies these subspaces from an eigendecomposition of the auto-correlation matrix of update directions across different tasks. Demonstrably, we can identify low-dimensional suitable subspaces for few-shot learning of dynamical systems, which have varying properties described by one or few parameters of the analytical system description. Such systems are ubiquitous among real-world applications in science and engineering. We experimentally corroborate the advantages of SubGD on three distinct dynamical systems problem settings, significantly outperforming popular few-shot learning methods both in terms of sample efficiency and performance.
Supervised machine learning classification for short straddles on the S&P500
Apr 26, 2022


Abstract:In this working paper we present our current progress in the training of machine learning models to execute short option strategies on the S&P500. As a first step, this paper is breaking this problem down to a supervised classification task to decide if a short straddle on the S&P500 should be executed or not on a daily basis. We describe our used framework and present an overview over our evaluation metrics on different classification models. In this preliminary work, using standard machine learning techniques and without hyperparameter search, we find no statistically significant outperformance to a simple "trade always" strategy, but gain additional insights on how we could proceed in further experiments.
Quantum Optical Experiments Modeled by Long Short-Term Memory
Oct 30, 2019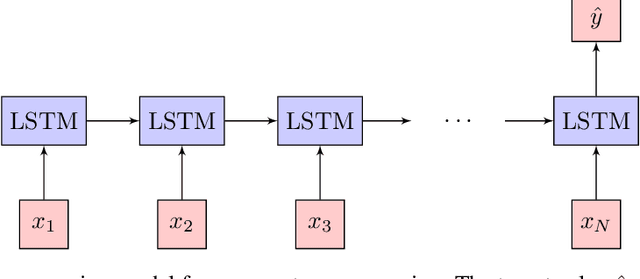
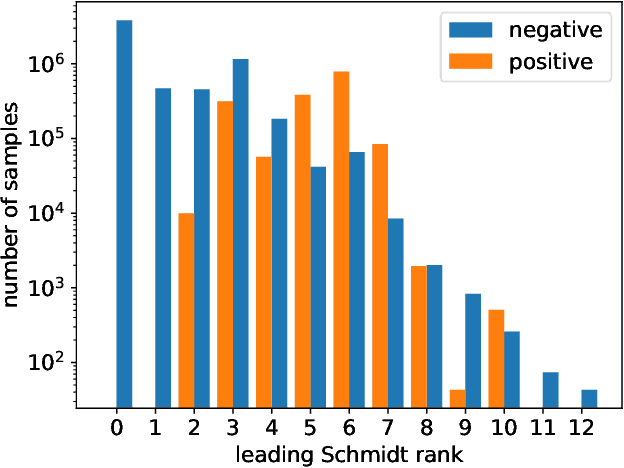
Abstract:We demonstrate how machine learning is able to model experiments in quantum physics. Quantum entanglement is a cornerstone for upcoming quantum technologies such as quantum computation and quantum cryptography. Of particular interest are complex quantum states with more than two particles and a large number of entangled quantum levels. Given such a multiparticle high-dimensional quantum state, it is usually impossible to reconstruct an experimental setup that produces it. To search for interesting experiments, one thus has to randomly create millions of setups on a computer and calculate the respective output states. In this work, we show that machine learning models can provide significant improvement over random search. We demonstrate that a long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network can successfully learn to model quantum experiments by correctly predicting output state characteristics for given setups without the necessity of computing the states themselves. This approach not only allows for faster search but is also an essential step towards automated design of multiparticle high-dimensional quantum experiments using generative machine learning models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge