Joann G. Elmore
CrossFusion: A Multi-Scale Cross-Attention Convolutional Fusion Model for Cancer Survival Prediction
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Cancer survival prediction from whole slide images (WSIs) is a challenging task in computational pathology due to the large size, irregular shape, and high granularity of the WSIs. These characteristics make it difficult to capture the full spectrum of patterns, from subtle cellular abnormalities to complex tissue interactions, which are crucial for accurate prognosis. To address this, we propose CrossFusion, a novel multi-scale feature integration framework that extracts and fuses information from patches across different magnification levels. By effectively modeling both scale-specific patterns and their interactions, CrossFusion generates a rich feature set that enhances survival prediction accuracy. We validate our approach across six cancer types from public datasets, demonstrating significant improvements over existing state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, when coupled with domain-specific feature extraction backbones, our method shows further gains in prognostic performance compared to general-purpose backbones. The source code is available at: https://github.com/RustinS/CrossFusion
PathFinder: A Multi-Modal Multi-Agent System for Medical Diagnostic Decision-Making Applied to Histopathology
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:Diagnosing diseases through histopathology whole slide images (WSIs) is fundamental in modern pathology but is challenged by the gigapixel scale and complexity of WSIs. Trained histopathologists overcome this challenge by navigating the WSI, looking for relevant patches, taking notes, and compiling them to produce a final holistic diagnostic. Traditional AI approaches, such as multiple instance learning and transformer-based models, fail short of such a holistic, iterative, multi-scale diagnostic procedure, limiting their adoption in the real-world. We introduce PathFinder, a multi-modal, multi-agent framework that emulates the decision-making process of expert pathologists. PathFinder integrates four AI agents, the Triage Agent, Navigation Agent, Description Agent, and Diagnosis Agent, that collaboratively navigate WSIs, gather evidence, and provide comprehensive diagnoses with natural language explanations. The Triage Agent classifies the WSI as benign or risky; if risky, the Navigation and Description Agents iteratively focus on significant regions, generating importance maps and descriptive insights of sampled patches. Finally, the Diagnosis Agent synthesizes the findings to determine the patient's diagnostic classification. Our Experiments show that PathFinder outperforms state-of-the-art methods in skin melanoma diagnosis by 8% while offering inherent explainability through natural language descriptions of diagnostically relevant patches. Qualitative analysis by pathologists shows that the Description Agent's outputs are of high quality and comparable to GPT-4o. PathFinder is also the first AI-based system to surpass the average performance of pathologists in this challenging melanoma classification task by 9%, setting a new record for efficient, accurate, and interpretable AI-assisted diagnostics in pathology. Data, code and models available at https://pathfinder-dx.github.io/
Semantics-Aware Attention Guidance for Diagnosing Whole Slide Images
Apr 16, 2024
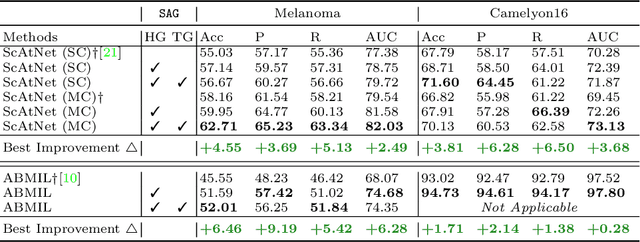


Abstract:Accurate cancer diagnosis remains a critical challenge in digital pathology, largely due to the gigapixel size and complex spatial relationships present in whole slide images. Traditional multiple instance learning (MIL) methods often struggle with these intricacies, especially in preserving the necessary context for accurate diagnosis. In response, we introduce a novel framework named Semantics-Aware Attention Guidance (SAG), which includes 1) a technique for converting diagnostically relevant entities into attention signals, and 2) a flexible attention loss that efficiently integrates various semantically significant information, such as tissue anatomy and cancerous regions. Our experiments on two distinct cancer datasets demonstrate consistent improvements in accuracy, precision, and recall with two state-of-the-art baseline models. Qualitative analysis further reveals that the incorporation of heuristic guidance enables the model to focus on regions critical for diagnosis. SAG is not only effective for the models discussed here, but its adaptability extends to any attention-based diagnostic model. This opens up exciting possibilities for further improving the accuracy and efficiency of cancer diagnostics.
Classifying Breast Histopathology Images with a Ductal Instance-Oriented Pipeline
Dec 11, 2020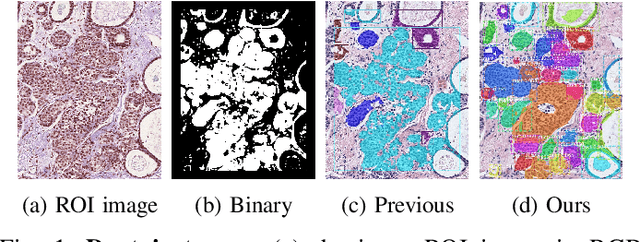
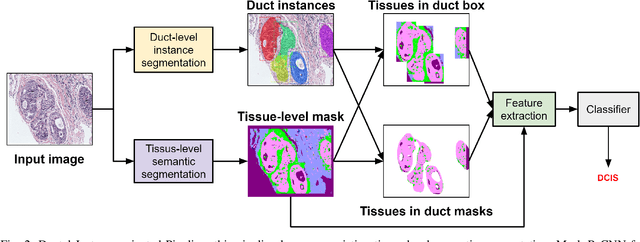
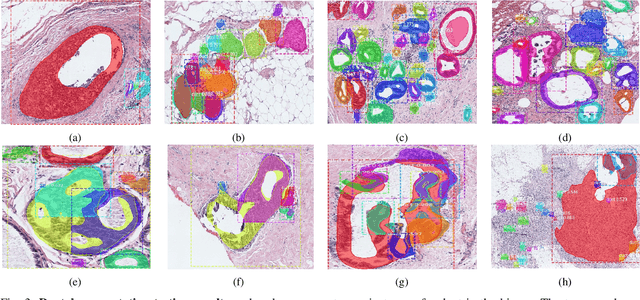
Abstract:In this study, we propose the Ductal Instance-Oriented Pipeline (DIOP) that contains a duct-level instance segmentation model, a tissue-level semantic segmentation model, and three-levels of features for diagnostic classification. Based on recent advancements in instance segmentation and the Mask R-CNN model, our duct-level segmenter tries to identify each ductal individual inside a microscopic image; then, it extracts tissue-level information from the identified ductal instances. Leveraging three levels of information obtained from these ductal instances and also the histopathology image, the proposed DIOP outperforms previous approaches (both feature-based and CNN-based) in all diagnostic tasks; for the four-way classification task, the DIOP achieves comparable performance to general pathologists in this unique dataset. The proposed DIOP only takes a few seconds to run in the inference time, which could be used interactively on most modern computers. More clinical explorations are needed to study the robustness and generalizability of this system in the future.
HATNet: An End-to-End Holistic Attention Network for Diagnosis of Breast Biopsy Images
Jul 25, 2020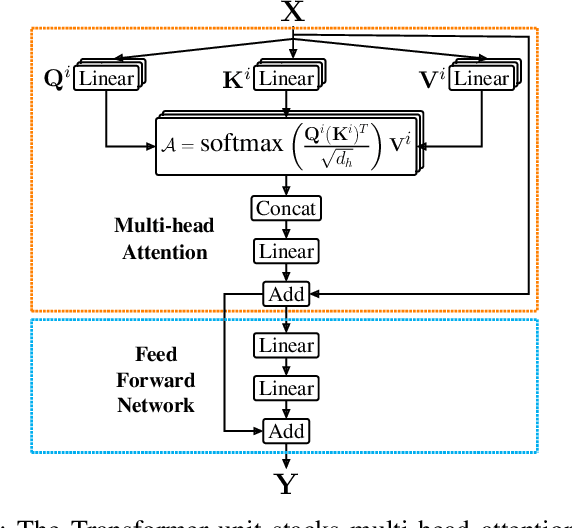
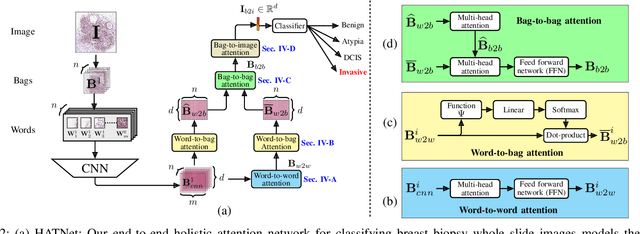
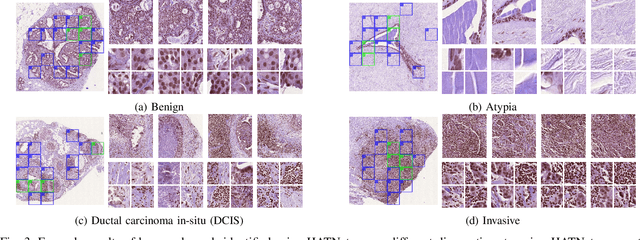
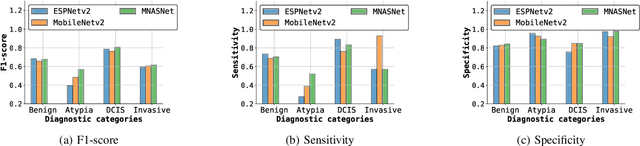
Abstract:Training end-to-end networks for classifying gigapixel size histopathological images is computationally intractable. Most approaches are patch-based and first learn local representations (patch-wise) before combining these local representations to produce image-level decisions. However, dividing large tissue structures into patches limits the context available to these networks, which may reduce their ability to learn representations from clinically relevant structures. In this paper, we introduce a novel attention-based network, the Holistic ATtention Network (HATNet) to classify breast biopsy images. We streamline the histopathological image classification pipeline and show how to learn representations from gigapixel size images end-to-end. HATNet extends the bag-of-words approach and uses self-attention to encode global information, allowing it to learn representations from clinically relevant tissue structures without any explicit supervision. It outperforms the previous best network Y-Net, which uses supervision in the form of tissue-level segmentation masks, by 8%. Importantly, our analysis reveals that HATNet learns representations from clinically relevant structures, and it matches the classification accuracy of human pathologists for this challenging test set. Our source code is available at \url{https://github.com/sacmehta/HATNet}
Y-Net: Joint Segmentation and Classification for Diagnosis of Breast Biopsy Images
Jun 04, 2018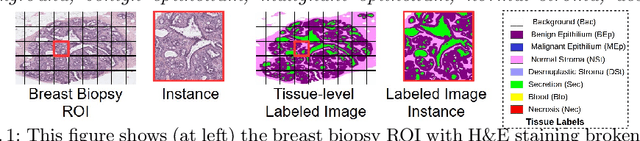
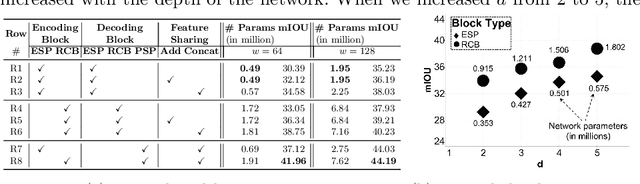
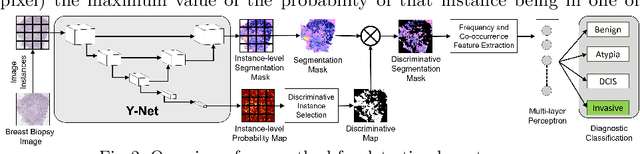
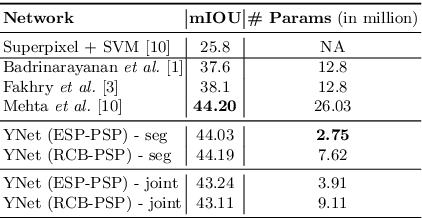
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a conceptually simple network for generating discriminative tissue-level segmentation masks for the purpose of breast cancer diagnosis. Our method efficiently segments different types of tissues in breast biopsy images while simultaneously predicting a discriminative map for identifying important areas in an image. Our network, Y-Net, extends and generalizes U-Net by adding a parallel branch for discriminative map generation and by supporting convolutional block modularity, which allows the user to adjust network efficiency without altering the network topology. Y-Net delivers state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy while learning 6.6x fewer parameters than its closest competitors. The addition of descriptive power from Y-Net's discriminative segmentation masks improve diagnostic classification accuracy by 7% over state-of-the-art methods for diagnostic classification. Source code is available at: https://sacmehta.github.io/YNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge