Jiwei Liu
Nemotron-4 340B Technical Report
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:We release the Nemotron-4 340B model family, including Nemotron-4-340B-Base, Nemotron-4-340B-Instruct, and Nemotron-4-340B-Reward. Our models are open access under the NVIDIA Open Model License Agreement, a permissive model license that allows distribution, modification, and use of the models and its outputs. These models perform competitively to open access models on a wide range of evaluation benchmarks, and were sized to fit on a single DGX H100 with 8 GPUs when deployed in FP8 precision. We believe that the community can benefit from these models in various research studies and commercial applications, especially for generating synthetic data to train smaller language models. Notably, over 98% of data used in our model alignment process is synthetically generated, showcasing the effectiveness of these models in generating synthetic data. To further support open research and facilitate model development, we are also open-sourcing the synthetic data generation pipeline used in our model alignment process.
Nemotron-4 15B Technical Report
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Nemotron-4 15B, a 15-billion-parameter large multilingual language model trained on 8 trillion text tokens. Nemotron-4 15B demonstrates strong performance when assessed on English, multilingual, and coding tasks: it outperforms all existing similarly-sized open models on 4 out of 7 downstream evaluation areas and achieves competitive performance to the leading open models in the remaining ones. Specifically, Nemotron-4 15B exhibits the best multilingual capabilities of all similarly-sized models, even outperforming models over four times larger and those explicitly specialized for multilingual tasks.
Heterogenous Ensemble of Models for Molecular Property Prediction
Nov 20, 2022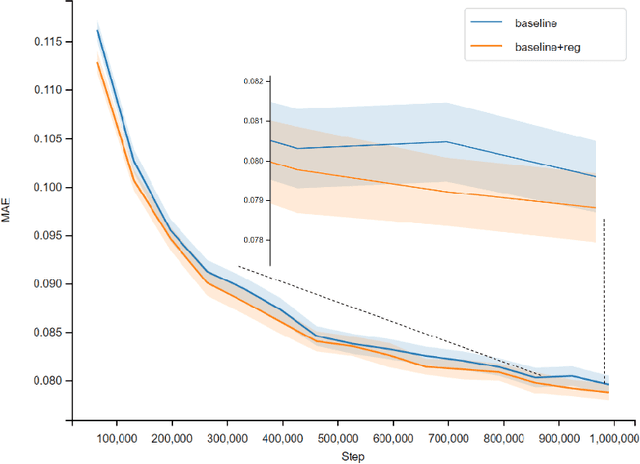
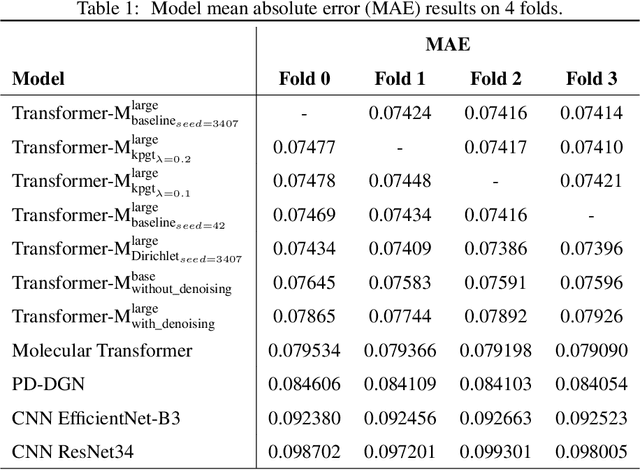
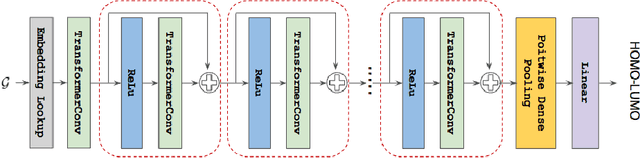
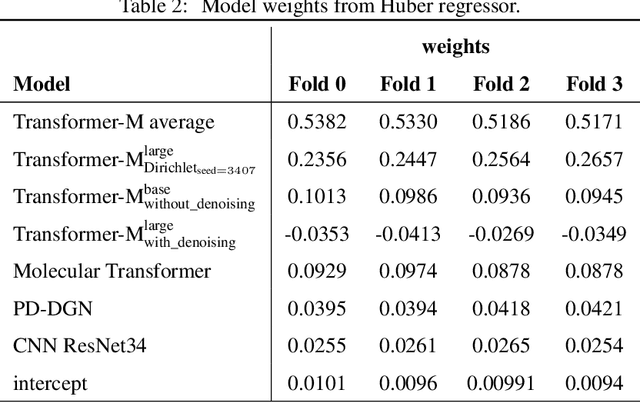
Abstract:Previous works have demonstrated the importance of considering different modalities on molecules, each of which provide a varied granularity of information for downstream property prediction tasks. Our method combines variants of the recent TransformerM architecture with Transformer, GNN, and ResNet backbone architectures. Models are trained on the 2D data, 3D data, and image modalities of molecular graphs. We ensemble these models with a HuberRegressor. The models are trained on 4 different train/validation splits of the original train + valid datasets. This yields a winning solution to the 2\textsuperscript{nd} edition of the OGB Large-Scale Challenge (2022) on the PCQM4Mv2 molecular property prediction dataset. Our proposed method achieves a test-challenge MAE of $0.0723$ and a validation MAE of $0.07145$. Total inference time for our solution is less than 2 hours. We open-source our code at https://github.com/jfpuget/NVIDIA-PCQM4Mv2.
GPU Accelerated Exhaustive Search for Optimal Ensemble of Black-Box Optimization Algorithms
Dec 12, 2020
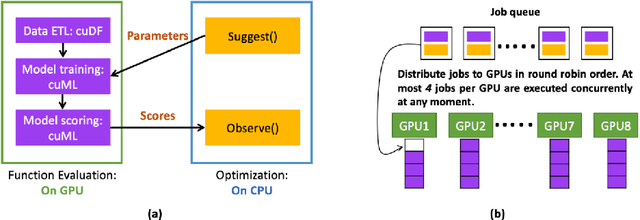
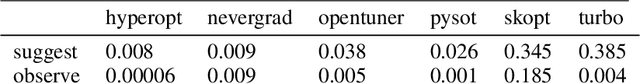
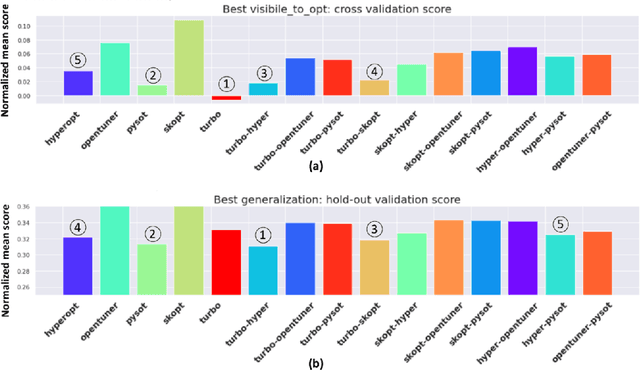
Abstract:Black-box optimization is essential for tuning complex machine learning algorithms which are easier to experiment with than to understand. In this paper, we show that a simple ensemble of black-box optimization algorithms can outperform any single one of them. However, searching for such an optimal ensemble requires a large number of experiments. We propose a Multi-GPU-optimized framework to accelerate a brute force search for the optimal ensemble of black-box optimization algorithms by running many experiments in parallel. The lightweight optimizations are performed by CPU while expensive model training and evaluations are assigned to GPUs. We evaluate 15 optimizers by training 2.7 million models and running 541,440 optimizations. On a DGX-1, the search time is reduced from more than 10 days on two 20-core CPUs to less than 24 hours on 8-GPUs. With the optimal ensemble found by GPU-accelerated exhaustive search, we won the 2nd place of NeurIPS 2020 black-box optimization challenge.
A Locating Model for Pulmonary Tuberculosis Diagnosis in Radiographs
Oct 22, 2019



Abstract:Objective: We propose an end-to-end CNN-based locating model for pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis in radiographs. This model makes full use of chest radiograph (X-ray) for its improved accessibility, reduced cost and high accuracy for TB disease. Methods: Several specialized improvements are proposed for detection task in medical field. A false positive (FP) restrictor head is introduced for FP reduction. Anchor-oriented network heads is proposed in the position regression section. An optimization of loss function is designed for hard example mining. Results: The experimental results show that when the threshold of intersection over union (IoU) is set to 0.3, the average precision (AP) of two test data sets provided by different hospitals reaches 0.9023 and 0.9332. Ablation experiments shows that hard example mining and change of regressor heads contribute most in this work, but FP restriction is necessary in a CAD diagnose system. Conclusion: The results prove the high precision and good generalization ability of our proposed model comparing to previous works. Significance: We first make full use of the feature extraction ability of CNNs in TB diagnostic field and make exploration in localization of TB, when the previous works focus on the weaker task of healthy-sick subject classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge