Jinpeng Chen
PhoStream: Benchmarking Real-World Streaming for Omnimodal Assistants in Mobile Scenarios
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models excel at offline audio-visual understanding, but their ability to serve as mobile assistants in continuous real-world streams remains underexplored. In daily phone use, mobile assistants must track streaming audio-visual inputs and respond at the right time, yet existing benchmarks are often restricted to multiple-choice questions or use shorter videos. In this paper, we introduce PhoStream, the first mobile-centric streaming benchmark that unifies on-screen and off-screen scenarios to evaluate video, audio, and temporal reasoning. PhoStream contains 5,572 open-ended QA pairs from 578 videos across 4 scenarios and 10 capabilities. We build it with an Automated Generative Pipeline backed by rigorous human verification, and evaluate models using a realistic Online Inference Pipeline and LLM-as-a-Judge evaluation for open-ended responses. Experiments reveal a temporal asymmetry in LLM-judged scores (0-100): models perform well on Instant and Backward tasks (Gemini 3 Pro exceeds 80), but drop sharply on Forward tasks (16.40), largely due to early responses before the required visual and audio cues appear. This highlights a fundamental limitation: current MLLMs struggle to decide when to speak, not just what to say. Code and datasets used in this work will be made publicly accessible at https://github.com/Lucky-Lance/PhoStream.
VP-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Visual Prompting in Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have enabled a wide range of advanced vision-language applications, including fine-grained object recognition and contextual understanding. When querying specific regions or objects in an image, human users naturally use "visual prompts" (VPs), such as bounding boxes, to provide reference. However, no existing benchmark systematically evaluates the ability of MLLMs to interpret such VPs. This gap leaves it unclear whether current MLLMs can effectively recognize VPs, an intuitive prompting method for humans, and use them to solve problems. To address this limitation, we introduce VP-Bench, a benchmark for assessing MLLMs' capability in VP perception and utilization. VP-Bench employs a two-stage evaluation framework: Stage 1 examines models' ability to perceive VPs in natural scenes, using 30k visualized prompts spanning eight shapes and 355 attribute combinations. Stage 2 investigates the impact of VPs on downstream tasks, measuring their effectiveness in real-world problem-solving scenarios. Using VP-Bench, we evaluate 28 MLLMs, including proprietary systems (e.g., GPT-4o) and open-source models (e.g., InternVL3 and Qwen2.5-VL), and provide a comprehensive analysis of factors that affect VP understanding, such as variations in VP attributes, question arrangement, and model scale. VP-Bench establishes a new reference framework for studying how MLLMs comprehend and resolve grounded referring questions.
From Exploration to Exploitation: A Two-Stage Entropy RLVR Approach for Noise-Tolerant MLLM Training
Nov 11, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) is highly dependent on high-quality labeled data, which is often scarce and prone to substantial annotation noise in real-world scenarios. Existing unsupervised RLVR methods, including pure entropy minimization, can overfit to incorrect labels and limit the crucial reward ranking signal for Group-Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). To address these challenges and enhance noise tolerance, we propose a novel two-stage, token-level entropy optimization method for RLVR. This approach dynamically guides the model from exploration to exploitation during training. In the initial exploration phase, token-level entropy maximization promotes diverse and stochastic output generation, serving as a strong regularizer that prevents premature convergence to noisy labels and ensures sufficient intra-group variation, which enables more reliable reward gradient estimation in GRPO. As training progresses, the method transitions into the exploitation phase, where token-level entropy minimization encourages the model to produce confident and deterministic outputs, thereby consolidating acquired knowledge and refining prediction accuracy. Empirically, across three MLLM backbones - Qwen2-VL-2B, Qwen2-VL-7B, and Qwen2.5-VL-3B - spanning diverse noise settings and multiple tasks, our phased strategy consistently outperforms prior approaches by unifying and enhancing external, internal, and entropy-based methods, delivering robust and superior performance across the board.
SEFE: Superficial and Essential Forgetting Eliminator for Multimodal Continual Instruction Tuning
May 05, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Continual Instruction Tuning (MCIT) aims to enable Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to incrementally learn new tasks without catastrophic forgetting. In this paper, we explore forgetting in this context, categorizing it into superficial forgetting and essential forgetting. Superficial forgetting refers to cases where the model's knowledge may not be genuinely lost, but its responses to previous tasks deviate from expected formats due to the influence of subsequent tasks' answer styles, making the results unusable. By contrast, essential forgetting refers to situations where the model provides correctly formatted but factually inaccurate answers, indicating a true loss of knowledge. Assessing essential forgetting necessitates addressing superficial forgetting first, as severe superficial forgetting can obscure the model's knowledge state. Hence, we first introduce the Answer Style Diversification (ASD) paradigm, which defines a standardized process for transforming data styles across different tasks, unifying their training sets into similarly diversified styles to prevent superficial forgetting caused by style shifts. Building on this, we propose RegLoRA to mitigate essential forgetting. RegLoRA stabilizes key parameters where prior knowledge is primarily stored by applying regularization, enabling the model to retain existing competencies. Experimental results demonstrate that our overall method, SEFE, achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Strike a Balance in Continual Panoptic Segmentation
Jul 23, 2024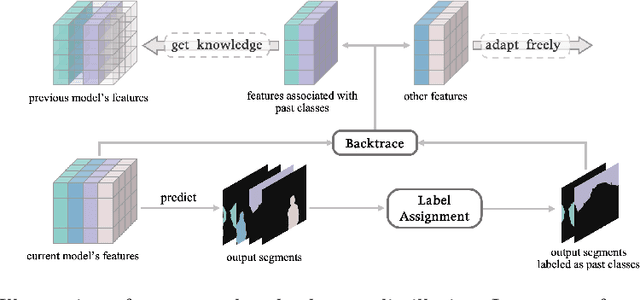
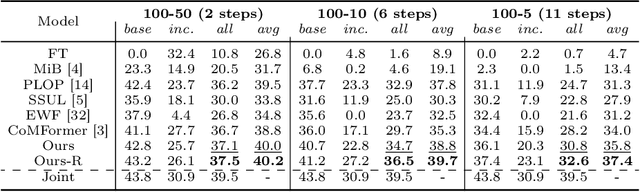
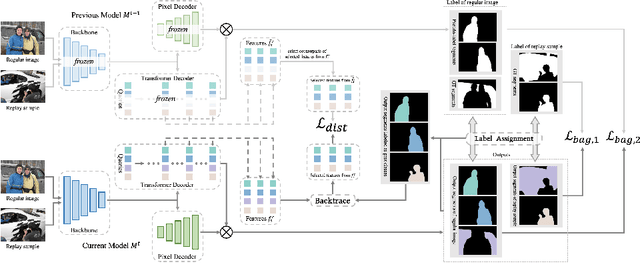
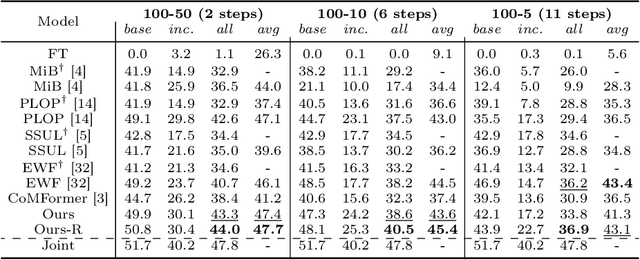
Abstract:This study explores the emerging area of continual panoptic segmentation, highlighting three key balances. First, we introduce past-class backtrace distillation to balance the stability of existing knowledge with the adaptability to new information. This technique retraces the features associated with past classes based on the final label assignment results, performing knowledge distillation targeting these specific features from the previous model while allowing other features to flexibly adapt to new information. Additionally, we introduce a class-proportional memory strategy, which aligns the class distribution in the replay sample set with that of the historical training data. This strategy maintains a balanced class representation during replay, enhancing the utility of the limited-capacity replay sample set in recalling prior classes. Moreover, recognizing that replay samples are annotated only for the classes of their original step, we devise balanced anti-misguidance losses, which combat the impact of incomplete annotations without incurring classification bias. Building upon these innovations, we present a new method named Balanced Continual Panoptic Segmentation (BalConpas). Our evaluation on the challenging ADE20K dataset demonstrates its superior performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. The official code is available at https://github.com/jinpeng0528/BalConpas.
Query-guided Prototype Evolution Network for Few-Shot Segmentation
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Previous Few-Shot Segmentation (FSS) approaches exclusively utilize support features for prototype generation, neglecting the specific requirements of the query. To address this, we present the Query-guided Prototype Evolution Network (QPENet), a new method that integrates query features into the generation process of foreground and background prototypes, thereby yielding customized prototypes attuned to specific queries. The evolution of the foreground prototype is accomplished through a \textit{support-query-support} iterative process involving two new modules: Pseudo-prototype Generation (PPG) and Dual Prototype Evolution (DPE). The PPG module employs support features to create an initial prototype for the preliminary segmentation of the query image, resulting in a pseudo-prototype reflecting the unique needs of the current query. Subsequently, the DPE module performs reverse segmentation on support images using this pseudo-prototype, leading to the generation of evolved prototypes, which can be considered as custom solutions. As for the background prototype, the evolution begins with a global background prototype that represents the generalized features of all training images. We also design a Global Background Cleansing (GBC) module to eliminate potential adverse components mirroring the characteristics of the current foreground class. Experimental results on the PASCAL-$5^i$ and COCO-$20^i$ datasets attest to the substantial enhancements achieved by QPENet over prevailing state-of-the-art techniques, underscoring the validity of our ideas.
SDDNet: Style-guided Dual-layer Disentanglement Network for Shadow Detection
Aug 17, 2023



Abstract:Despite significant progress in shadow detection, current methods still struggle with the adverse impact of background color, which may lead to errors when shadows are present on complex backgrounds. Drawing inspiration from the human visual system, we treat the input shadow image as a composition of a background layer and a shadow layer, and design a Style-guided Dual-layer Disentanglement Network (SDDNet) to model these layers independently. To achieve this, we devise a Feature Separation and Recombination (FSR) module that decomposes multi-level features into shadow-related and background-related components by offering specialized supervision for each component, while preserving information integrity and avoiding redundancy through the reconstruction constraint. Moreover, we propose a Shadow Style Filter (SSF) module to guide the feature disentanglement by focusing on style differentiation and uniformization. With these two modules and our overall pipeline, our model effectively minimizes the detrimental effects of background color, yielding superior performance on three public datasets with a real-time inference speed of 32 FPS.
SimCGNN: Simple Contrastive Graph Neural Network for Session-based Recommendation
Feb 08, 2023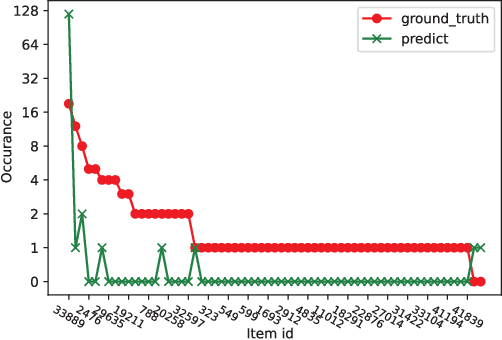
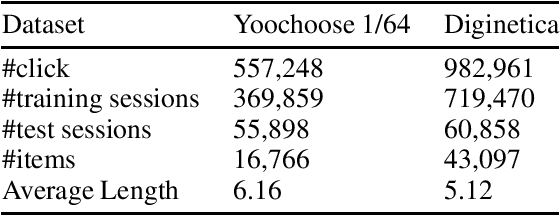
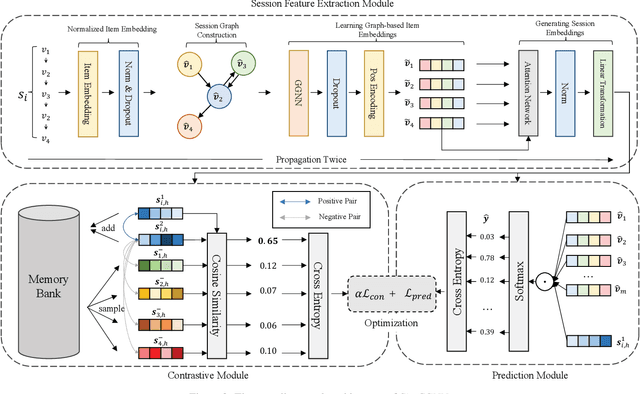
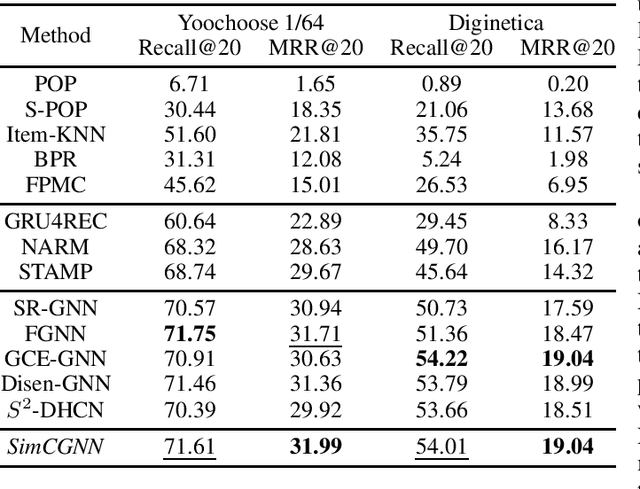
Abstract:Session-based recommendation (SBR) problem, which focuses on next-item prediction for anonymous users, has received increasingly more attention from researchers. Existing graph-based SBR methods all lack the ability to differentiate between sessions with the same last item, and suffer from severe popularity bias. Inspired by nowadays emerging contrastive learning methods, this paper presents a Simple Contrastive Graph Neural Network for Session-based Recommendation (SimCGNN). In SimCGNN, we first obtain normalized session embeddings on constructed session graphs. We next construct positive and negative samples of the sessions by two forward propagation and a novel negative sample selection strategy, and then calculate the constructive loss. Finally, session embeddings are used to give prediction. Extensive experiments conducted on two real-word datasets show our SimCGNN achieves a significant improvement over state-of-the-art methods.
Session-based Recommendation with Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network
Aug 12, 2021



Abstract:The purpose of the Session-Based Recommendation System is to predict the user's next click according to the previous session sequence. The current studies generally learn user preferences according to the transitions of items in the user's session sequence. However, other effective information in the session sequence, such as user profiles, are largely ignored which may lead to the model unable to learn the user's specific preferences. In this paper, we propose a heterogeneous graph neural network-based session recommendation method, named SR-HetGNN, which can learn session embeddings by heterogeneous graph neural network (HetGNN), and capture the specific preferences of anonymous users. Specifically, SR-HetGNN first constructs heterogeneous graphs containing various types of nodes according to the session sequence, which can capture the dependencies among items, users, and sessions. Second, HetGNN captures the complex transitions between items and learns the item embeddings containing user information. Finally, to consider the influence of users' long and short-term preferences, local and global session embeddings are combined with the attentional network to obtain the final session embedding. SR-HetGNN is shown to be superior to the existing state-of-the-art session-based recommendation methods through extensive experiments over two real large datasets Diginetica and Tmall.
CelebHair: A New Large-Scale Dataset for Hairstyle Recommendation based on CelebA
Apr 14, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we present a new large-scale dataset for hairstyle recommendation, CelebHair, based on the celebrity facial attributes dataset, CelebA. Our dataset inherited the majority of facial images along with some beauty-related facial attributes from CelebA. Additionally, we employed facial landmark detection techniques to extract extra features such as nose length and pupillary distance, and deep convolutional neural networks for face shape and hairstyle classification. Empirical comparison has demonstrated the superiority of our dataset to other existing hairstyle-related datasets regarding variety, veracity, and volume. Analysis and experiments have been conducted on the dataset in order to evaluate its robustness and usability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge