Jinchang Hou
Safety-Utility Conflicts Are Not Global: Surgical Alignment via Head-Level Diagnosis
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Safety alignment in Large Language Models (LLMs) inherently presents a multi-objective optimization conflict, often accompanied by an unintended degradation of general capabilities. Existing mitigation strategies typically rely on global gradient geometry to resolve these conflicts, yet they overlook Modular Heterogeneity within Transformers, specifically that the functional sensitivity and degree of conflict vary substantially across different attention heads. Such global approaches impose uniform update rules across all parameters, often resulting in suboptimal trade-offs by indiscriminately updating utility sensitive heads that exhibit intense gradient conflicts. To address this limitation, we propose Conflict-Aware Sparse Tuning (CAST), a framework that integrates head-level diagnosis with sparse fine-tuning. CAST first constructs a pre-alignment conflict map by synthesizing Optimization Conflict and Functional Sensitivity, which then guides the selective update of parameters. Experiments reveal that alignment conflicts in LLMs are not uniformly distributed. We find that the drop in general capabilities mainly comes from updating a small group of ``high-conflict'' heads. By simply skipping these heads during training, we significantly reduce this loss without compromising safety, offering an interpretable and parameter-efficient approach to improving the safety-utility trade-off.
Can MLLMs Understand the Deep Implication Behind Chinese Images?
Oct 17, 2024
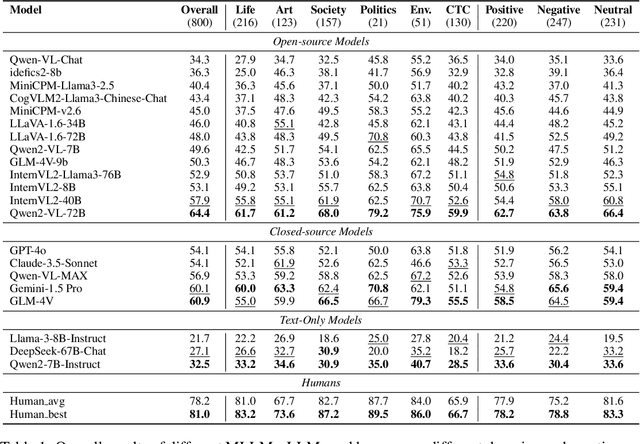
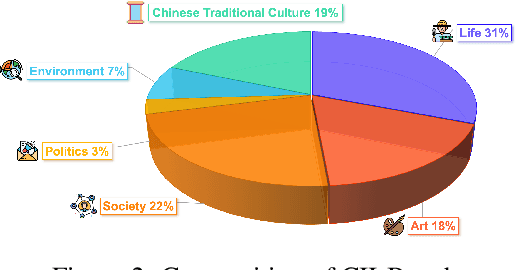
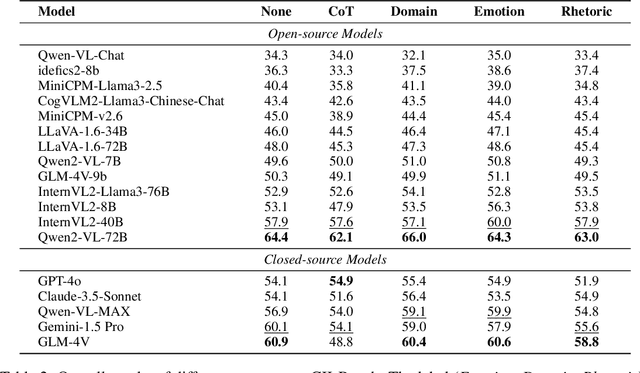
Abstract:As the capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) continue to improve, the need for higher-order capability evaluation of MLLMs is increasing. However, there is a lack of work evaluating MLLM for higher-order perception and understanding of Chinese visual content. To fill the gap, we introduce the **C**hinese **I**mage **I**mplication understanding **Bench**mark, **CII-Bench**, which aims to assess the higher-order perception and understanding capabilities of MLLMs for Chinese images. CII-Bench stands out in several ways compared to existing benchmarks. Firstly, to ensure the authenticity of the Chinese context, images in CII-Bench are sourced from the Chinese Internet and manually reviewed, with corresponding answers also manually crafted. Additionally, CII-Bench incorporates images that represent Chinese traditional culture, such as famous Chinese traditional paintings, which can deeply reflect the model's understanding of Chinese traditional culture. Through extensive experiments on CII-Bench across multiple MLLMs, we have made significant findings. Initially, a substantial gap is observed between the performance of MLLMs and humans on CII-Bench. The highest accuracy of MLLMs attains 64.4%, where as human accuracy averages 78.2%, peaking at an impressive 81.0%. Subsequently, MLLMs perform worse on Chinese traditional culture images, suggesting limitations in their ability to understand high-level semantics and lack a deep knowledge base of Chinese traditional culture. Finally, it is observed that most models exhibit enhanced accuracy when image emotion hints are incorporated into the prompts. We believe that CII-Bench will enable MLLMs to gain a better understanding of Chinese semantics and Chinese-specific images, advancing the journey towards expert artificial general intelligence (AGI). Our project is publicly available at https://cii-bench.github.io/.
CLHA: A Simple yet Effective Contrastive Learning Framework for Human Alignment
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is a crucial technique in aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences, ensuring these LLMs behave in beneficial and comprehensible ways to users. However, a longstanding challenge in human alignment techniques based on reinforcement learning lies in their inherent complexity and difficulty in training. To address this challenge, we present a simple yet effective Contrastive Learning Framework for Human Alignment (CLHA) to align LLMs with human preferences directly. CLHA employs a novel rescoring strategy to evaluate the noise within the data by considering its inherent quality and dynamically adjusting the training process. Simultaneously, CLHA utilizes pairwise contrastive loss and adaptive supervised fine-tuning loss to adaptively modify the likelihood of generating responses, ensuring enhanced alignment with human preferences. Using advanced methods, CLHA surpasses other algorithms, showcasing superior performance in terms of reward model scores, automatic evaluations, and human assessments on the widely used ``Helpful and Harmless'' dataset.
E-EVAL: A Comprehensive Chinese K-12 Education Evaluation Benchmark for Large Language Models
Jan 29, 2024



Abstract:With the accelerating development of Large Language Models (LLMs), many LLMs are beginning to be used in the Chinese K-12 education domain. The integration of LLMs and education is getting closer and closer, however, there is currently no benchmark for evaluating LLMs that focuses on the Chinese K-12 education domain. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a comprehensive natural language processing benchmark to accurately assess the capabilities of various LLMs in the Chinese K-12 education domain. To address this, we introduce the E-EVAL, the first comprehensive evaluation benchmark specifically designed for the Chinese K-12 education field. The E-EVAL consists of 4,351 multiple-choice questions at the primary, middle, and high school levels across a wide range of subjects, including Chinese, English, Politics, History, Ethics, Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, and Geography. We conducted a comprehensive evaluation of E-EVAL on advanced LLMs, including both English-dominant and Chinese-dominant models. Findings show that Chinese-dominant models perform well compared to English-dominant models, with many scoring even above the GPT 4.0. However, almost all models perform poorly in complex subjects such as mathematics. We also found that most Chinese-dominant LLMs did not achieve higher scores at the primary school level compared to the middle school level. We observe that the mastery of higher-order knowledge by the model does not necessarily imply the mastery of lower-order knowledge as well. Additionally, the experimental results indicate that the Chain of Thought (CoT) technique is effective only for the challenging science subjects, while Few-shot prompting is more beneficial for liberal arts subjects. With E-EVAL, we aim to analyze the strengths and limitations of LLMs in educational applications, and to contribute to the progress and development of Chinese K-12 education and LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge