Jina Kim
FRIEDA: Benchmarking Multi-Step Cartographic Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Cartographic reasoning is the skill of interpreting geographic relationships by aligning legends, map scales, compass directions, map texts, and geometries across one or more map images. Although essential as a concrete cognitive capability and for critical tasks such as disaster response and urban planning, it remains largely unevaluated. Building on progress in chart and infographic understanding, recent large vision language model studies on map visual question-answering often treat maps as a special case of charts. In contrast, map VQA demands comprehension of layered symbology (e.g., symbols, geometries, and text labels) as well as spatial relations tied to orientation and distance that often span multiple maps and are not captured by chart-style evaluations. To address this gap, we introduce FRIEDA, a benchmark for testing complex open-ended cartographic reasoning in LVLMs. FRIEDA sources real map images from documents and reports in various domains and geographical areas. Following classifications in Geographic Information System (GIS) literature, FRIEDA targets all three categories of spatial relations: topological (border, equal, intersect, within), metric (distance), and directional (orientation). All questions require multi-step inference, and many require cross-map grounding and reasoning. We evaluate eleven state-of-the-art LVLMs under two settings: (1) the direct setting, where we provide the maps relevant to the question, and (2) the contextual setting, where the model may have to identify the maps relevant to the question before reasoning. Even the strongest models, Gemini-2.5-Pro and GPT-5-Think, achieve only 38.20% and 37.20% accuracy, respectively, far below human performance of 84.87%. These results reveal a persistent gap in multi-step cartographic reasoning, positioning FRIEDA as a rigorous benchmark to drive progress on spatial intelligence in LVLMs.
StreetLens: Enabling Human-Centered AI Agents for Neighborhood Assessment from Street View Imagery
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Traditionally, neighborhood studies have employed interviews, surveys, and manual image annotation guided by detailed protocols to identify environmental characteristics, including physical disorder, decay, street safety, and sociocultural symbols, and to examine their impact on developmental and health outcomes. While these methods yield rich insights, they are time-consuming and require intensive expert intervention. Recent technological advances, including vision-language models (VLMs), have begun to automate parts of this process; however, existing efforts are often ad hoc and lack adaptability across research designs and geographic contexts. In this demo paper, we present StreetLens, a human-centered, researcher-configurable workflow that embeds relevant social science expertise in a VLM for scalable neighborhood environmental assessments. StreetLens mimics the process of trained human coders by grounding the analysis in questions derived from established interview protocols, retrieving relevant street view imagery (SVI), and generating a wide spectrum of semantic annotations from objective features (e.g., the number of cars) to subjective perceptions (e.g., the sense of disorder in an image). By enabling researchers to define the VLM's role through domain-informed prompting, StreetLens places domain knowledge at the core of the analysis process. It also supports the integration of prior survey data to enhance robustness and expand the range of characteristics assessed across diverse settings. We provide a Google Colab notebook to make StreetLens accessible and extensible for researchers working with public or custom SVI datasets. StreetLens represents a shift toward flexible, agentic AI systems that work closely with researchers to accelerate and scale neighborhood studies.
Robust Molecular Property Prediction via Densifying Scarce Labeled Data
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:A widely recognized limitation of molecular prediction models is their reliance on structures observed in the training data, resulting in poor generalization to out-of-distribution compounds. Yet in drug discovery, the compounds most critical for advancing research often lie beyond the training set, making the bias toward the training data particularly problematic. This mismatch introduces substantial covariate shift, under which standard deep learning models produce unstable and inaccurate predictions. Furthermore, the scarcity of labeled data, stemming from the onerous and costly nature of experimental validation, further exacerbates the difficulty of achieving reliable generalization. To address these limitations, we propose a novel meta-learning-based approach that leverages unlabeled data to interpolate between in-distribution (ID) and out-of-distribution (OOD) data, enabling the model to meta-learn how to generalize beyond the training distribution. We demonstrate significant performance gains over state-of-the-art methods on challenging real-world datasets that exhibit substantial covariate shift.
SNeRV: Spectra-preserving Neural Representation for Video
Jan 03, 2025Abstract:Neural representation for video (NeRV), which employs a neural network to parameterize video signals, introduces a novel methodology in video representations. However, existing NeRV-based methods have difficulty in capturing fine spatial details and motion patterns due to spectral bias, in which a neural network learns high-frequency (HF) components at a slower rate than low-frequency (LF) components. In this paper, we propose spectra-preserving NeRV (SNeRV) as a novel approach to enhance implicit video representations by efficiently handling various frequency components. SNeRV uses 2D discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to decompose video into LF and HF features, preserving spatial structures and directly addressing the spectral bias issue. To balance the compactness, we encode only the LF components, while HF components that include fine textures are generated by a decoder. Specialized modules, including a multi-resolution fusion unit (MFU) and a high-frequency restorer (HFR), are integrated into a backbone to facilitate the representation. Furthermore, we extend SNeRV to effectively capture temporal correlations between adjacent video frames, by casting the extension as additional frequency decomposition to a temporal domain. This approach allows us to embed spatio-temporal LF features into the network, using temporally extended up-sampling blocks (TUBs). Experimental results demonstrate that SNeRV outperforms existing NeRV models in capturing fine details and achieves enhanced reconstruction, making it a promising approach in the field of implicit video representations. The codes are available at https://github.com/qwertja/SNeRV.
Context-Aware Trajectory Anomaly Detection
Oct 24, 2024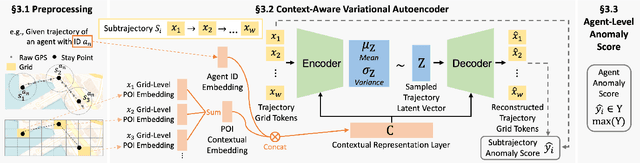
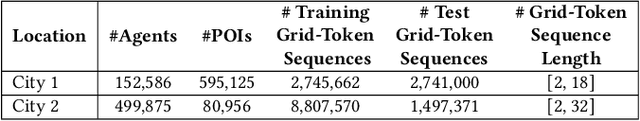
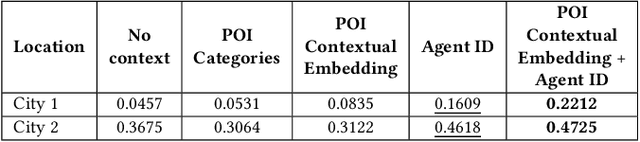
Abstract:Trajectory anomaly detection is crucial for effective decision-making in urban and human mobility management. Existing methods of trajectory anomaly detection generally focus on training a trajectory generative model and evaluating the likelihood of reconstructing a given trajectory. However, previous work often lacks important contextual information on the trajectory, such as the agent's information (e.g., agent ID) or geographic information (e.g., Points of Interest (POI)), which could provide additional information on accurately capturing anomalous behaviors. To fill this gap, we propose a context-aware anomaly detection approach that models contextual information related to trajectories. The proposed method is based on a trajectory reconstruction framework guided by contextual factors such as agent ID and contextual POI embedding. The injection of contextual information aims to improve the performance of anomaly detection. We conducted experiments in two cities and demonstrated that the proposed approach significantly outperformed existing methods by effectively modeling contextual information. Overall, this paper paves a new direction for advancing trajectory anomaly detection.
Automatic Search of Multiword Place Names on Historical Maps
Oct 21, 2024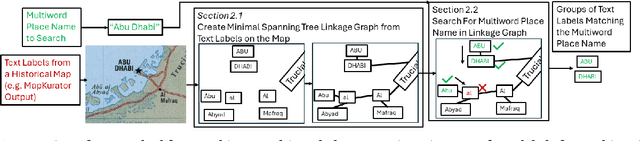
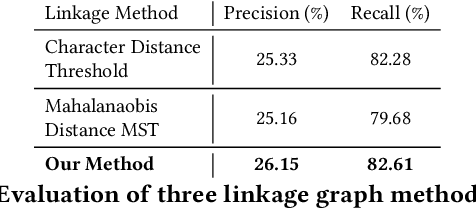
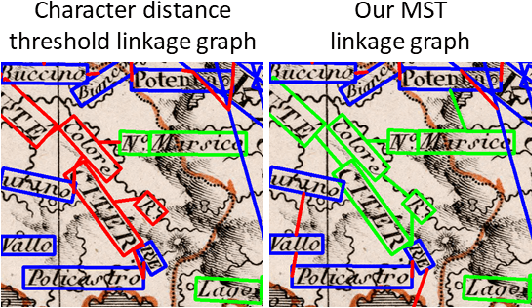
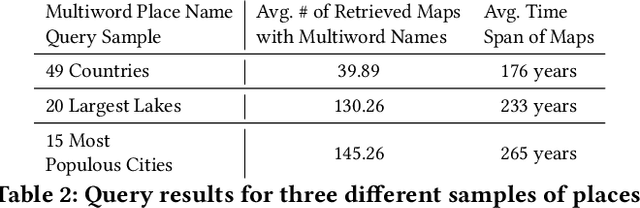
Abstract:Historical maps are invaluable sources of information about the past, and scanned historical maps are increasingly accessible in online libraries. To retrieve maps from these large libraries that contain specific places of interest, previous work has applied computer vision techniques to recognize words on historical maps, enabling searches for maps that contain specific place names. However, searching for multiword place names is challenging due to complex layouts of text labels on historical maps. This paper proposes an efficient query method for searching a given multiword place name on historical maps. Using existing methods to recognize words on historical maps, we link single-word text labels into potential multiword phrases by constructing minimum spanning trees. These trees aim to link pairs of text labels that are spatially close and have similar height, angle, and capitalization. We then query these trees for the given multiword place name. We evaluate the proposed method in two experiments: 1) to evaluate the accuracy of the minimum spanning tree approach at linking multiword place names and 2) to evaluate the number and time range of maps retrieved by the query approach. The resulting maps reveal how places using multiword names have changed on a large number of maps from across history.
HiP Attention: Sparse Sub-Quadratic Attention with Hierarchical Attention Pruning
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:In modern large language models (LLMs), increasing sequence lengths is a crucial challenge for enhancing their comprehension and coherence in handling complex tasks such as multi-modal question answering. However, handling long context sequences with LLMs is prohibitively costly due to the conventional attention mechanism's quadratic time and space complexity, and the context window size is limited by the GPU memory. Although recent works have proposed linear and sparse attention mechanisms to address this issue, their real-world applicability is often limited by the need to re-train pre-trained models. In response, we propose a novel approach, Hierarchically Pruned Attention (HiP), which simultaneously reduces the training and inference time complexity from $O(T^2)$ to $O(T \log T)$ and the space complexity from $O(T^2)$ to $O(T)$. To this end, we devise a dynamic sparse attention mechanism that generates an attention mask through a novel tree-search-like algorithm for a given query on the fly. HiP is training-free as it only utilizes the pre-trained attention scores to spot the positions of the top-$k$ most significant elements for each query. Moreover, it ensures that no token is overlooked, unlike the sliding window-based sub-quadratic attention methods, such as StreamingLLM. Extensive experiments on diverse real-world benchmarks demonstrate that HiP significantly reduces prompt (i.e., prefill) and decoding latency and memory usage while maintaining high generation performance with little or no degradation. As HiP allows pretrained LLMs to scale to millions of tokens on commodity GPUs with no additional engineering due to its easy plug-and-play deployment, we believe that our work will have a large practical impact, opening up the possibility to many long-context LLM applications previously infeasible.
SEA: Sparse Linear Attention with Estimated Attention Mask
Oct 03, 2023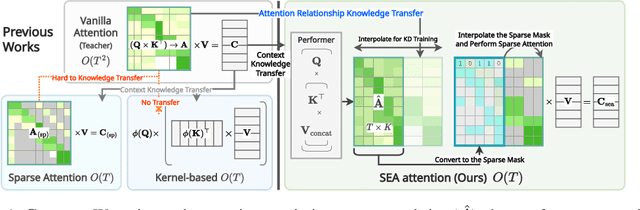
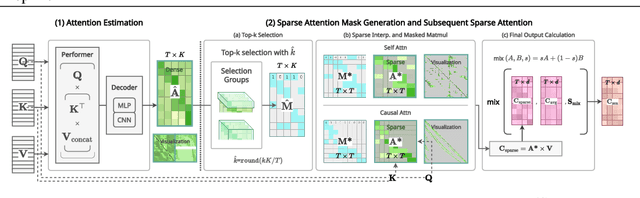
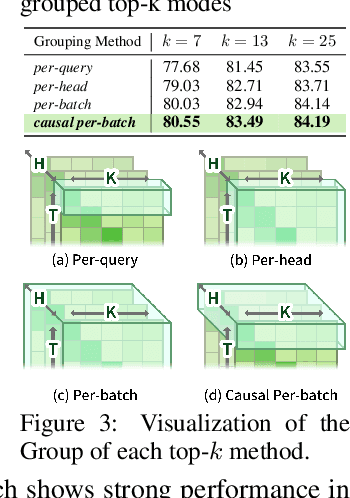
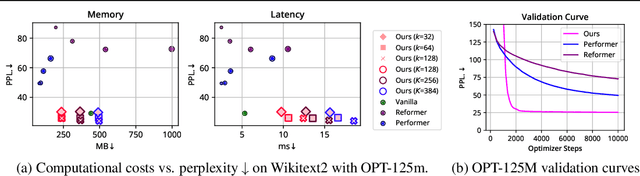
Abstract:The transformer architecture has made breakthroughs in recent years on tasks which require modeling pairwise relationships between sequential elements, as is the case in natural language understanding. However, transformers struggle with long sequences due to the quadratic complexity of the attention operation, and previous research has aimed to lower the complexity by sparsifying or linearly approximating the attention matrix. Yet, these approaches cannot straightforwardly distill knowledge from a teacher's attention matrix, and often require complete retraining from scratch. Furthermore, previous sparse and linear approaches may also lose interpretability if they do not produce full quadratic attention matrices. To address these challenges, we propose SEA: Sparse linear attention with an Estimated Attention mask. SEA estimates the attention matrix with linear complexity via kernel-based linear attention, then creates a sparse approximation to the full attention matrix with a top-k selection to perform a sparse attention operation. For language modeling tasks (Wikitext2), previous linear and sparse attention methods show a roughly two-fold worse perplexity scores over the quadratic OPT-125M baseline, while SEA achieves an even better perplexity than OPT-125M, using roughly half as much memory as OPT-125M. Moreover, SEA maintains an interpretable attention matrix and can utilize knowledge distillation to lower the complexity of existing pretrained transformers. We believe that our work will have a large practical impact, as it opens the possibility of running large transformers on resource-limited devices with less memory.
The mapKurator System: A Complete Pipeline for Extracting and Linking Text from Historical Maps
Jul 03, 2023Abstract:Scanned historical maps in libraries and archives are valuable repositories of geographic data that often do not exist elsewhere. Despite the potential of machine learning tools like the Google Vision APIs for automatically transcribing text from these maps into machine-readable formats, they do not work well with large-sized images (e.g., high-resolution scanned documents), cannot infer the relation between the recognized text and other datasets, and are challenging to integrate with post-processing tools. This paper introduces the mapKurator system, an end-to-end system integrating machine learning models with a comprehensive data processing pipeline. mapKurator empowers automated extraction, post-processing, and linkage of text labels from large numbers of large-dimension historical map scans. The output data, comprising bounding polygons and recognized text, is in the standard GeoJSON format, making it easily modifiable within Geographic Information Systems (GIS). The proposed system allows users to quickly generate valuable data from large numbers of historical maps for in-depth analysis of the map content and, in turn, encourages map findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability (FAIR principles). We deployed the mapKurator system and enabled the processing of over 60,000 maps and over 100 million text/place names in the David Rumsey Historical Map collection. We also demonstrated a seamless integration of mapKurator with a collaborative web platform to enable accessing automated approaches for extracting and linking text labels from historical map scans and collective work to improve the results.
LAnoBERT : System Log Anomaly Detection based on BERT Masked Language Model
Nov 20, 2021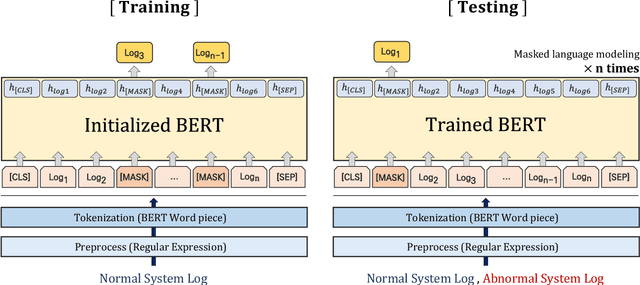
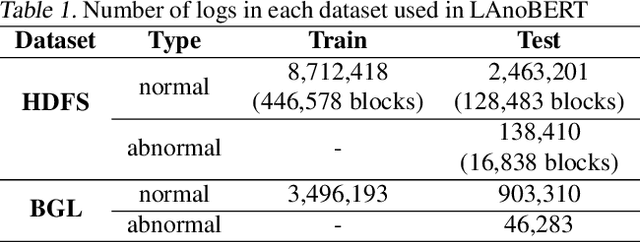
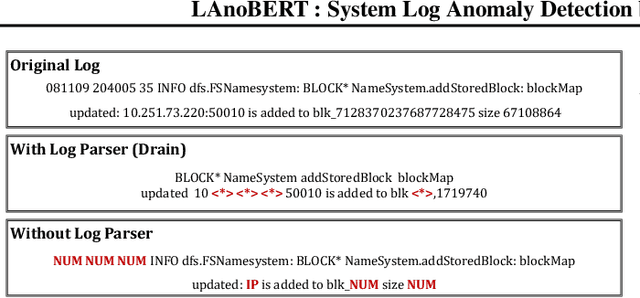

Abstract:The system log generated in a computer system refers to large-scale data that are collected simultaneously and used as the basic data for determining simple errors and detecting external adversarial intrusion or the abnormal behaviors of insiders. The aim of system log anomaly detection is to promptly identify anomalies while minimizing human intervention, which is a critical problem in the industry. Previous studies performed anomaly detection through algorithms after converting various forms of log data into a standardized template using a parser. These methods involved generating a template for refining the log key. Particularly, a template corresponding to a specific event should be defined in advance for all the log data using which the information within the log key may get lost.In this study, we propose LAnoBERT, a parser free system log anomaly detection method that uses the BERT model, exhibiting excellent natural language processing performance. The proposed method, LAnoBERT, learns the model through masked language modeling, which is a BERT-based pre-training method, and proceeds with unsupervised learning-based anomaly detection using the masked language modeling loss function per log key word during the inference process. LAnoBERT achieved better performance compared to previous methodology in an experiment conducted using benchmark log datasets, HDFS, and BGL, and also compared to certain supervised learning-based models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge