Pilsung Kang
COMET: Codebook-based Online-adaptive Multi-scale Embedding for Time-series Anomaly Detection
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Time series anomaly detection is a critical task across various industrial domains. However, capturing temporal dependencies and multivariate correlations within patch-level representation learning remains underexplored, and reliance on single-scale patterns limits the detection of anomalies across different temporal ranges. Furthermore, focusing on normal data representations makes models vulnerable to distribution shifts at inference time. To address these limitations, we propose Codebook-based Online-adaptive Multi-scale Embedding for Time-series anomaly detection (COMET), which consists of three key components: (1) Multi-scale Patch Encoding captures temporal dependencies and inter-variable correlations across multiple patch scales. (2) Vector-Quantized Coreset learns representative normal patterns via codebook and detects anomalies with a dual-score combining quantization error and memory distance. (3) Online Codebook Adaptation generates pseudo-labels based on codebook entries and dynamically adapts the model at inference through contrastive learning. Experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate that COMET achieves the best performance in 36 out of 45 evaluation metrics, validating its effectiveness across diverse environments.
naPINN: Noise-Adaptive Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Recovering Physics from Corrupted Measurement
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) are effective methods for solving inverse problems and discovering governing equations from observational data. However, their performance degrades significantly under complex measurement noise and gross outliers. To address this issue, we propose the Noise-Adaptive Physics-Informed Neural Network (naPINN), which robustly recovers physical solutions from corrupted measurements without prior knowledge of the noise distribution. naPINN embeds an energy-based model into the training loop to learn the latent distribution of prediction residuals. Leveraging the learned energy landscape, a trainable reliability gate adaptively filters data points exhibiting high energy, while a rejection cost regularization prevents trivial solutions where valid data are discarded. We demonstrate the efficacy of naPINN on various benchmark partial differential equations corrupted by non-Gaussian noise and varying rates of outliers. The results show that naPINN significantly outperforms existing robust PINN baselines, successfully isolating outliers and accurately reconstructing the dynamics under severe data corruption.
AlienLM: Alienization of Language for API-Boundary Privacy in Black-Box LLMs
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Modern LLMs are increasingly accessed via black-box APIs, requiring users to transmit sensitive prompts, outputs, and fine-tuning data to external providers, creating a critical privacy risk at the API boundary. We introduce AlienLM, a deployable API-only privacy layer that protects text by translating it into an Alien Language via a vocabulary-scale bijection, enabling lossless recovery on the client side. Using only standard fine-tuning APIs, Alien Adaptation Training (AAT) adapts target models to operate directly on alienized inputs. Across four LLM backbones and seven benchmarks, AlienLM retains over 81\% of plaintext-oracle performance on average, substantially outperforming random-bijection and character-level baselines. Under adversaries with access to model weights, corpus statistics, and learning-based inverse translation, recovery attacks reconstruct fewer than 0.22\% of alienized tokens. Our results demonstrate a practical pathway for privacy-preserving LLM deployment under API-only access, substantially reducing plaintext exposure while maintaining task performance.
Interaction as Interference: A Quantum-Inspired Aggregation Approach
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Classical approaches often treat interaction as engineered product terms or as emergent patterns in flexible models, offering little control over how synergy or antagonism arises. We take a quantum-inspired view: following the Born rule (probability as squared amplitude), \emph{coherent} aggregation sums complex amplitudes before squaring, creating an interference cross-term, whereas an \emph{incoherent} proxy sums squared magnitudes and removes it. In a minimal linear-amplitude model, this cross-term equals the standard potential-outcome interaction contrast \(Δ_{\mathrm{INT}}\) in a \(2\times 2\) factorial design, giving relative phase a direct, mechanism-level control over synergy versus antagonism. We instantiate this idea in a lightweight \emph{Interference Kernel Classifier} (IKC) and introduce two diagnostics: \emph{Coherent Gain} (log-likelihood gain of coherent over the incoherent proxy) and \emph{Interference Information} (the induced Kullback-Leibler gap). A controlled phase sweep recovers the identity. On a high-interaction synthetic task (XOR), IKC outperforms strong baselines under paired, budget-matched comparisons; on real tabular data (\emph{Adult} and \emph{Bank Marketing}) it is competitive overall but typically trails the most capacity-rich baseline in paired differences. Holding learned parameters fixed, toggling aggregation from incoherent to coherent consistently improves negative log-likelihood, Brier score, and expected calibration error, with positive Coherent Gain on both datasets.
Quantum Entanglement as Super-Confounding: From Bell's Theorem to Robust Machine Learning
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Bell's theorem reveals a profound conflict between quantum mechanics and local realism, a conflict we reinterpret through the modern lens of causal inference. We propose and computationally validate a framework where quantum entanglement acts as a "super-confounding" resource, generating correlations that violate the classical causal bounds set by Bell's inequalities. This work makes three key contributions: First, we establish a physical hierarchy of confounding (Quantum > Classical) and introduce Confounding Strength (CS) to quantify this effect. Second, we provide a circuit-based implementation of the quantum $\mathcal{DO}$-calculus to distinguish causality from spurious correlation. Finally, we apply this calculus to a quantum machine learning problem, where causal feature selection yields a statistically significant 11.3% average absolute improvement in model robustness. Our framework bridges quantum foundations and causal AI, offering a new, practical perspective on quantum correlations.
QFFN-BERT: An Empirical Study of Depth, Performance, and Data Efficiency in Hybrid Quantum-Classical Transformers
Jul 03, 2025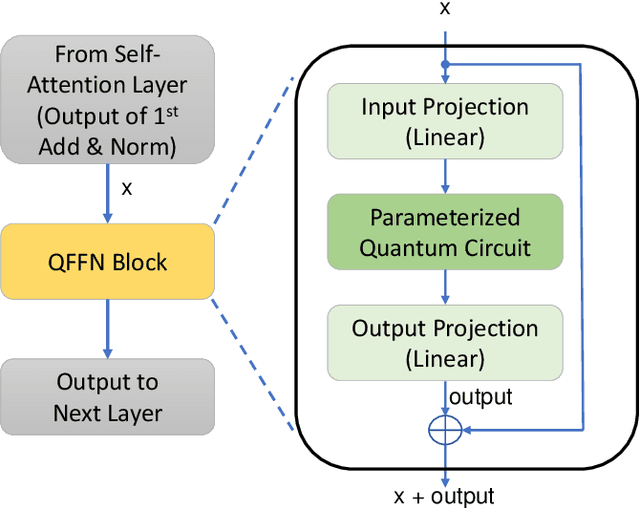
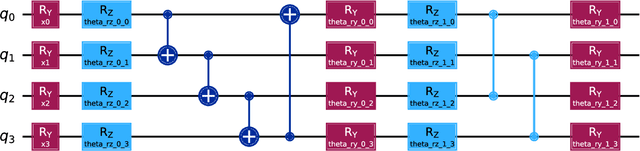
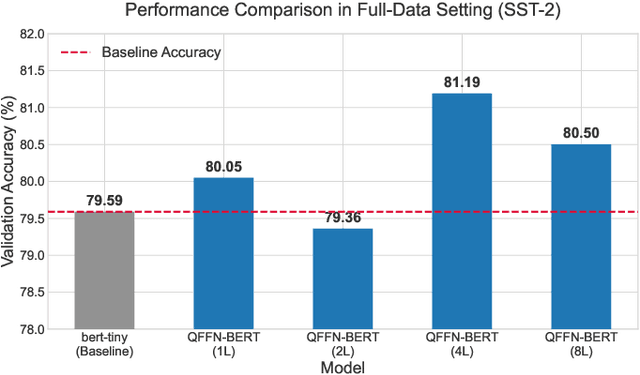
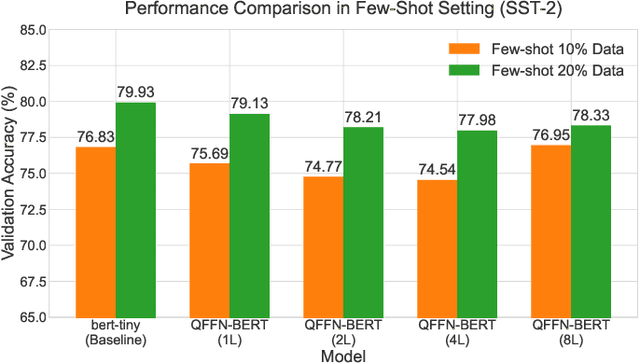
Abstract:Parameterized quantum circuits (PQCs) have recently emerged as promising components for enhancing the expressibility of neural architectures. In this work, we introduce QFFN-BERT, a hybrid quantum-classical transformer where the feedforward network (FFN) modules of a compact BERT variant are replaced by PQC-based layers. This design is motivated by the dominant parameter contribution of FFNs, which account for approximately two-thirds of the parameters within standard Transformer encoder blocks. While prior studies have primarily integrated PQCs into self-attention modules, our work focuses on the FFN and systematically investigates the trade-offs between PQC depth, expressibility, and trainability. Our final PQC architecture incorporates a residual connection, both $R_Y$ and $R_Z$ rotations, and an alternating entanglement strategy to ensure stable training and high expressibility. Our experiments, conducted on a classical simulator, on the SST-2 and DBpedia benchmarks demonstrate two key findings. First, a carefully configured QFFN-BERT achieves up to 102.0% of the baseline accuracy, surpassing its classical counterpart in a full-data setting while reducing FFN-specific parameters by over 99%. Second, our model exhibits a consistent and competitive edge in few-shot learning scenarios, confirming its potential for superior data efficiency. These results, supported by an ablation study on a non-optimized PQC that failed to learn, confirm that PQCs can serve as powerful and parameter-efficient alternatives to classical FFNs when co-designed with foundational deep learning principles.
Domain Adaptation of Attention Heads for Zero-shot Anomaly Detection
May 28, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) in images is an approach that can detect anomalies without access to normal samples, which can be beneficial in various realistic scenarios where model training is not possible. However, existing ZSAD research has shown limitations by either not considering domain adaptation of general-purpose backbone models to anomaly detection domains or by implementing only partial adaptation to some model components. In this paper, we propose HeadCLIP to overcome these limitations by effectively adapting both text and image encoders to the domain. HeadCLIP generalizes the concepts of normality and abnormality through learnable prompts in the text encoder, and introduces learnable head weights to the image encoder to dynamically adjust the features held by each attention head according to domain characteristics. Additionally, we maximize the effect of domain adaptation by introducing a joint anomaly score that utilizes domain-adapted pixel-level information for image-level anomaly detection. Experimental results using multiple real datasets in both industrial and medical domains show that HeadCLIP outperforms existing ZSAD techniques at both pixel and image levels. In the industrial domain, improvements of up to 4.9%p in pixel-level mean anomaly detection score (mAD) and up to 3.0%p in image-level mAD were achieved, with similar improvements (3.2%p, 3.1%p) in the medical domain.
COUNTDOWN: Contextually Sparse Activation Filtering Out Unnecessary Weights in Down Projection
May 23, 2025Abstract:The growing size of large language models has created significant computational inefficiencies. To address this challenge, sparse activation methods selectively deactivates non-essential parameters during inference, reducing computational costs in FFNN layers. While existing methods focus on non-linear gating mechanisms, we hypothesize that the sparsity of the FFNN layer lies globally in the form of a linear combination over its internal down projection matrix. Based on this insight, we propose two methods: M-COUNTDOWN, leveraging indirect coefficients, and D-COUNTDOWN, utilizing direct coefficients of the linear combination. Experimental results demonstrate that D-COUNTDOWN can omit 90% of computations with performance loss as low as 5.5% ideally, while M-COUNTDOWN provides a predictor-free solution with up to 29.4% better performance preservation compared to existing methods. Our specialized kernel implementations effectively realize these theoretical gains into substantial real-world acceleration.
Avoid Wasted Annotation Costs in Open-set Active Learning with Pre-trained Vision-Language Model
Aug 09, 2024Abstract:Active learning (AL) aims to enhance model performance by selectively collecting highly informative data, thereby minimizing annotation costs. However, in practical scenarios, unlabeled data may contain out-of-distribution (OOD) samples, leading to wasted annotation costs if data is incorrectly selected. Recent research has explored methods to apply AL to open-set data, but these methods often require or incur unavoidable cost losses to minimize them. To address these challenges, we propose a novel selection strategy, CLIPN for AL (CLIPNAL), which minimizes cost losses without requiring OOD samples. CLIPNAL sequentially evaluates the purity and informativeness of data. First, it utilizes a pre-trained vision-language model to detect and exclude OOD data by leveraging linguistic and visual information of in-distribution (ID) data without additional training. Second, it selects highly informative data from the remaining ID data, and then the selected samples are annotated by human experts. Experimental results on datasets with various open-set conditions demonstrate that CLIPNAL achieves the lowest cost loss and highest performance across all scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/DSBA-Lab/OpenAL.
A Gradient Accumulation Method for Dense Retriever under Memory Constraint
Jun 18, 2024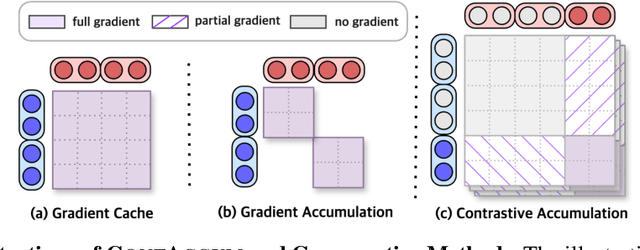
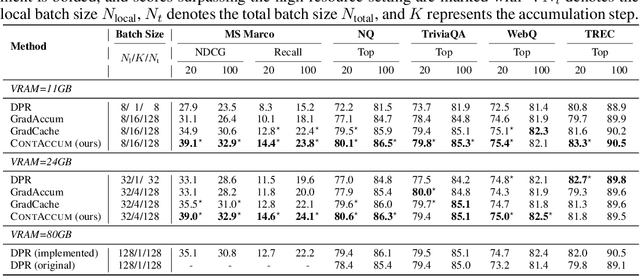
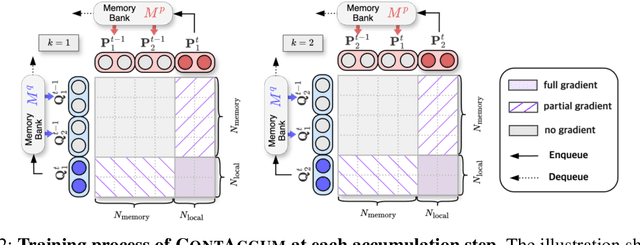
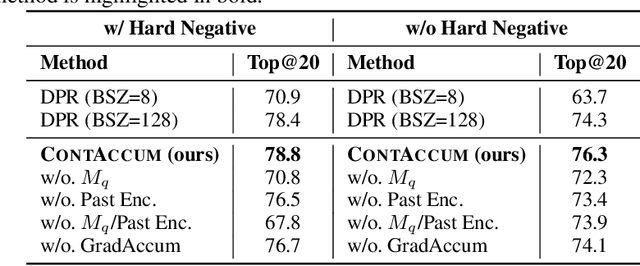
Abstract:InfoNCE loss is commonly used to train dense retriever in information retrieval tasks. It is well known that a large batch is essential to stable and effective training with InfoNCE loss, which requires significant hardware resources. Due to the dependency of large batch, dense retriever has bottleneck of application and research. Recently, memory reduction methods have been broadly adopted to resolve the hardware bottleneck by decomposing forward and backward or using a memory bank. However, current methods still suffer from slow and unstable training. To address these issues, we propose \longmodelname\ (\modelname), a stable and efficient memory reduction method for dense retriever trains that uses a dual memory bank structure to leverage previously generated query and passage representations. Experiments on widely used five information retrieval datasets indicate that \modelname\ can surpass not only existing memory reduction methods but also high-resource scenario. Moreover, theoretical analysis and experimental results confirm that \modelname\ provides more stable dual-encoder training than current memory bank utilization methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge