Jaehee Kim
AlienLM: Alienization of Language for API-Boundary Privacy in Black-Box LLMs
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Modern LLMs are increasingly accessed via black-box APIs, requiring users to transmit sensitive prompts, outputs, and fine-tuning data to external providers, creating a critical privacy risk at the API boundary. We introduce AlienLM, a deployable API-only privacy layer that protects text by translating it into an Alien Language via a vocabulary-scale bijection, enabling lossless recovery on the client side. Using only standard fine-tuning APIs, Alien Adaptation Training (AAT) adapts target models to operate directly on alienized inputs. Across four LLM backbones and seven benchmarks, AlienLM retains over 81\% of plaintext-oracle performance on average, substantially outperforming random-bijection and character-level baselines. Under adversaries with access to model weights, corpus statistics, and learning-based inverse translation, recovery attacks reconstruct fewer than 0.22\% of alienized tokens. Our results demonstrate a practical pathway for privacy-preserving LLM deployment under API-only access, substantially reducing plaintext exposure while maintaining task performance.
Verbosity-Aware Rationale Reduction: Effective Reduction of Redundant Rationale via Principled Criteria
Dec 30, 2024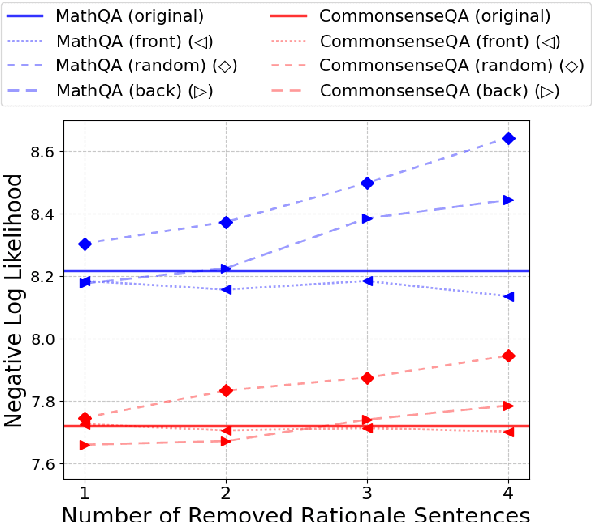
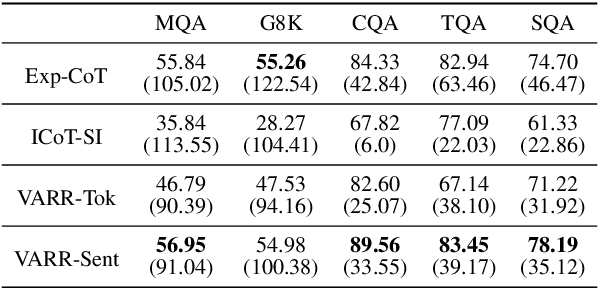
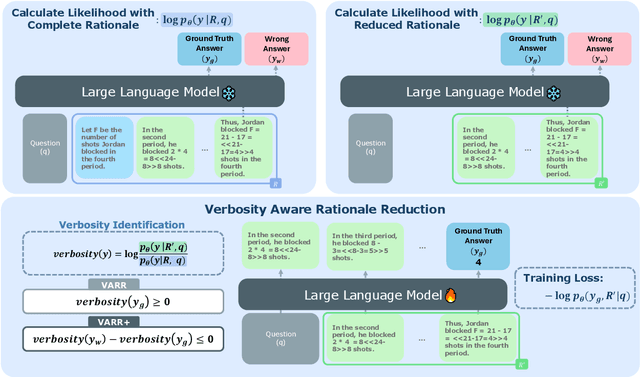
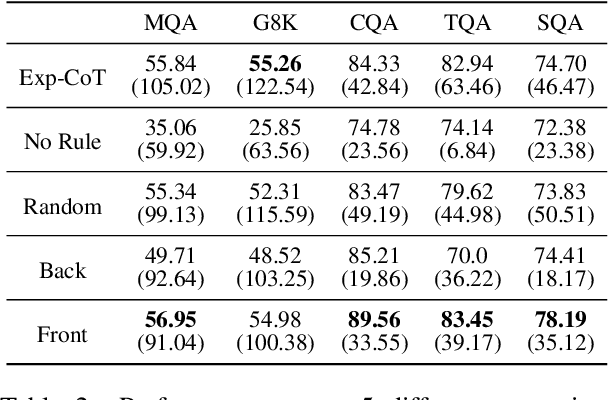
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) rely on generating extensive intermediate reasoning units (e.g., tokens, sentences) to enhance final answer quality across a wide range of complex tasks. While generating multiple reasoning paths or iteratively refining rationales proves effective for improving performance, these approaches inevitably result in significantly higher inference costs. In this work, we propose a novel sentence-level rationale reduction training framework that leverages likelihood-based criteria, verbosity, to identify and remove redundant reasoning sentences. Unlike previous approaches that utilize token-level reduction, our sentence-level reduction framework maintains model performance while reducing generation length. This preserves the original reasoning abilities of LLMs and achieves an average 17.15% reduction in generation costs across various models and tasks.
A Gradient Accumulation Method for Dense Retriever under Memory Constraint
Jun 18, 2024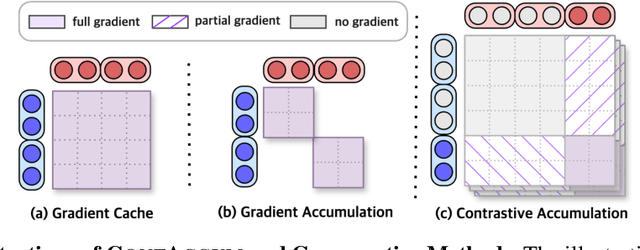
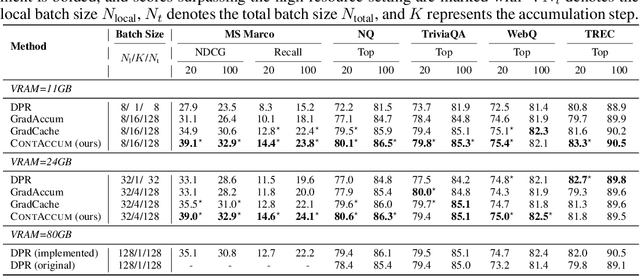
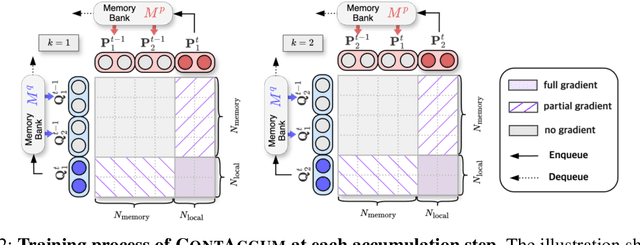
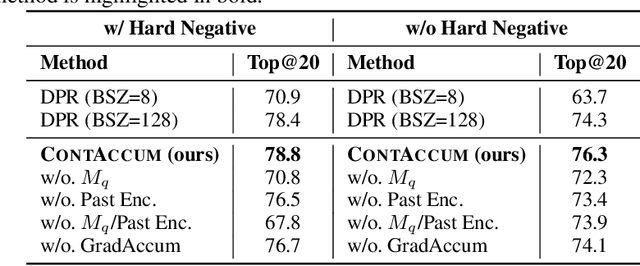
Abstract:InfoNCE loss is commonly used to train dense retriever in information retrieval tasks. It is well known that a large batch is essential to stable and effective training with InfoNCE loss, which requires significant hardware resources. Due to the dependency of large batch, dense retriever has bottleneck of application and research. Recently, memory reduction methods have been broadly adopted to resolve the hardware bottleneck by decomposing forward and backward or using a memory bank. However, current methods still suffer from slow and unstable training. To address these issues, we propose \longmodelname\ (\modelname), a stable and efficient memory reduction method for dense retriever trains that uses a dual memory bank structure to leverage previously generated query and passage representations. Experiments on widely used five information retrieval datasets indicate that \modelname\ can surpass not only existing memory reduction methods but also high-resource scenario. Moreover, theoretical analysis and experimental results confirm that \modelname\ provides more stable dual-encoder training than current memory bank utilization methods.
CheckEval: Robust Evaluation Framework using Large Language Model via Checklist
Mar 27, 2024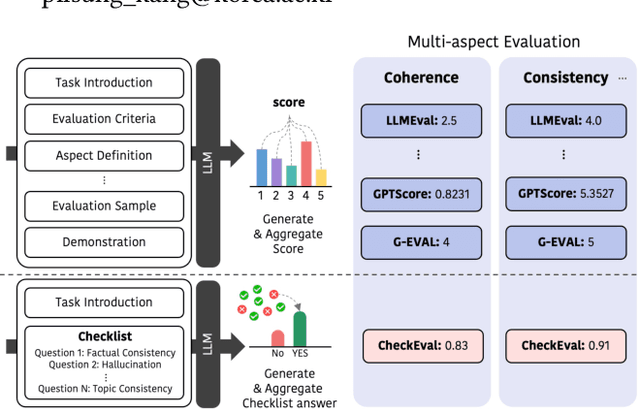
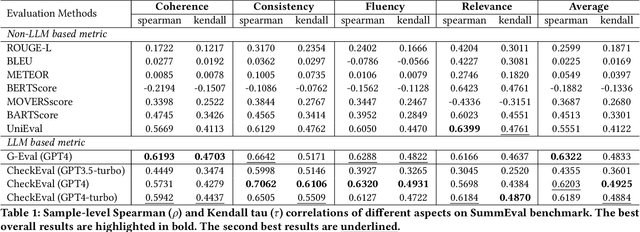
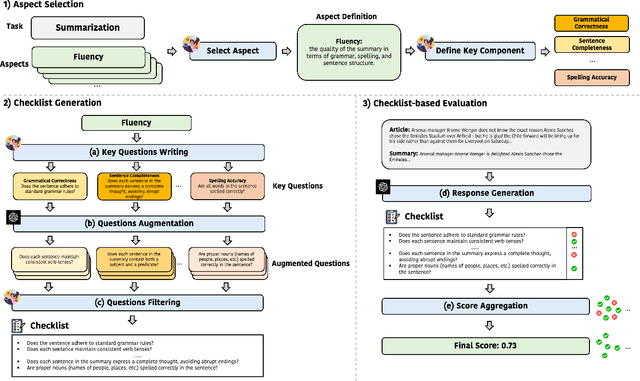
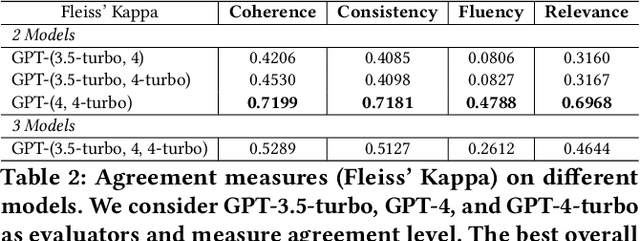
Abstract:We introduce CheckEval, a novel evaluation framework using Large Language Models, addressing the challenges of ambiguity and inconsistency in current evaluation methods. CheckEval addresses these challenges by dividing evaluation criteria into detailed sub-aspects and constructing a checklist of Boolean questions for each, simplifying the evaluation. This approach not only renders the process more interpretable but also significantly enhances the robustness and reliability of results by focusing on specific evaluation dimensions. Validated through a focused case study using the SummEval benchmark, CheckEval indicates a strong correlation with human judgments. Furthermore, it demonstrates a highly consistent Inter-Annotator Agreement. These findings highlight the effectiveness of CheckEval for objective, flexible, and precise evaluations. By offering a customizable and interactive framework, CheckEval sets a new standard for the use of LLMs in evaluation, responding to the evolving needs of the field and establishing a clear method for future LLM-based evaluation.
Boosting Prompt-Based Self-Training With Mapping-Free Automatic Verbalizer for Multi-Class Classification
Dec 08, 2023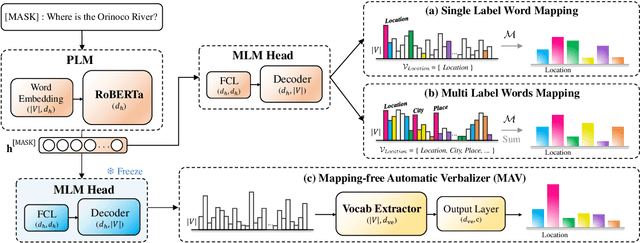
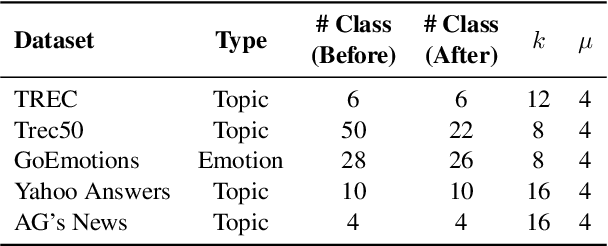
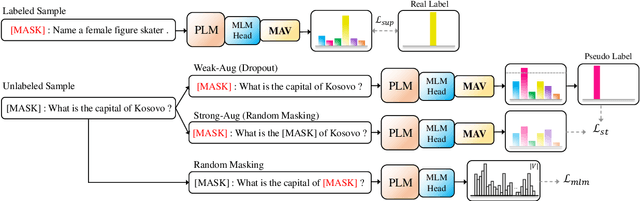
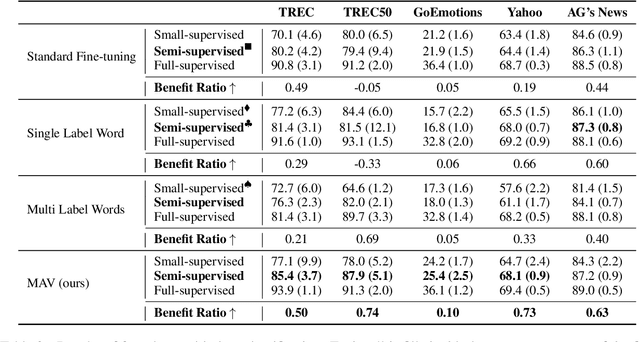
Abstract:Recently, prompt-based fine-tuning has garnered considerable interest as a core technique for few-shot text classification task. This approach reformulates the fine-tuning objective to align with the Masked Language Modeling (MLM) objective. Leveraging unlabeled data, prompt-based self-training has shown greater effectiveness in binary and three-class classification. However, prompt-based self-training for multi-class classification has not been adequately investigated, despite its significant applicability to real-world scenarios. Moreover, extending current methods to multi-class classification suffers from the verbalizer that extracts the predicted value of manually pre-defined single label word for each class from MLM predictions. Consequently, we introduce a novel, efficient verbalizer structure, named Mapping-free Automatic Verbalizer (MAV). Comprising two fully connected layers, MAV serves as a trainable verbalizer that automatically extracts the requisite word features for classification by capitalizing on all available information from MLM predictions. Experimental results on five multi-class classification datasets indicate MAV's superior self-training efficacy.
Painsight: An Extendable Opinion Mining Framework for Detecting Pain Points Based on Online Customer Reviews
Jun 03, 2023Abstract:As the e-commerce market continues to expand and online transactions proliferate, customer reviews have emerged as a critical element in shaping the purchasing decisions of prospective buyers. Previous studies have endeavored to identify key aspects of customer reviews through the development of sentiment analysis models and topic models. However, extracting specific dissatisfaction factors remains a challenging task. In this study, we delineate the pain point detection problem and propose Painsight, an unsupervised framework for automatically extracting distinct dissatisfaction factors from customer reviews without relying on ground truth labels. Painsight employs pre-trained language models to construct sentiment analysis and topic models, leveraging attribution scores derived from model gradients to extract dissatisfaction factors. Upon application of the proposed methodology to customer review data spanning five product categories, we successfully identified and categorized dissatisfaction factors within each group, as well as isolated factors for each type. Notably, Painsight outperformed benchmark methods, achieving substantial performance enhancements and exceptional results in human evaluations.
REVECA -- Rich Encoder-decoder framework for Video Event CAptioner
Jun 18, 2022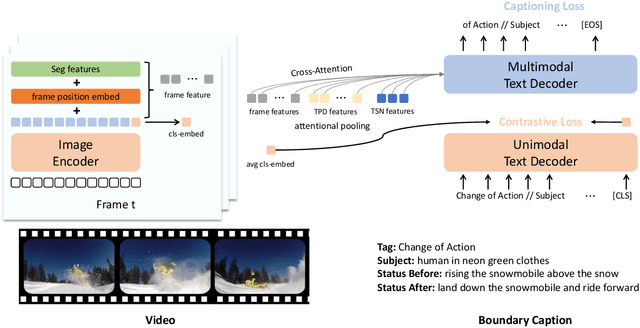
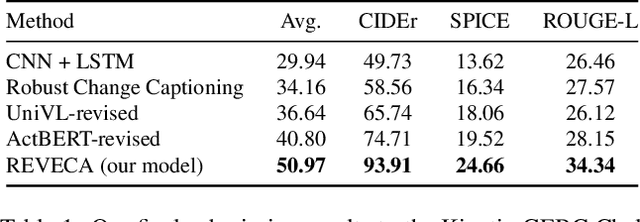
Abstract:We describe an approach used in the Generic Boundary Event Captioning challenge at the Long-Form Video Understanding Workshop held at CVPR 2022. We designed a Rich Encoder-decoder framework for Video Event CAptioner (REVECA) that utilizes spatial and temporal information from the video to generate a caption for the corresponding the event boundary. REVECA uses frame position embedding to incorporate information before and after the event boundary. Furthermore, it employs features extracted using the temporal segment network and temporal-based pairwise difference method to learn temporal information. A semantic segmentation mask for the attentional pooling process is adopted to learn the subject of an event. Finally, LoRA is applied to fine-tune the image encoder to enhance the learning efficiency. REVECA yielded an average score of 50.97 on the Kinetics-GEBC test data, which is an improvement of 10.17 over the baseline method. Our code is available in https://github.com/TooTouch/REVECA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge